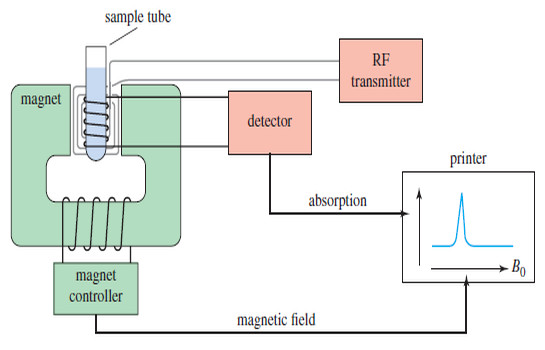
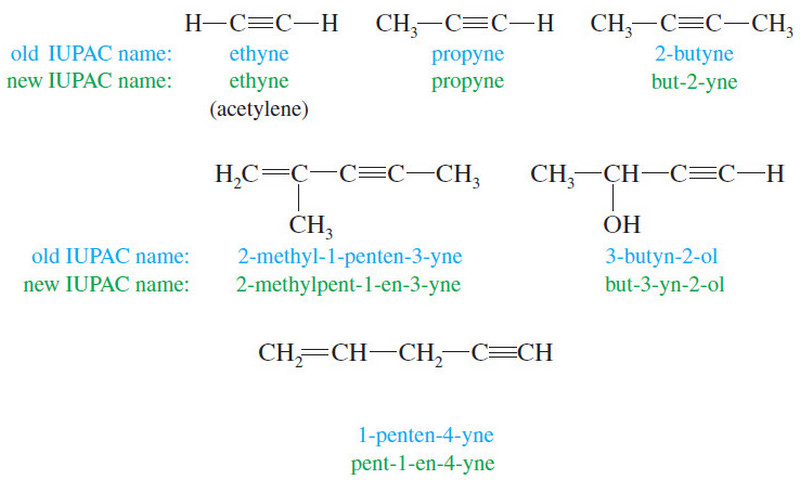
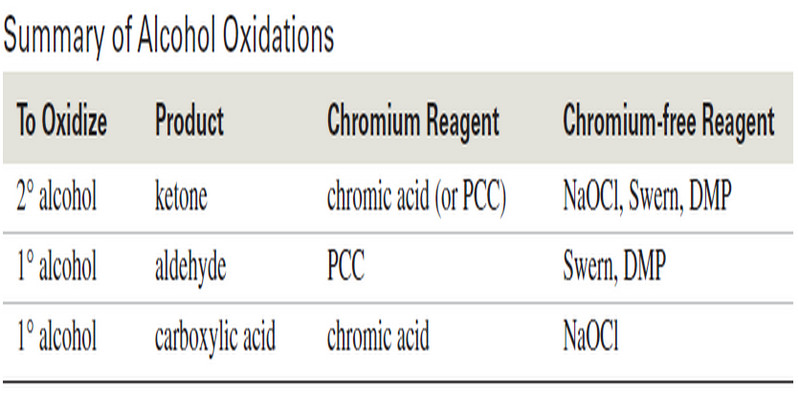
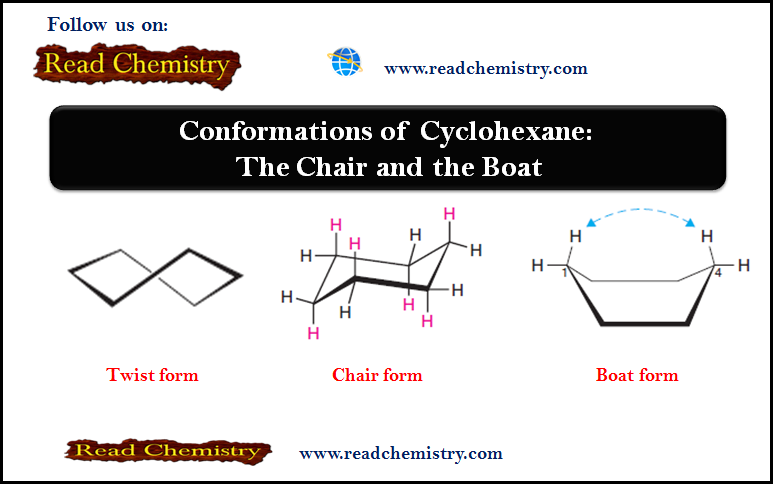
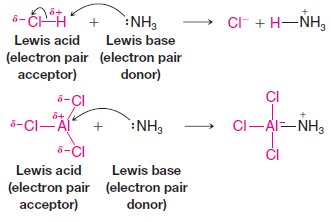
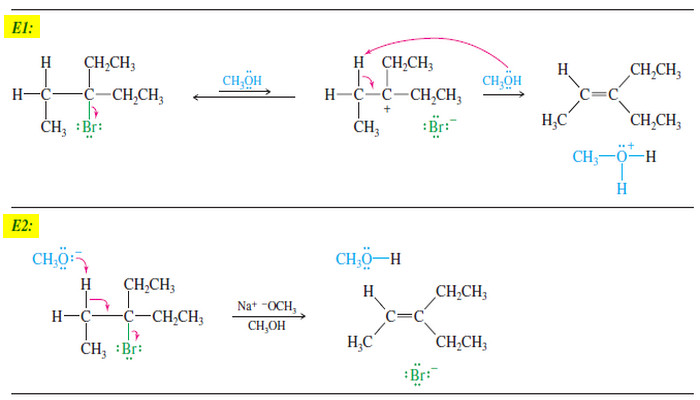
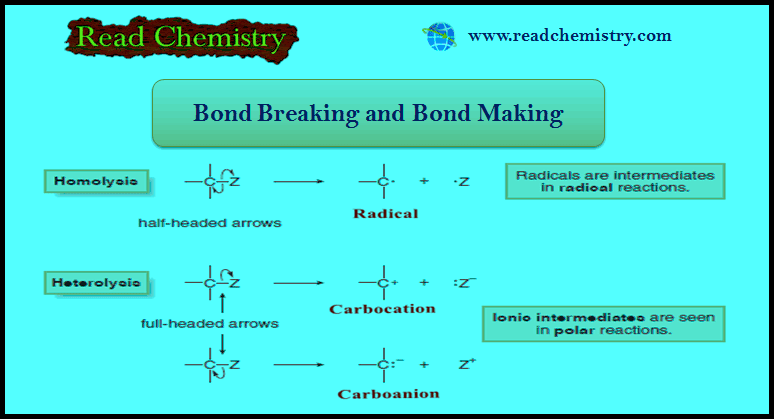
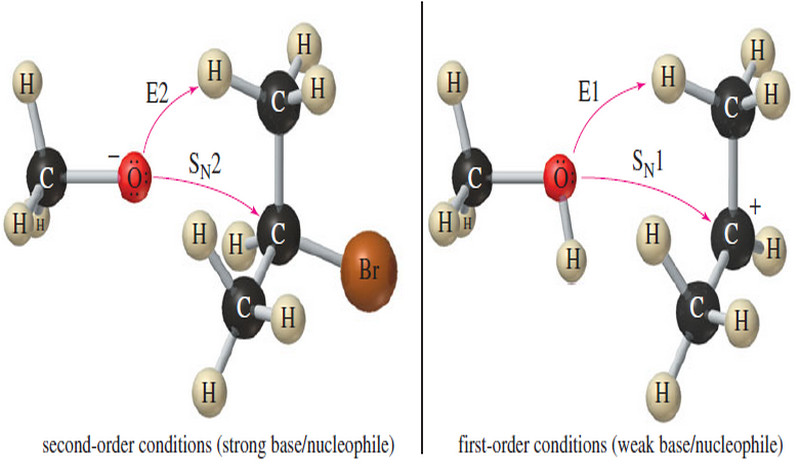
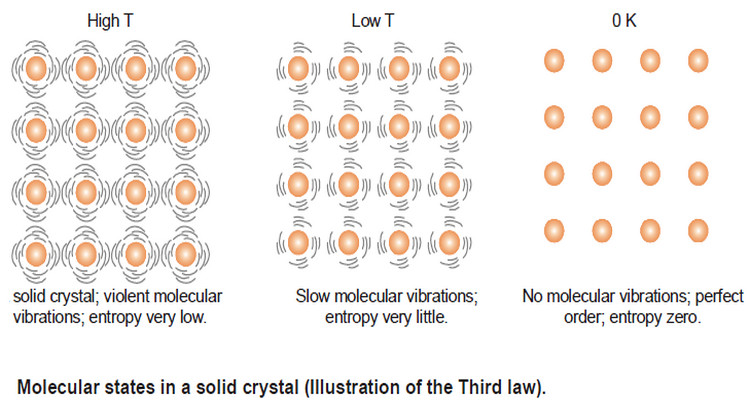
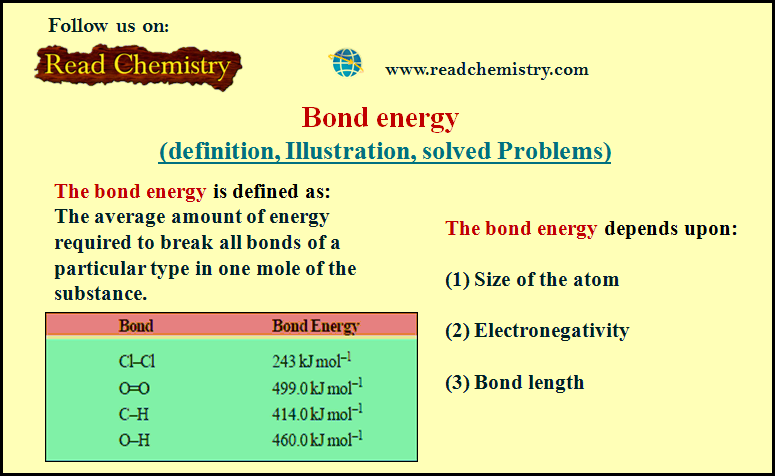
