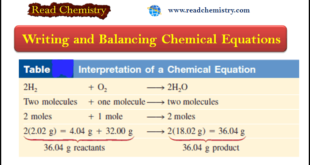
– In this subject, we will discuss Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations. Chemical Reactions and Chemical Equations – A chemical reaction is a process in which a substance (or substances) is changed into one or more new substances. – To communicate with one another about chemical reactions, chemists have devised …
Read More »How To Predict Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model
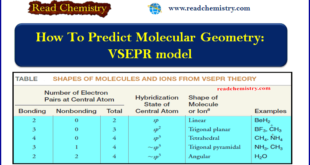
How To Predict Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model ** We can predict the arrangement of atoms in molecules and ions on the basis of a relatively simple idea called the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model. ** We apply the VSEPR model in the following way: (1) We …
Read More »Important concepts in Hybridization That Come from Quantum Mechanics
Important concepts in Hybridization (1) An atomic orbital (AO) corresponds to a region of space about the nucleus of a single atom where there is a high probability of finding an electron. Atomic orbitals called s orbitals are spherical; those called p orbitals are like two almost-tangent spheres. Orbitals can hold …
Read More »The Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene): sp Hybridization
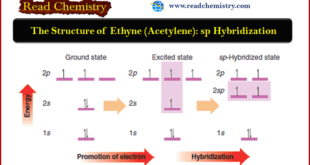
The Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene): sp Hybridization ** Hydrocarbons in which two carbon atoms share three pairs of electrons between them, and are thus bonded by a triple bond, are called alkynes. The two simplest alkynes are ethyne and propyne. ** Ethyne, a compound that is also called acetylene, …
Read More »Half-life time and radioactive decay: Equations, Calculations
– In this subject, we will discuss the Half-life time and radioactive decay: Equations, Calculations Rate of radioactive decay – The decay of a radioactive isotope takes place by disintegration of the atomic nucleus. – It is not influenced by any external conditions. – Therefore the rate of decay is …
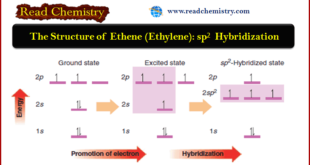
Read More »The Structure of Ethene (Ethylene): sp2 Hybridization
The Structure of Ethene (Ethylene): sp2 Hybridization ** The carbon atoms of many of the molecules that we have considered so far have used their four valence electrons to form four single covalent (sigma) bonds to four other atoms. ** We find, however, that many important organic compounds …
Read More »Radioactive Disintegration Series: Definition, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Radioactive Disintegration Series: Definition, Examples Radioactivity – Several elements such as uranium and radium are unstable. – Their atomic nucleus breaks off its own accord to form a smaller atomic nucleus of another element. – The protons and neutrons in the unstable …
Read More »The Structure of Methane and Ethane: sp3 Hybridization
** The (s) and (p) orbitals used in the quantum mechanical description of the carbon atom, were based on calculations for hydrogen atoms. These simple (s) and (p) orbitals do not, when taken alone, provide a satisfactory model for the tetravalent–tetrahedral carbon of methane. ** However, a satisfactory …
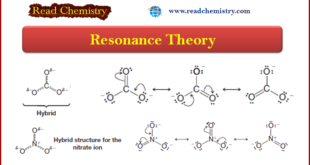
Read More »Resonance Theory
Introduction to Resonance (Resonance in carbonate ion (CO32-) ** Often more than one equivalent Lewis structure can be written for a molecule or ion. Consider, for example, the carbonate ion (CO32-). We can write three different but equivalent structures, 1–3: ** Notice two important features of these …
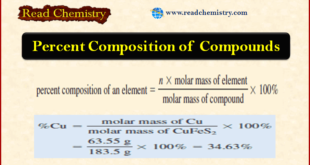
Read More »Percent Composition of Compounds
Percent Composition of Compounds **As we have seen, the formula of a compound tells us the numbers of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound. ** However, suppose we needed to verify the purity of a compound for use in a laboratory experiment. We could calculate …
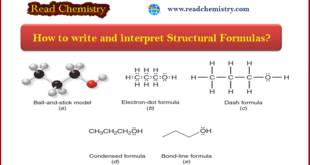
Read More »How to write and interpret Structural Formulas?
