-
Organic Chemistry
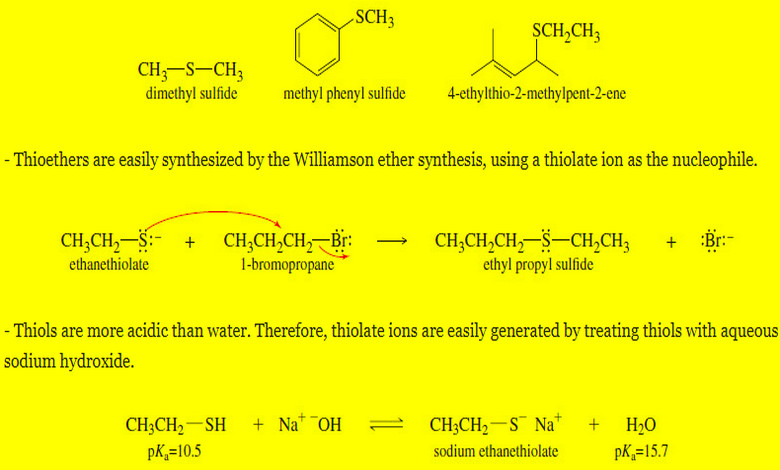
Thioethers (sulfides) and Silyl Ethers
Thioethers (sulfides) and Silyl Ethers – Thioethers, also called sulfides, are ethers with a sulfur atom replacing the oxygen atom…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
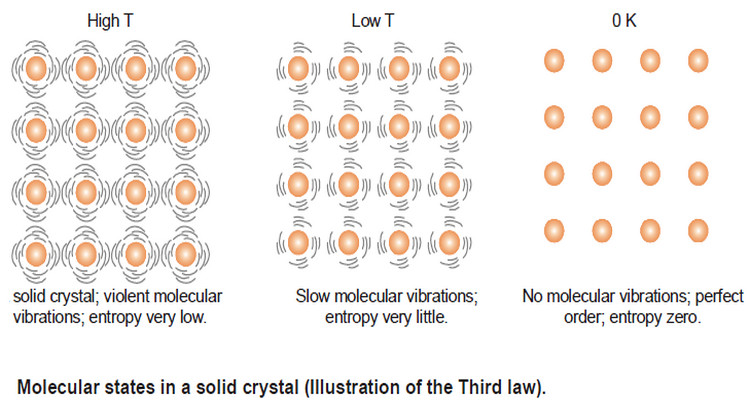
Laws of thermodynamics
Zeroth law of thermodynamics – The zeroth law of thermodynamics is a generalized statement about bodies in contact at thermal…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
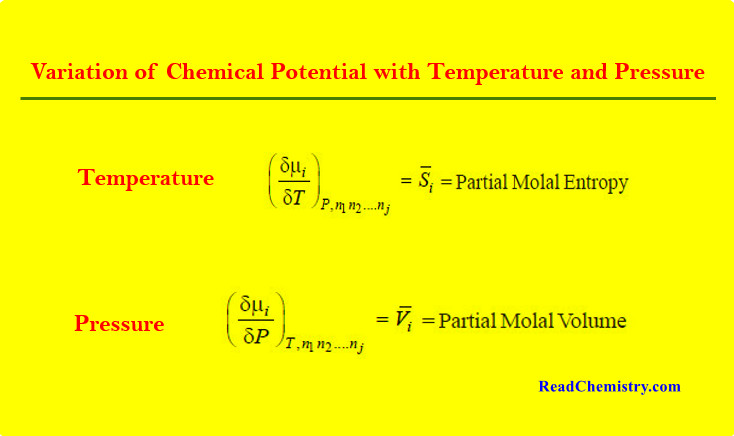
Chemical Potential
– In this topic, we will discuss The Chemical Potential and Variation of Chemical Potential with Temperature and Pressure. Partial…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
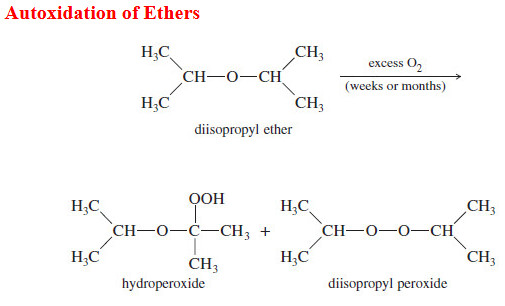
Autoxidation of Ethers
– In this topic, we will discuss The autoxidation of Ethers. What are Ethers? Ethers are compounds of formula R-O-R,…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