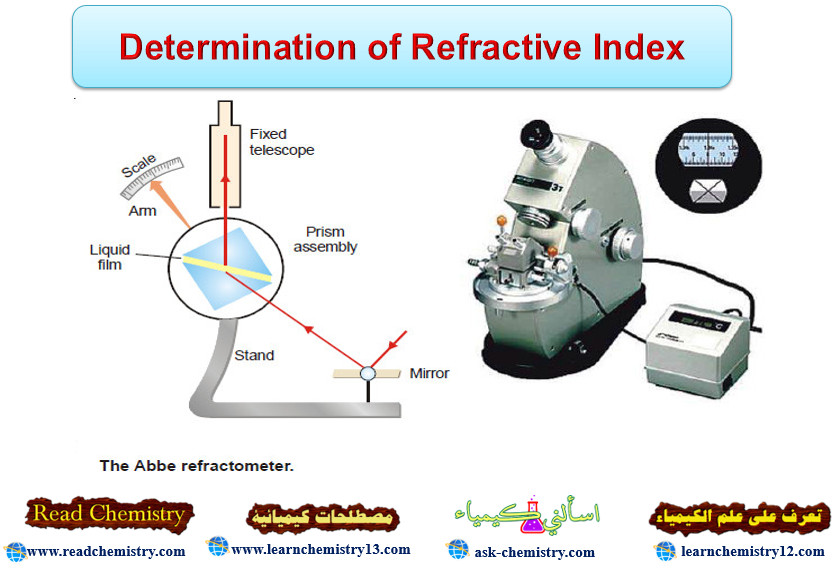
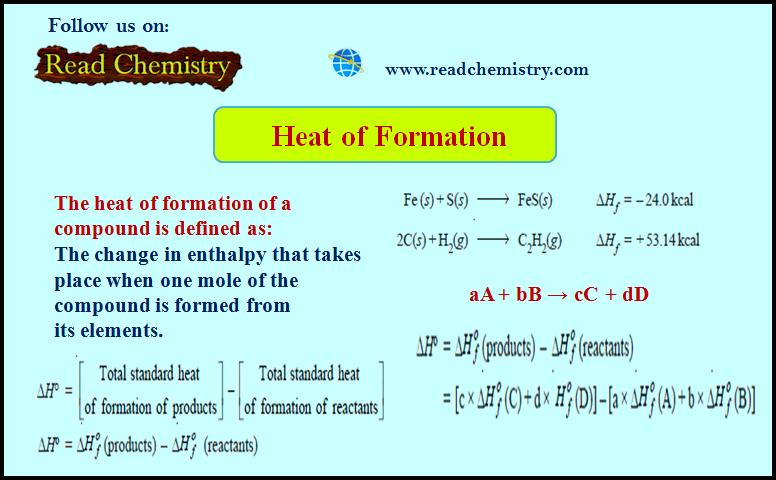
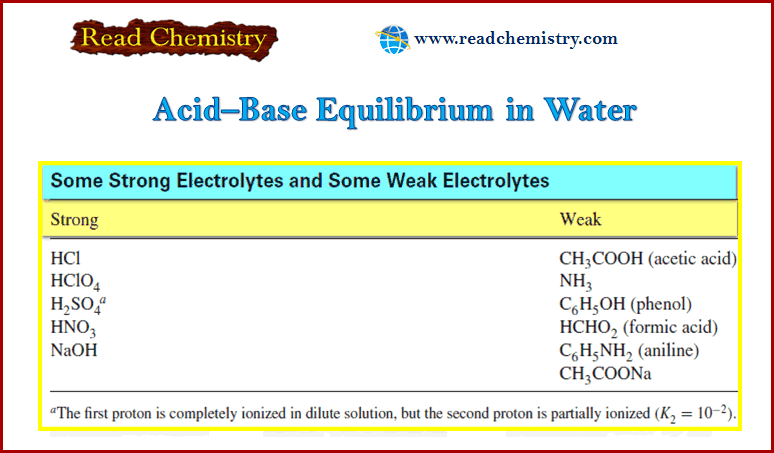
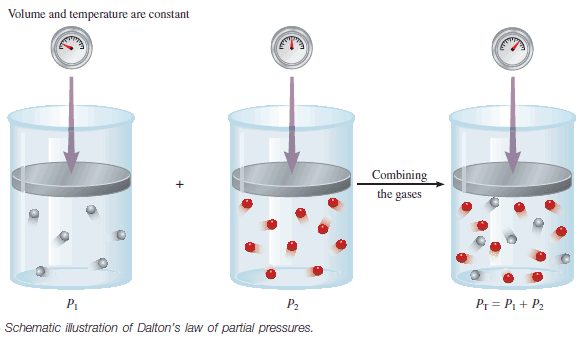
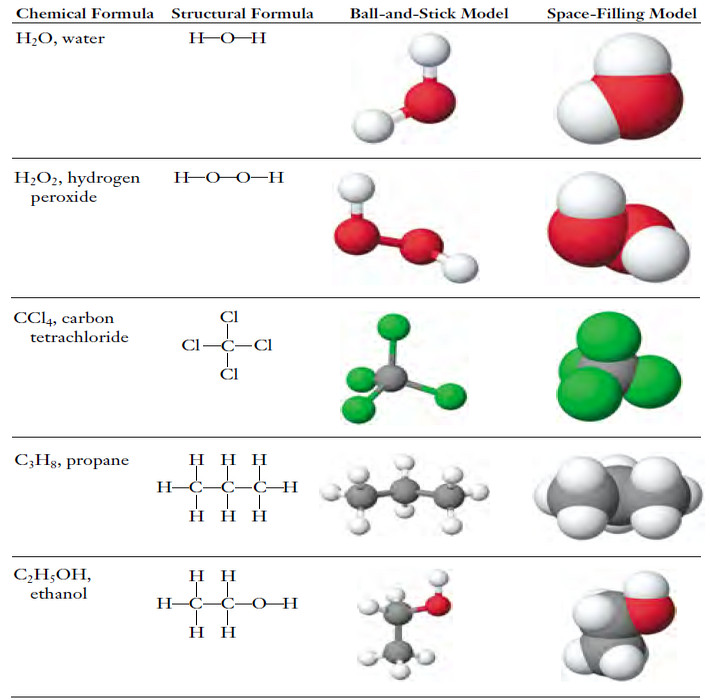
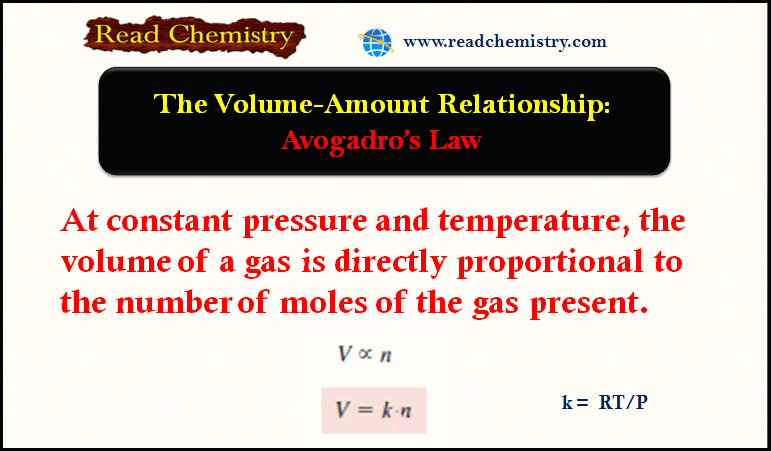
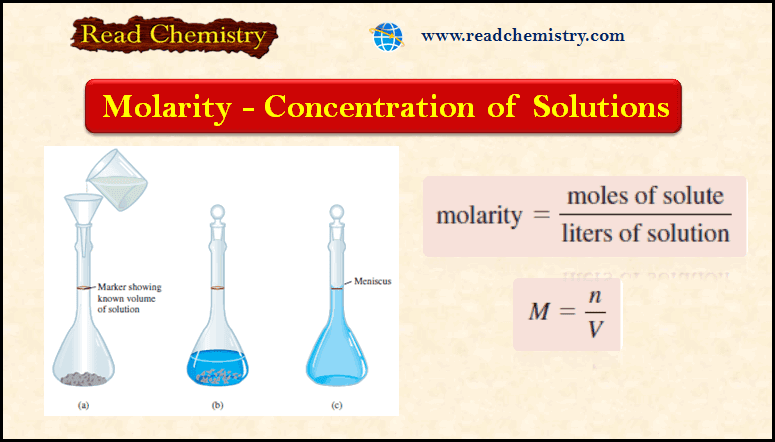
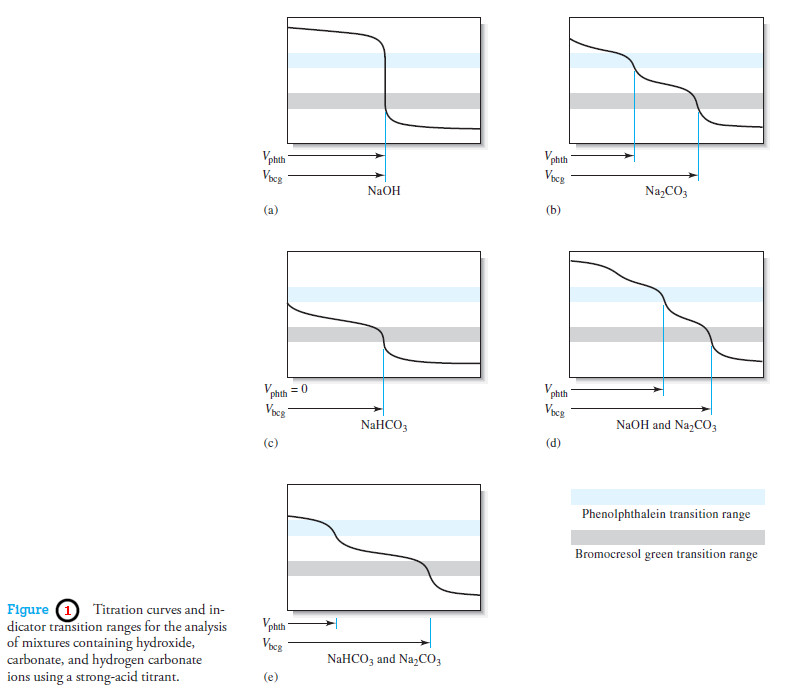
Popular Posts
-
Physical Chemistry
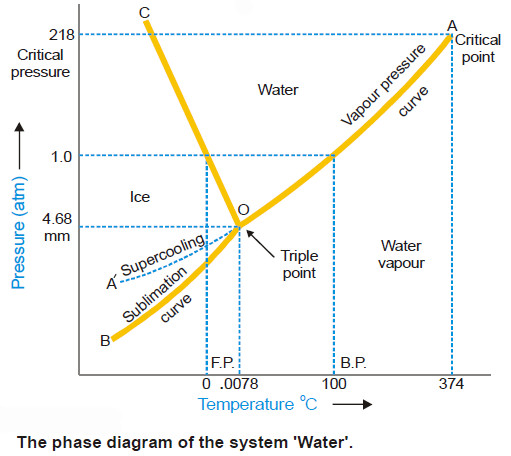
