Physical Chemistry blends chemistry with physics, studying matter’s behavior using concepts like thermodynamics, kinetics, quantum mechanics, and spectroscopy. It explains how and why chemical reactions occur at the molecular level.
Physical Chemistry
-
Distribution of Molecular velocities
– In this topic, we will discuss Distribution of Molecular velocities. Distribution of Molecular velocities – While deriving Kinetic Gas…
Read More » -
Deduction of Gas laws from the Kinetic Gas Equation
– In this topic, we will talk about Deduction of Gas laws from the Kinetic Gas Equation. Assumptions of the…
Read More » -
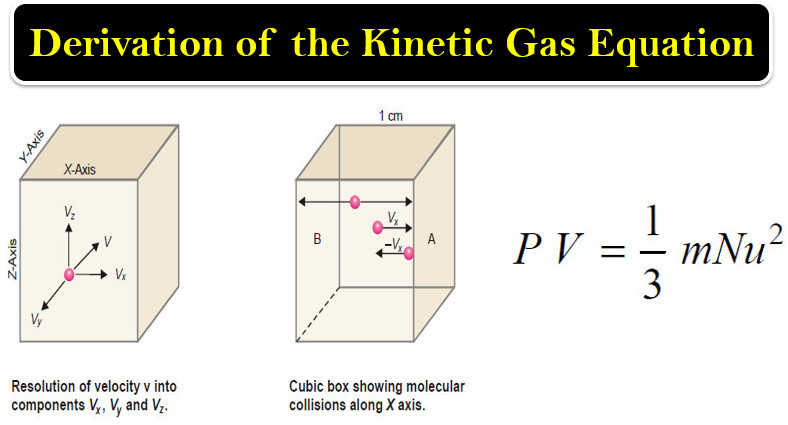
Derivation of the Kinetic Gas Equation
– In this topic, we will talk about Derivation of the Kinetic Gas Equation. Derivation of the Kinetic Gas Equation…
Read More » -
Laws of thermodynamics
Zeroth law of thermodynamics – The zeroth law of thermodynamics is a generalized statement about bodies in contact at thermal…
Read More » -
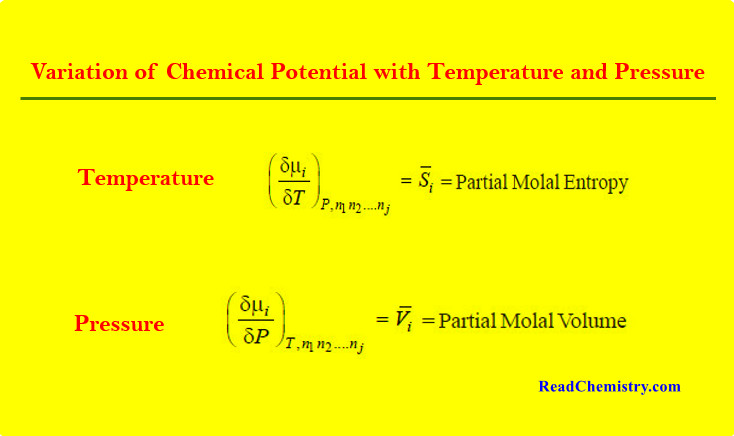
Chemical Potential