Fugacity and activity
– In general, it may be stated that each substance in a given state has a tendency to escape from…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
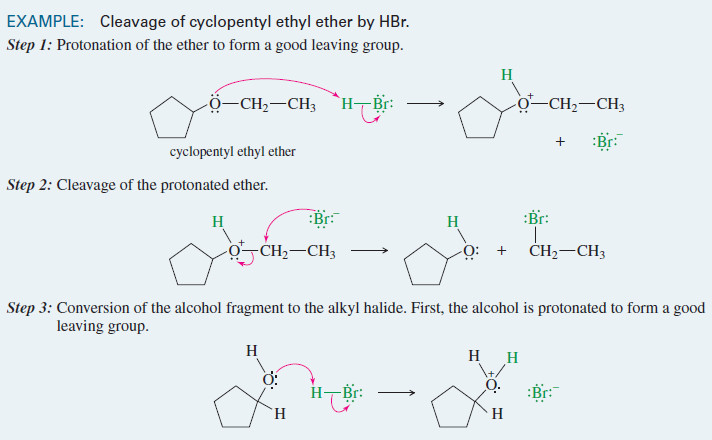
Cleavage of Ethers by HBr and HI
– In this topic, we will discuss the Cleavage of Ethers by HBr and HI Cleavage of Ethers by HBr…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
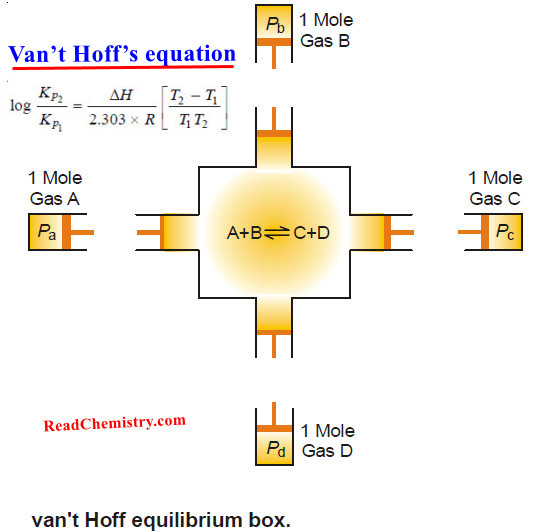
Van’t Hoff isotherm – Van’t Hoff Isochore
Van’t Hoff isotherm – The van’t Hoff isotherm gives the net work that can be obtained from a gaseous reactant…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
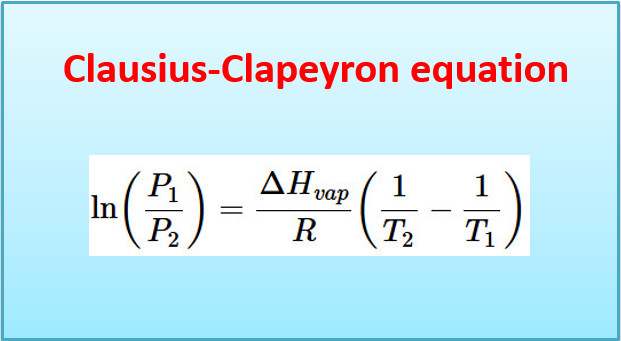
Clausius-Clapeyron equation – Derivation with Applications
– In this topic, we will discuss Clausius-Clapeyron equation – Derivation with Applications. The Clapeyron equation – A useful thermodynamic…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
