Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry focuses on the structure, properties, and reactions of carbon-containing compounds. It’s essential in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and biochemistry, exploring mechanisms, functional groups, and synthesis of complex molecules.
-
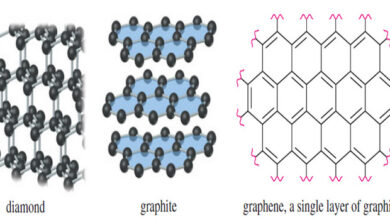
Aromatic Allotropes of Carbon
– In this subject, we will talk about Aromatic Allotropes of Carbon. Aromatic Allotropes of Carbon What do you get…
Read More » -
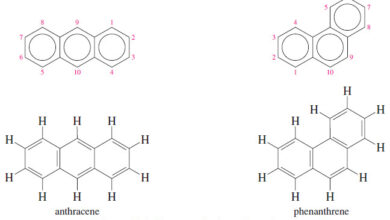
Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons
Polynuclear Aromatic Hydrocarbons – The polynuclear aromatic hydrocarbons (abbreviated PAHs or PNAs) are composed of two or more fused benzene…
Read More » -
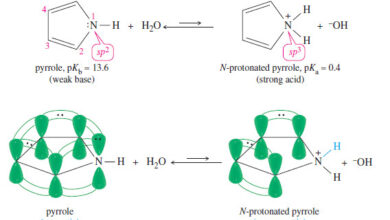
Heterocyclic Aromatic Compounds
Heterocyclic Aromatic Compounds – Nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur are the most common heteroatoms in heterocyclic aromatic compounds. – The criteria…
Read More » -
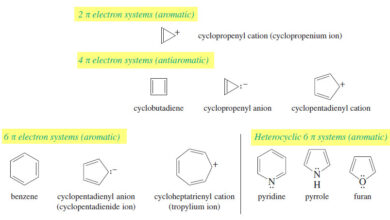
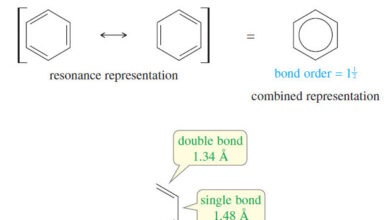
Aromatic, Antiaromatic, and Nonaromatic Compounds
Aromatic, Antiaromatic, and Nonaromatic Compounds – Our working definition of aromatic compounds has included cyclic compounds containing conjugated double bonds…
Read More » -
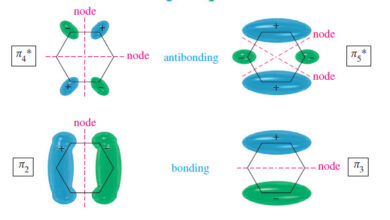
The Molecular Orbitals of Benzene
In this subject, we will talk about The Molecular Orbitals of Benzene The Molecular Orbitals of Benzene – Visualizing benzene…
Read More » -
The Structure and Properties of Benzene
In this subject, we we will talk about The Discovery of Benzene and The Structure and Properties of Benzene. The…
Read More » -
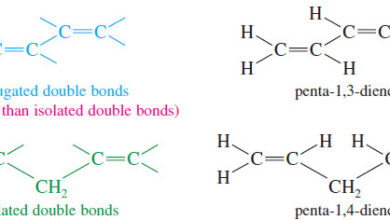
Stabilities of Dienes
– In this topic, we will talk about Stabilities of Dienes What are Dienes? – Double bonds can interact with…
Read More » -
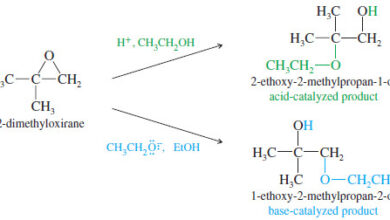
Ring Opening of Epoxides
– In this topic, we will talk aboutAcid-Catalyzed Ring Opening of Epoxides, Base-Catalyzed Ring Opening of Epoxides, and Orientation of…
Read More » -
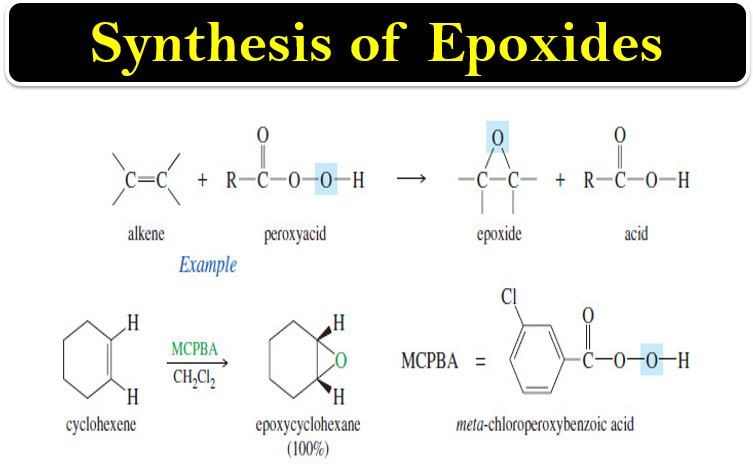
Synthesis of Epoxides
– In this topic, we will talk about Synthesis of Epoxides by two methods: Peroxyacid epoxidation and Base-promoted cyclization of…
Read More » -
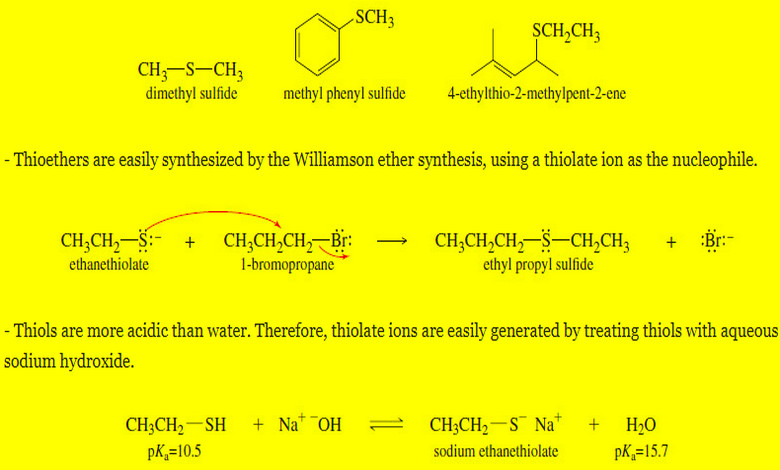