Water system, Phase diagram of Water
The Water system – Under normal conditions the Water system is a three-phase, one-component system. – The three phases involved…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
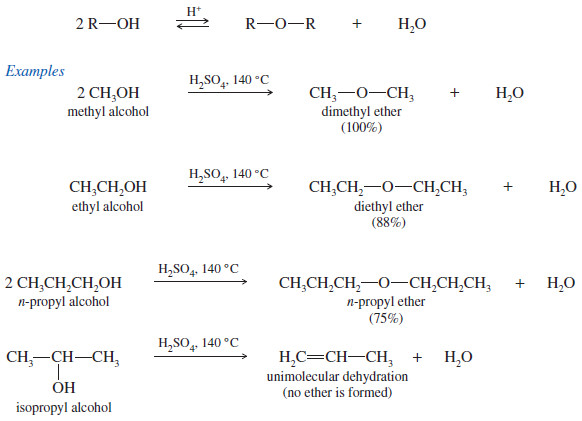
Synthesis of Ethers
Synthesis of Ethers – In this topic, we will discuss 6 methods for Synthesis of Ethers as follows: 1. Ethers…
Read More » -
Analytical Chemistry
Volumetric Flask: Overview, Uses, Function
Volumetric Flask – A volumetric flask is manufactured with capacities ranging from 5 mL to 5 L and is…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
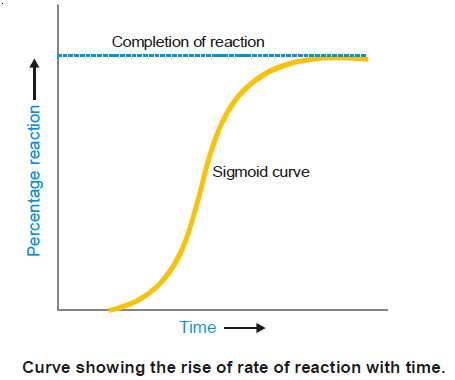
Autocatalysis, Catalytic poisoning and Negative Catalysis
– In this topic, we will discuss Autocatalysis, Catalytic poisoning and Negative Catalysis. Catalytic poisoning – Very often a heterogeneous…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
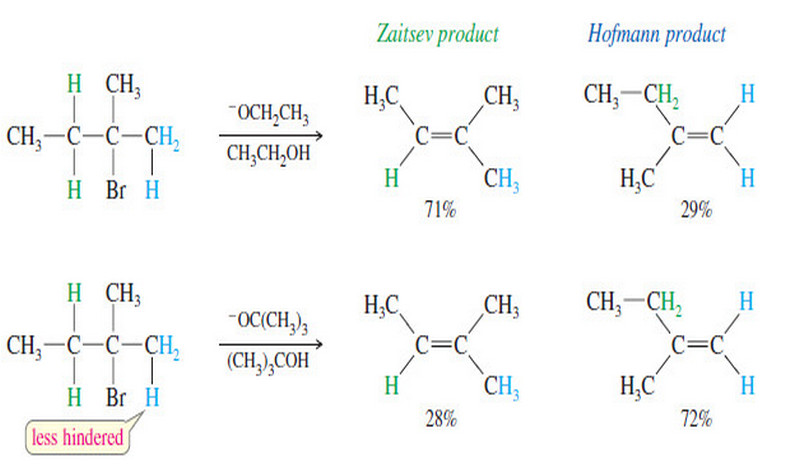
Alkene Synthesis by Elimination of Alkyl Halides
Alkene Synthesis by Elimination of Alkyl Halides – Dehydrohalogenation is the elimination of a hydrogen and a halogen from an…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
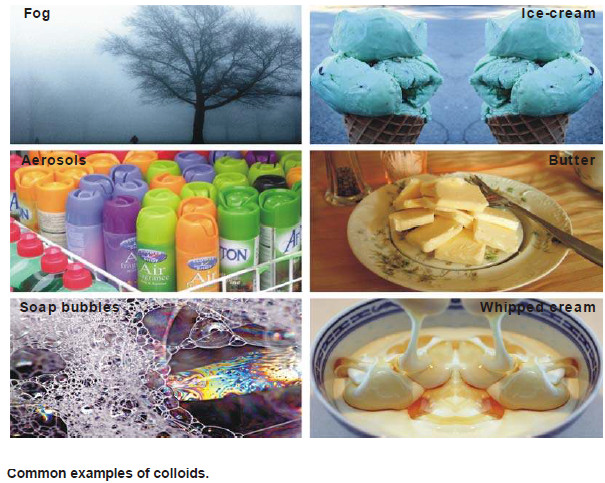
Colloids: Definition, History and Types
– In this topic, we will discuss the colloids: definition, History and Types History of colloids – Thomas Graham (1861)…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
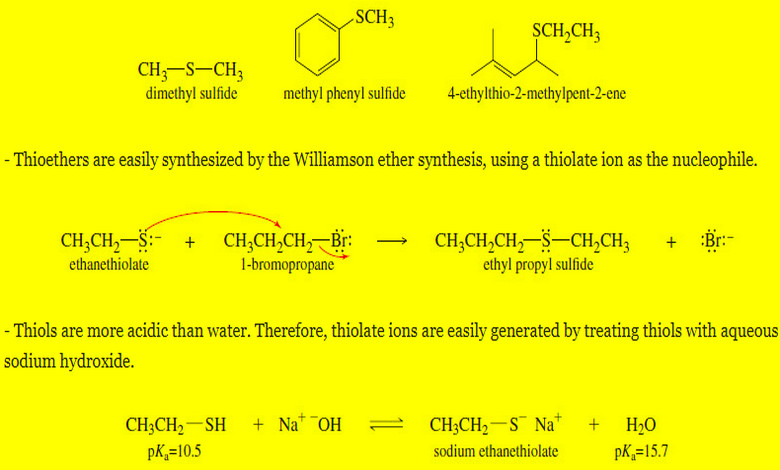
Thioethers (sulfides) and Silyl Ethers
Thioethers (sulfides) and Silyl Ethers – Thioethers, also called sulfides, are ethers with a