Gibbs Helmholtz Equations
Gibbs Helmholtz Equations – These are two equations derived by J.W. Gibbs and H.Von Helmholtz and are known as Gibbs…
Read More » -
Biochemistry
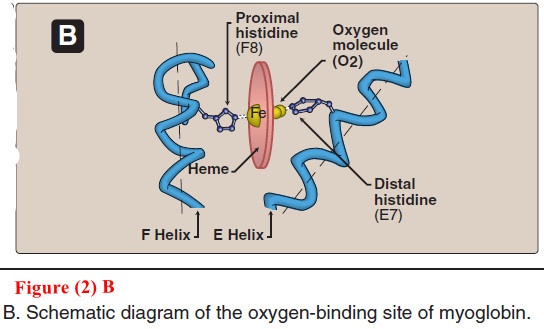
Globular Hemeproteins
Globular Hemeproteins – Hemeproteins are a group of specialized proteins that contain heme as a tightly bound prosthetic group. –…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
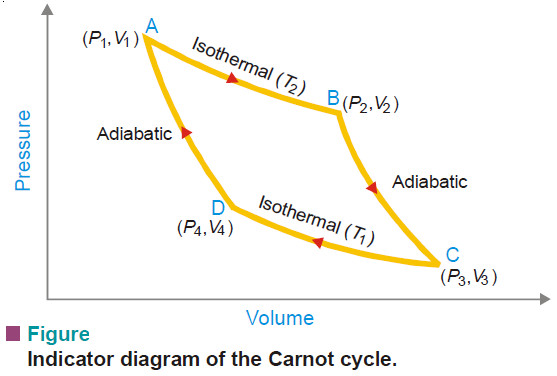
Carnot Cycle – Definition, Theorem, Efficiency, Derivation
– In this topic, we will discuss The Carnot Cycle : Definition, Theorem, Efficiency, Derivation and Sovled problems. The Carnot…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
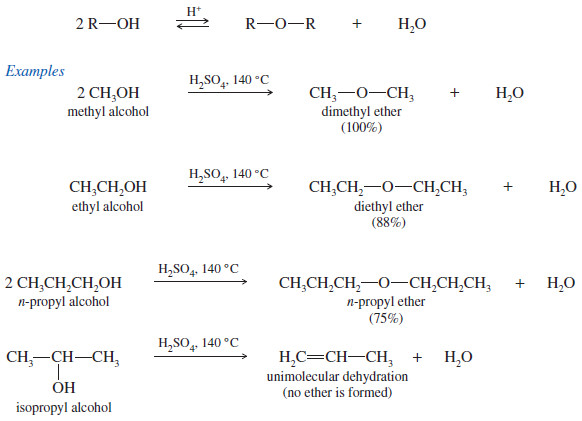
Synthesis of Ethers
Synthesis of Ethers – In this topic, we will discuss 6 methods for Synthesis of Ethers as follows: 1. Ethers…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
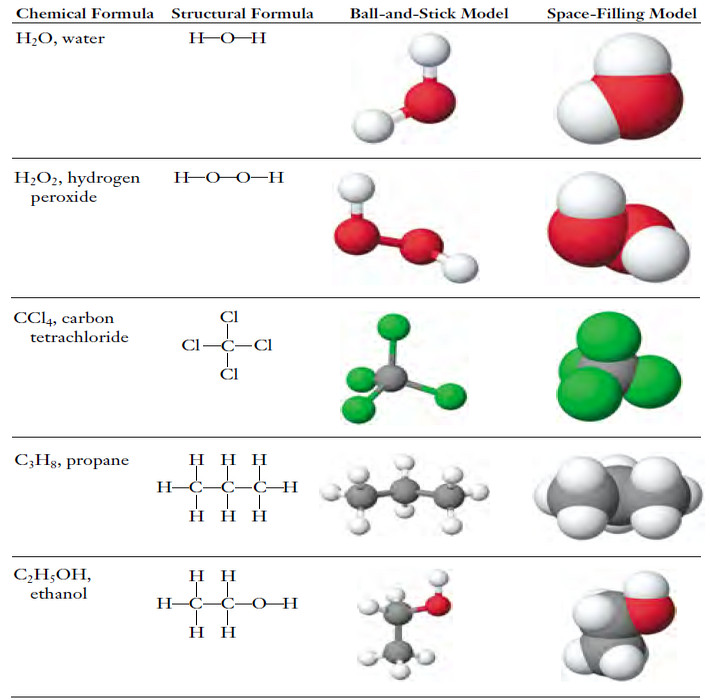
Chemical Formula – Structural Formula
Chemical Formula – The chemical formula for a substance shows its chemical composition. – This represents the elements present as…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
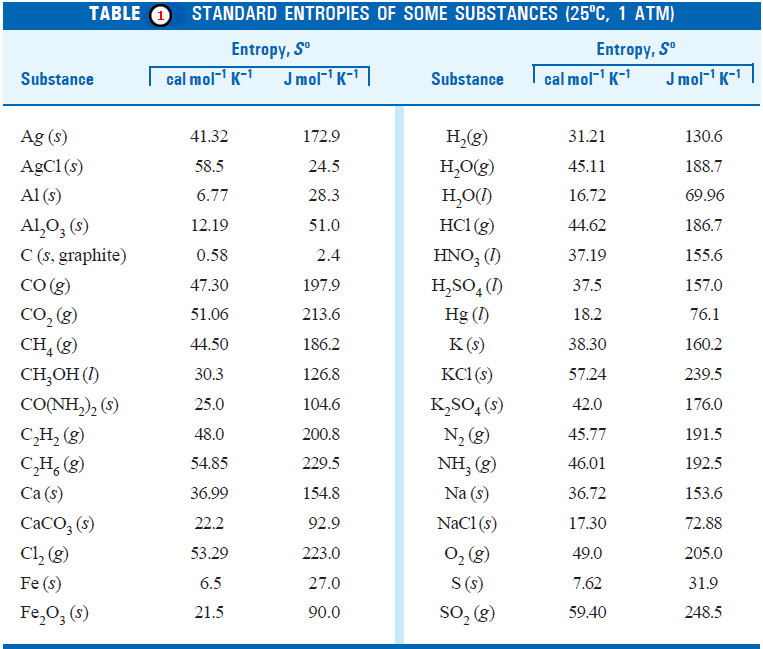
Entropy : Definition, Units, Solved Problems
Definition of entropy – Entropy is a thermodynamic state quantity that is a measure of the randomness or disorder of the…
Read More » -
Biochemistry
Protein Misfolding: Amyloid disease – Prion disease
– In this topic, we will talk about Protein Misfolding. Protein Misfolding – Protein folding is a complex, trial-and-error process…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
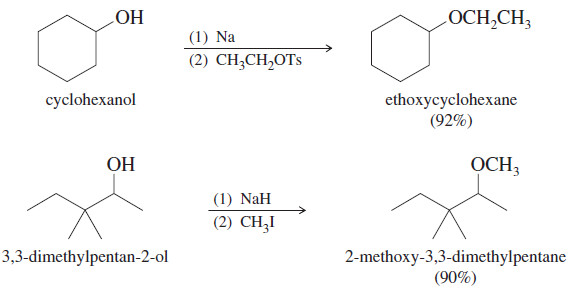
Williamson Ether Synthesis : Mechanism, Examples
– In this topic, we will discuss the Williamson Ether Synthesis : Mechanism, Examples and Solved problems. Williamson Ether Synthesis…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