Thioethers (sulfides) and Silyl Ethers
Thioethers (sulfides) and Silyl Ethers – Thioethers, also called sulfides, are ethers with a sulfur atom replacing the oxygen atom…
Read More » -
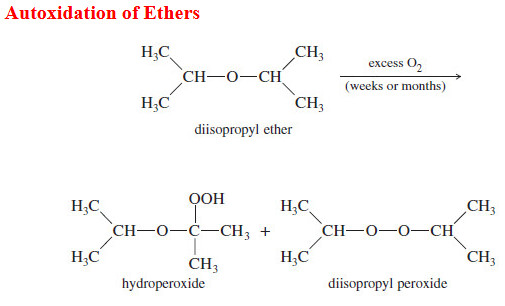
Autoxidation of Ethers
– In this topic, we will discuss The autoxidation of Ethers. What are Ethers? Ethers are compounds of formula R-O-R,…
Read More » -
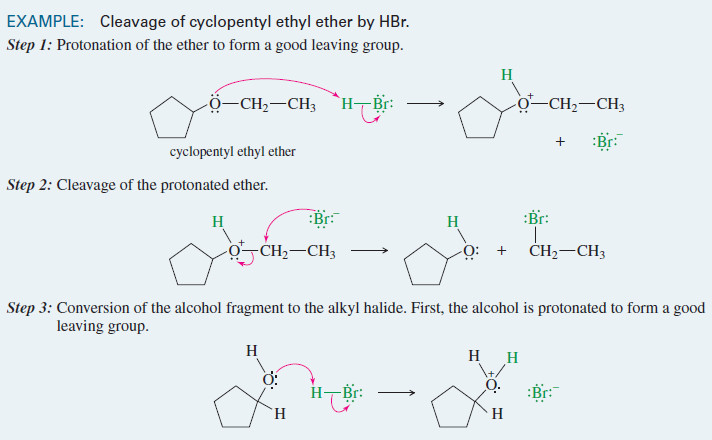
Cleavage of Ethers by HBr and HI
– In this topic, we will discuss the Cleavage of Ethers by HBr and HI Cleavage of Ethers by HBr…
Read More » -
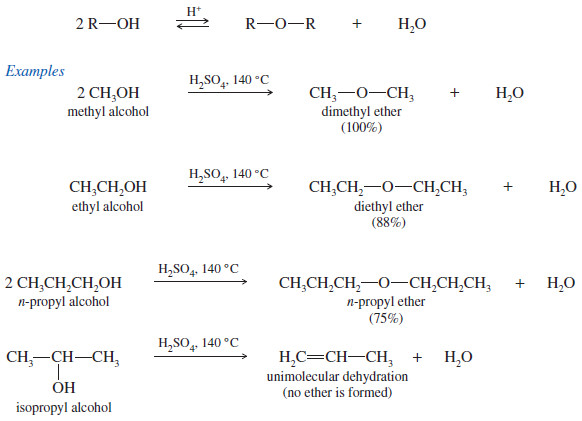
Synthesis of Ethers
Synthesis of Ethers – In this topic, we will discuss 6 methods for Synthesis of Ethers as follows: 1. Ethers…
Read More » -
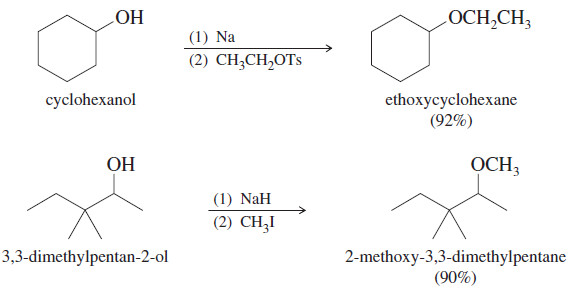
Williamson Ether Synthesis : Mechanism, Examples
– In this topic, we will discuss the Williamson Ether Synthesis : Mechanism, Examples and Solved problems. Williamson Ether Synthesis…
Read More » -
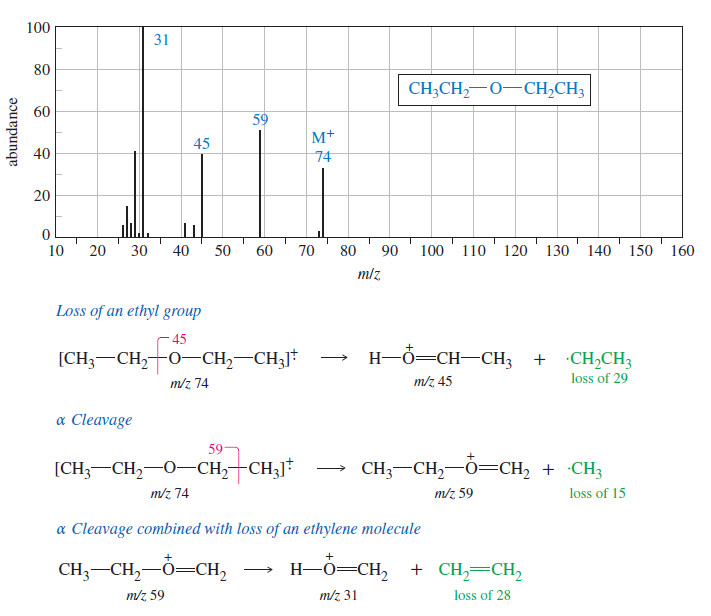
Spectroscopy of Ethers : IR, Mass, 13C NMR, 1H NMR
Spectroscopy of Ethers – Here we will discuss Spectroscopy of Ethers: IR Spectroscopy, Mass Spectroscopy, 13C NMR amd 1H NMR. …