sulfur…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Physical Chemistry
Laws of thermodynamics
Zeroth law of thermodynamics – The zeroth law of thermodynamics is a generalized statement about…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
General Chemistry
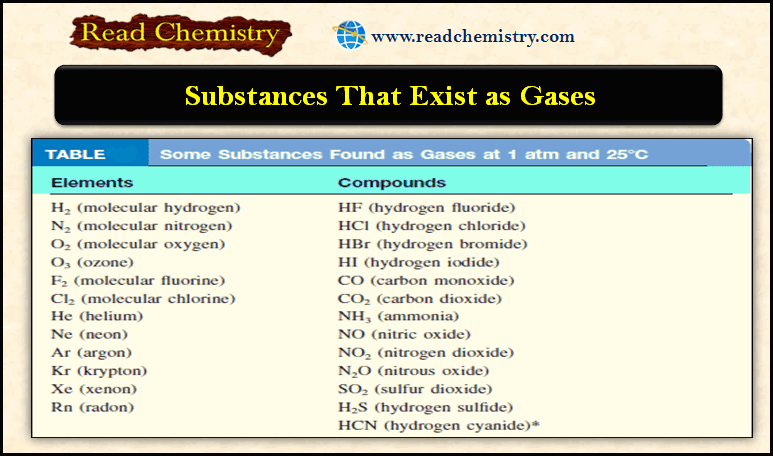
Gaseous Substances: Substances That Exist as Gases