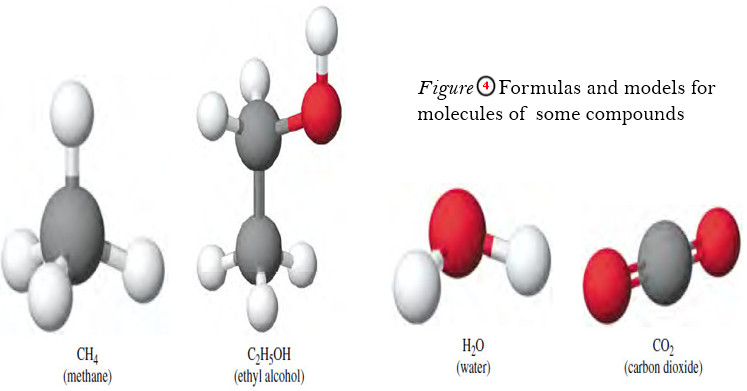
Atoms and Molecules
Democritus’s ideas about atoms – The Greek philosopher Democritus (470–400 BC) suggested that all matter is composed of tiny, discrete,…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
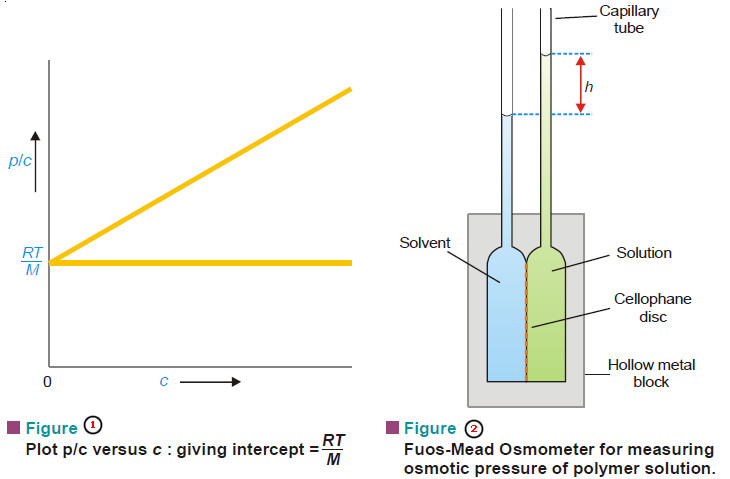
Macromolecules : Definition and Molecular Weight
– In this topic, we will discuss the Macromolecules : Definition and Molecular Weight What are Macromolecules? – Colloidal solutions…
Read More » -
Biochemistry
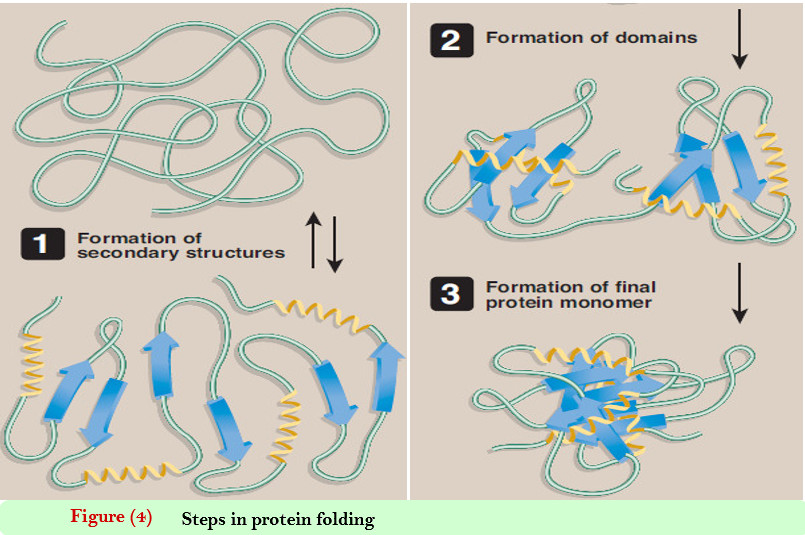
Tertiary structure of globular proteins
– In the last topic in biochemistry in our website, we talked about: Primary structure of Protein , Secondary Structure…
Read More » -
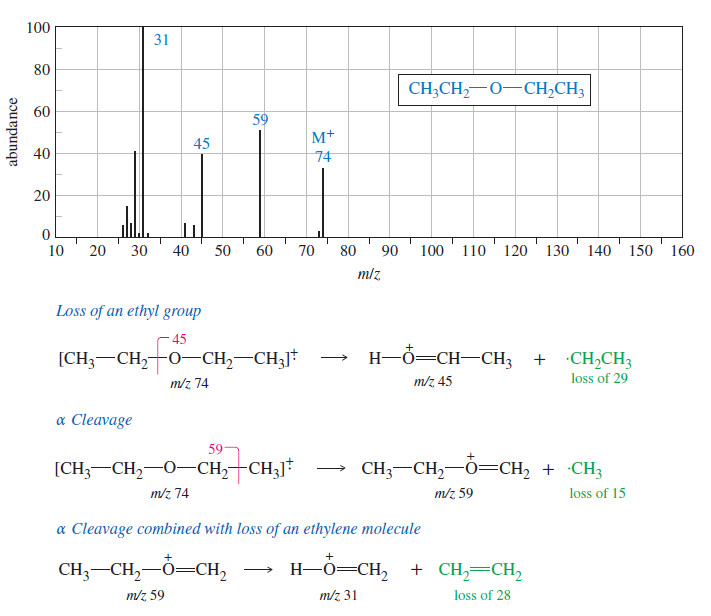
Organic Chemistry
Spectroscopy of Ethers : IR, Mass, 13C NMR, 1H NMR
Spectroscopy of Ethers – Here we will discuss Spectroscopy of Ethers: IR Spectroscopy, Mass Spectroscopy, 13C NMR amd 1H NMR. …
Read More »