– In this topic, we will discuss The Chemical Potential and Variation of Chemical Potential with Temperature and Pressure. Partial…
Read More » -
Fugacity and activity
– In general, it may be stated that each substance in a given state has a tendency to escape from…
Read More » -
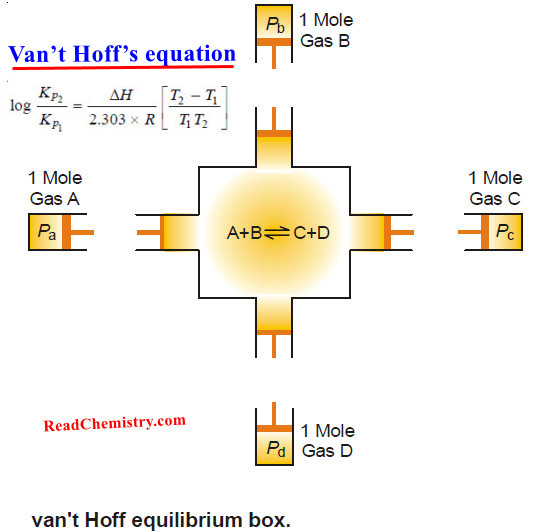
Van’t Hoff isotherm – Van’t Hoff Isochore
Van’t Hoff isotherm – The van’t Hoff isotherm gives the net work that can be obtained from a gaseous reactant…
Read More » -
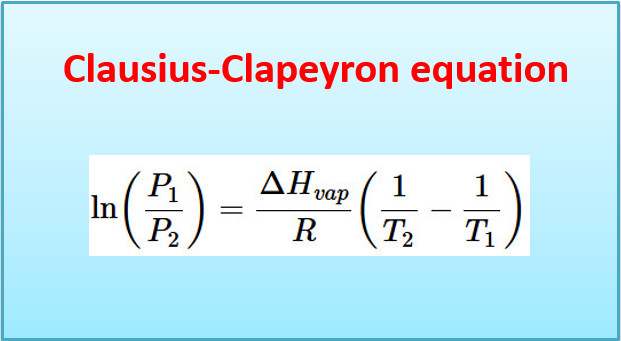
Clausius-Clapeyron equation – Derivation with Applications
– In this topic, we will discuss Clausius-Clapeyron equation – Derivation with Applications. The Clapeyron equation – A useful thermodynamic…
Read More » -
Gibbs Helmholtz Equations
Gibbs Helmholtz Equations – These are two equations derived by J.W. Gibbs and H.Von Helmholtz and are known as Gibbs…
Read More » -
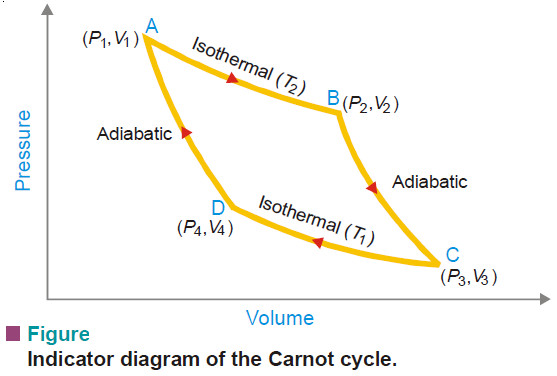
Carnot Cycle – Definition, Theorem, Efficiency, Derivation
– In this topic, we will discuss The Carnot Cycle : Definition, Theorem, Efficiency, Derivation and Sovled problems. The Carnot…
Read More » -
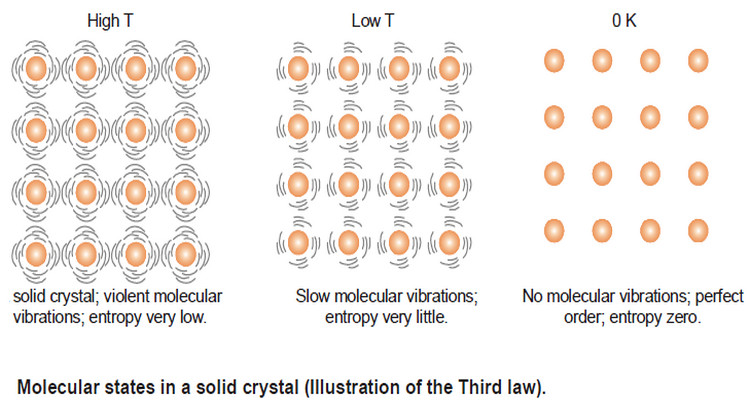
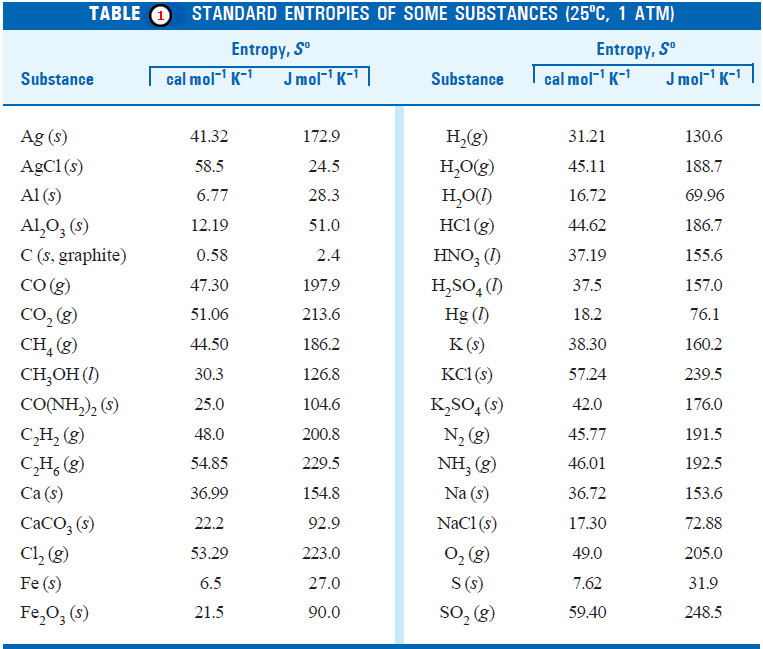
Entropy : Definition, Units, Solved Problems
Definition of entropy – Entropy is a thermodynamic state quantity that is a measure of the randomness or disorder of the…
Read More » -
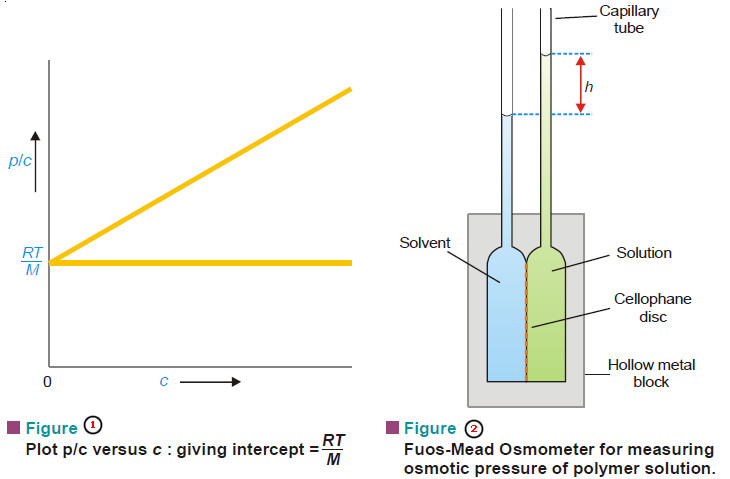
Macromolecules : Definition and Molecular Weight
– In this topic, we will discuss the Macromolecules : Definition and Molecular Weight What are Macromolecules? – Colloidal solutions…
Read More » -
Second Law of Thermodynamics: MCQ Quiz with answers
Second Law of Thermodynamics: MCQ Quiz with answers – In this subject, you will find 49 questions and answers MCQ…
Read More » -
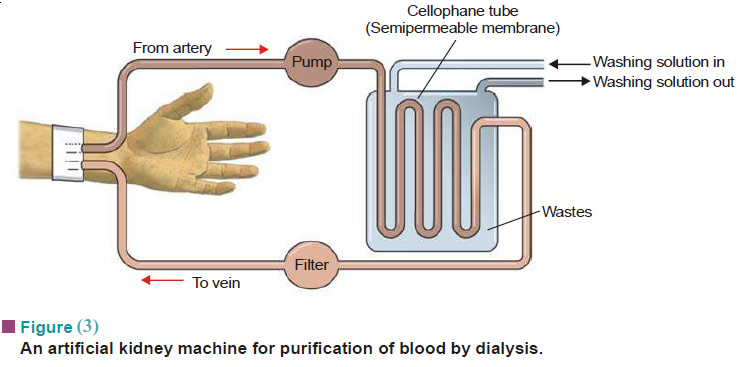
Applications of Colloids
– In this topic, we will discuss The Applications of Colloids. Applications of Colloids – Colloids play an important role…
Read More » -
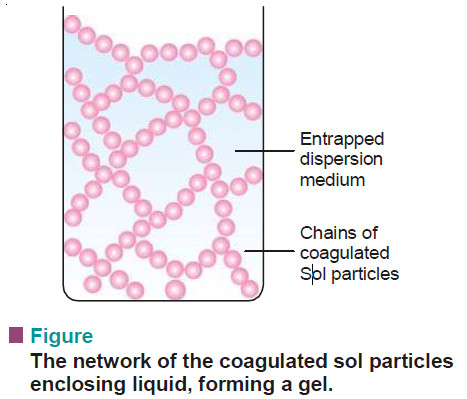
Gels : Defination, Types, Properties
– In this topic, we will discuss The Gels : Defination, Types, and Properties. What are Gels? – A gel…
Read More » -
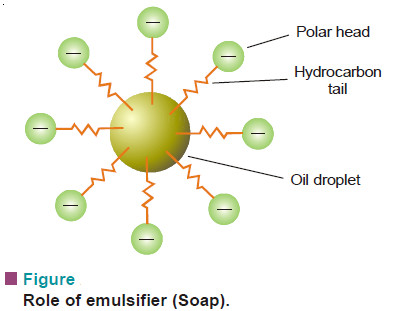
Emulsions : Defination, Types, Examples, Preparation
Defination of Emulsions – Emulsions are liquid-liquid colloidal systems. – In other words, an emulsion may be defined as a…
Read More » -
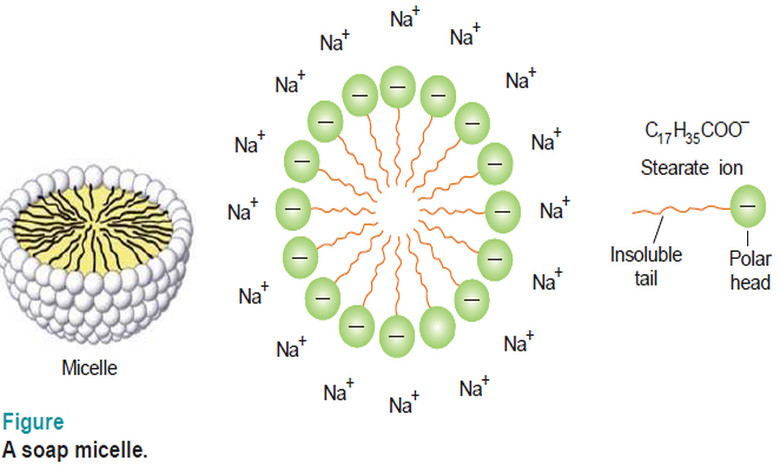
Associated Colloids
– In this subject, we will discuss the Associated Colloids. Associated Colloids – The molecules of substances as soaps and…
Read More » -
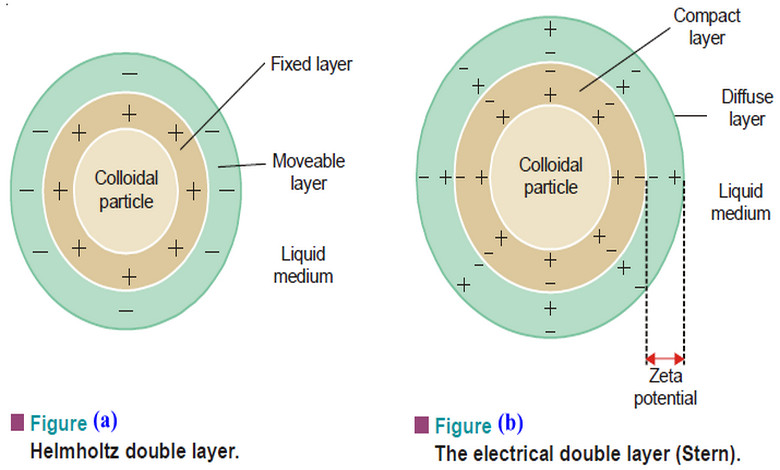
Electrical Properties of Sols
Electrical Properties of Sols – In this topic we will discuss the Electrical Properties of Sols as follow: (1) The…
Read More » -
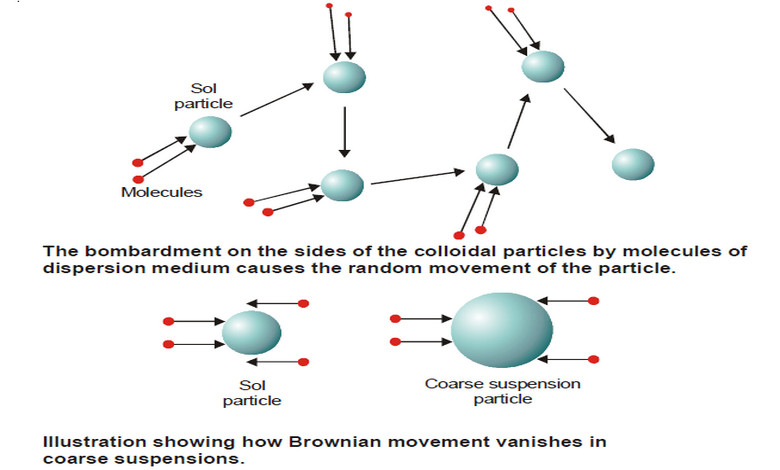
Kinetic Properties of Sols – Brownian movement
Kinetic Properties of Sols – In this topic, we will discuss Kinetic Properties of Sols. Brownian Movement – When a…
Read More » -
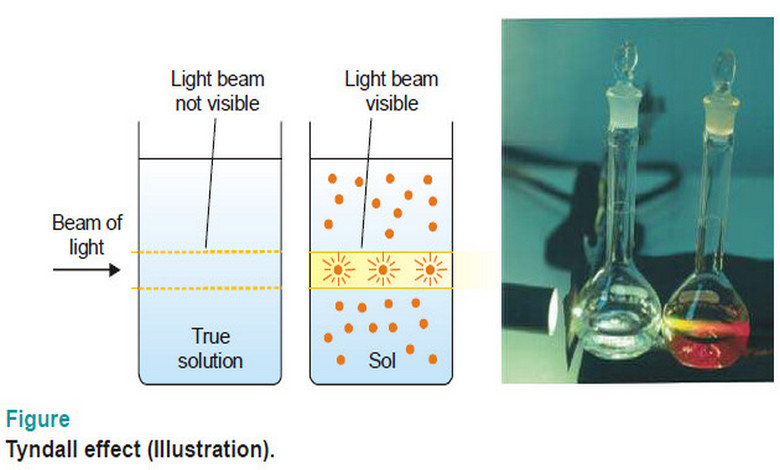
Optical Properties of Sols
Optical Properties of Sols – In this topic, we will discuss Optical Properties of Sols as follow: Sols exhibit Tyndall…
Read More »