Read More » -
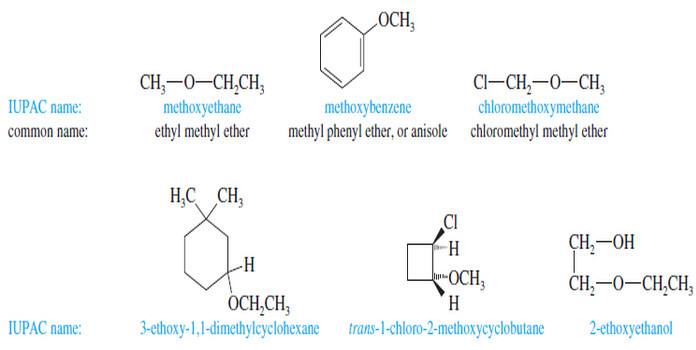
Nomenclature of Ethers : Rules, IUPAC Name, Common Name
Nomenclature of Ethers – We have been using the common nomenclature of ethers, which is sometimes called the alkyl alkyl…
Read More » -
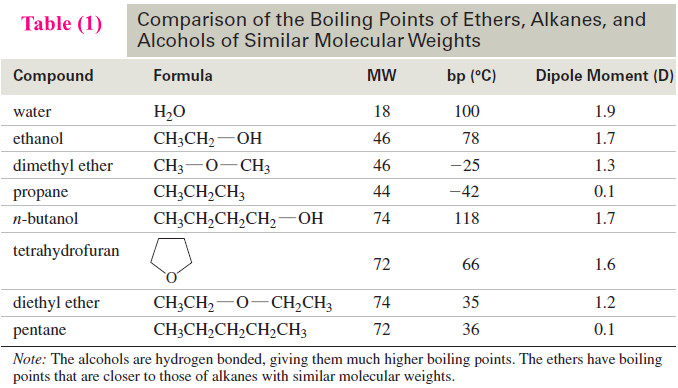
Physical Properties of Ethers
– In this topic, we will discuss The Physical Properties of Ethers. Introduction to Ethers – Ethers are compounds of…
Read More » -
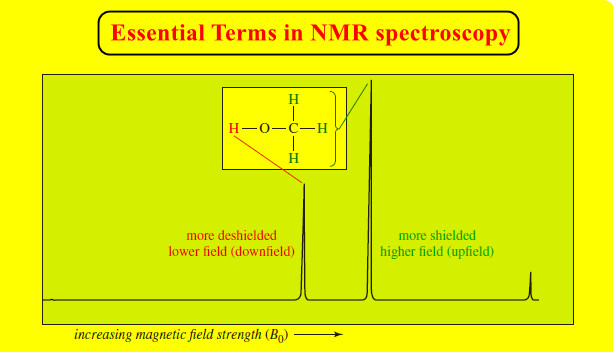
NMR – Essential Terms in NMR spectroscopy
– In this topic, we will discuss some Essential Terms in NMR spectroscopy. Essential Terms in NMR spectroscopy accidentally equivalent…
Read More » -
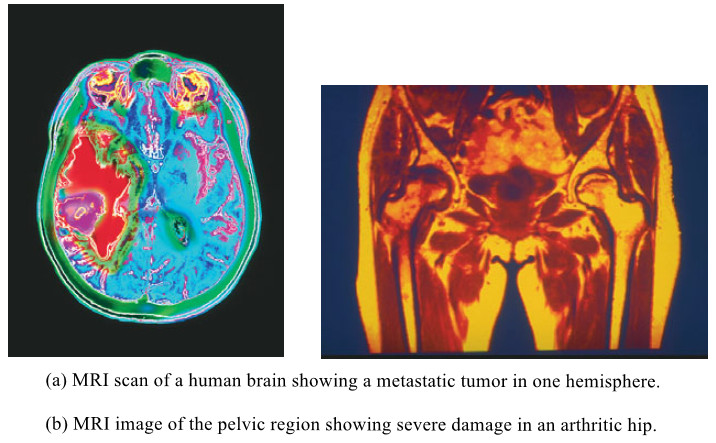
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging – NMR imaging
– In this topic, we will discuss Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging – When chemists use NMR…
Read More » -
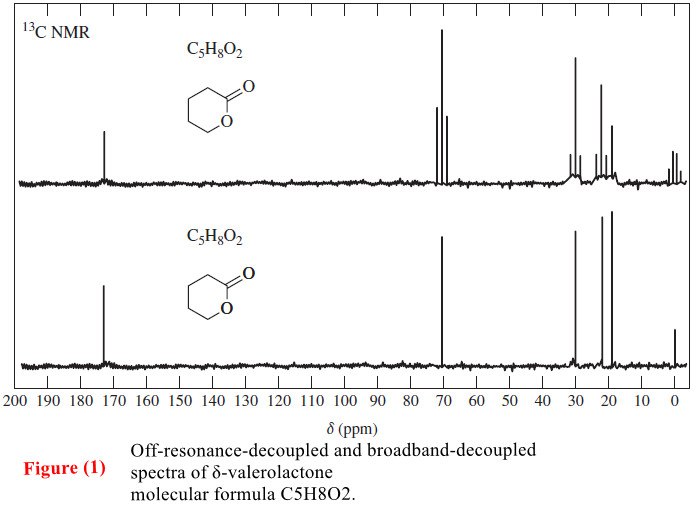
Interpreting Carbon NMR Spectra
Interpreting Carbon NMR Spectra – Interpreting Carbon NMR Spectra (13C NMR spectra) uses the same principles as interpreting 1H NMR…
Read More »