– In this subject, we will discuss the Gaseous Substances: Substances That Exist as Gases…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Analytical Chemistry
Calibration of Volumetric Glassware in the laboratory
– In this subject, we will discuss How to Calibrate Volumetric Glassware in the laboratory…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
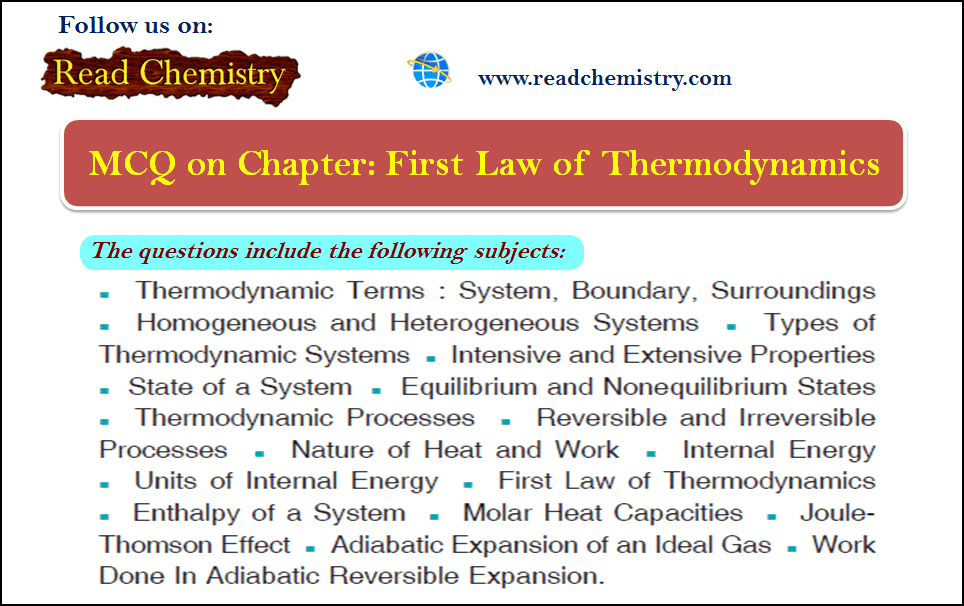
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-