** Organic chemists use a variety of formats to write structural formulas. ** Structural Formulas are written by: (1) Ball-and-stick model (2) Electron-dot formula (lewis structure) (3) Dash formula (4) Condensed formula (5) Bond-line formula ** Examples of these types of structural formulas are shown in the …
Read More »Radioactive decay: Definition, Types, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Radioactive decay: Definition, Types, Examples Types of Radioactive Decay – According to the theory put forward by Rutherford and Soddy (1903), radioactivity is a nuclear property. – The nucleus of a radioactive atom is unstable. – It undergoes decay or disintegration by …
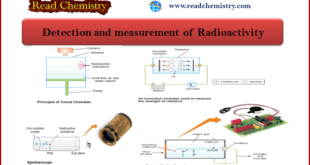
Read More »Radioactivity: Detection and Measurement
– In this subject, we will discuss the Detection and measurement of Radioactivity. Detection and measurement of Radioactivity – Radioactivity can be detected and measured by several methods. – The important ones used in modern practice are listed below. (1) Cloud Chamber (2) Ionization Chamber (3) Geiger-Muller Counter (4) Scintillation …
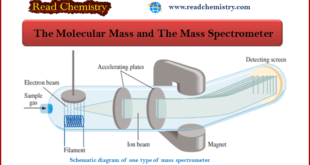
Read More »The Molecular Mass and The Mass Spectrometer
Molecular Mass ** If we know the atomic masses of the component atoms, we can calculate the mass of a molecule. ** The molecular mass: (sometimes called molecular weight) is the sum of the atomic masses (in amu) in the molecule. ** For example, the molecular mass of …
Read More »Avogadro’s Number and the Molar Mass of an Element
Avogadro’s Number (NA) ** Atomic mass units provide a relative scale for the masses of the elements. ** But because atoms have such small masses, no usable scale can be devised to weigh them in calibrated units of atomic mass units. ** In any real situation, we deal with macroscopic …
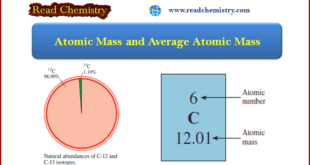
Read More »Atomic Mass and Average Atomic Mass: Definition, Calculation
– In this subject, we will discuss the Atomic Mass and Average Atomic Mass: Definition, Formula, and Calculation Atomic Mass – The mass of an atom depends on the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons it contains. – Knowledge of an atom’s mass is important in laboratory work. – But …
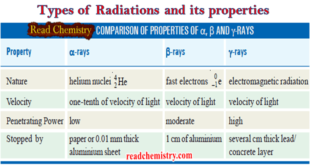
Read More »Types of Radiations and its properties
Nuclear reaction ** A nuclear reaction is different from a chemical reaction. ** In a chemical reaction, atoms of the reactants combine by a rearrangement of extranuclear electrons but the nuclei of the atoms remain unchanged. ** In a nuclear reaction, on the other hand, it is the …
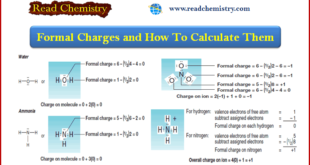
Read More »Formal Charge: Definition, Formula, Calculation, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Formal Charge: Definition, Formula, Calculation, Examples Formal Charge and How To Calculate – Many Lewis structures are incomplete until we decide whether any of their atoms have a formal charge. – Calculating the formal charge on an atom in a Lewis structure …
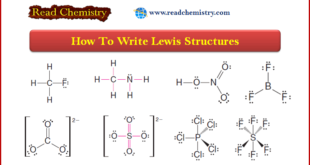
Read More »Lewis Structures: Definition, Structural Formula, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Lewis Structures: Definition, Overview, Structural Formula, Examples Definition of Lewis structures – A Lewis structure is a structural representation of a molecule where dots are used to show electron positions around the atoms and lines or dot pairs represent covalent bonds between …
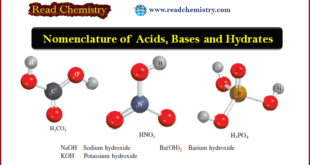
Read More »Nomenclature of Acids, Bases and Hydrates
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nomenclature of Acids, Bases and Hydrates Nomenclature of Acids – An acid can be described as a substance that yields hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. (H+ is equivalent to one proton, and is often referred to that way.) – Formulas …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry