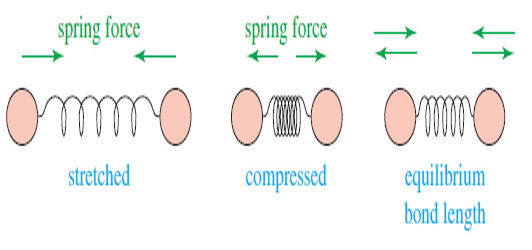
Physical Chemistry blends chemistry with physics, studying matter’s behavior using concepts like thermodynamics, kinetics, quantum mechanics, and spectroscopy. It explains how and why chemical reactions occur at the molecular level.
Physical Chemistry
-
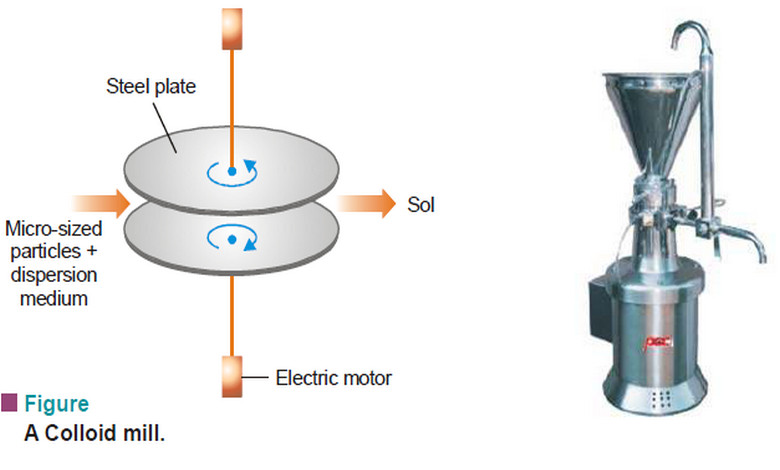
Preparation of Sols and Purification of Sols
– In this topic, we will discuss Preparation of Sols, Purification of Sols and its colors Preparation of Sols –…
Read More » -
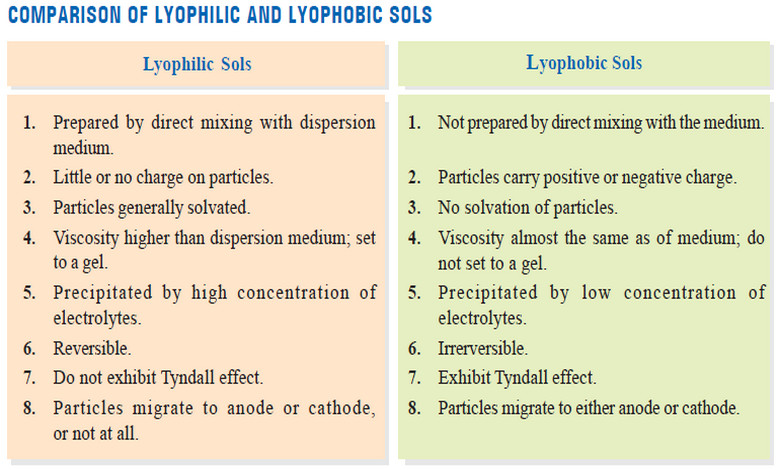
Lyophilic and Lyophobic sols : Defination, Properties, Comparison
– In this topic, we will discuss The Lyophilic and Lyophobic sols : Defination, Characteristics, and Comparison. Defination of Lyophilic…
Read More » -
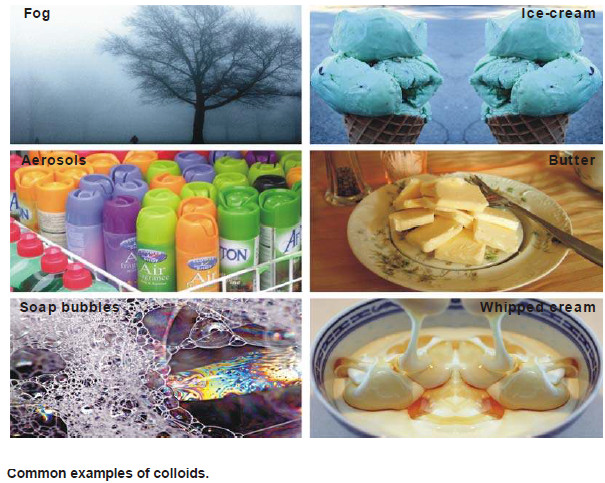
Colloids: Definition, History and Types
– In this topic, we will discuss the colloids: definition, History and Types History of colloids – Thomas Graham (1861)…
Read More » -
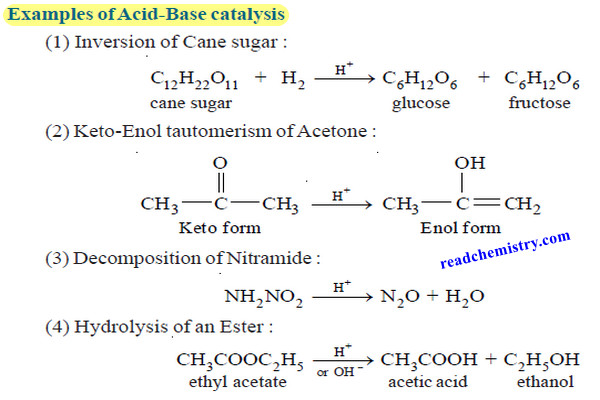
Acid-Base catalysis (definition – Examples – Mechanism)
– In this topic, we will discuss Acid-Base catalysis: definition, Examples and Mechanism. Acid-Base catalysis – A number of homogeneous…
Read More » -
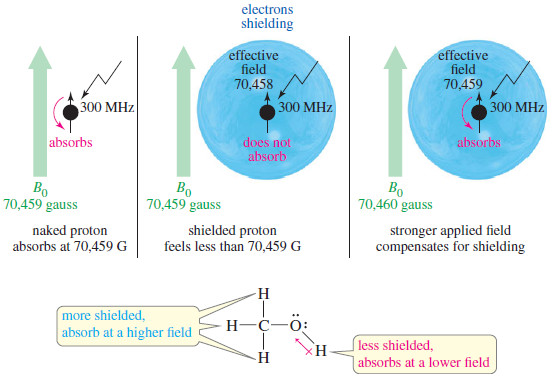
Magnetic Shielding by Electrons
– In this topic, we will discuss the Magnetic Shielding by Electrons Magnetic Shielding by Electrons – Up to now,…
Read More » -
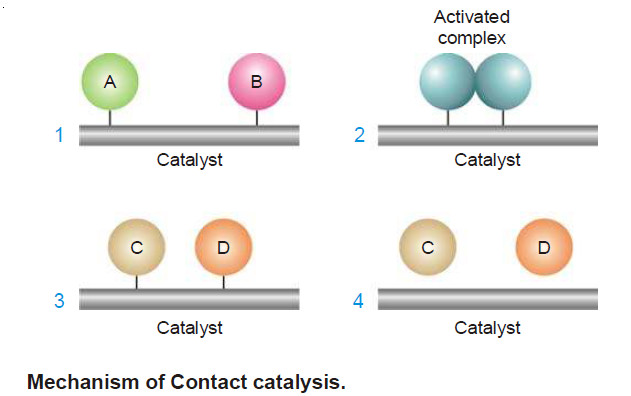
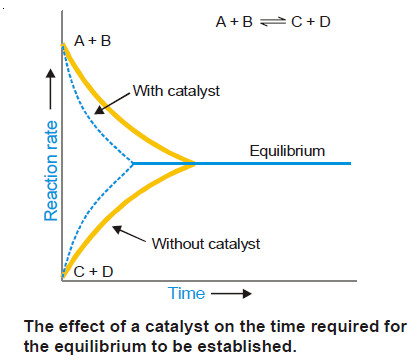
Theories of catalysis
Theories of Catalysis – There are two main theories of catalysis: (1) Intermediate Compound Formation theory. (2) The Adsorption theory.…
Read More » -
Autocatalysis, Catalytic poisoning and Negative Catalysis
– In this topic, we will discuss Autocatalysis, Catalytic poisoning and Negative Catalysis. Catalytic poisoning – Very often a heterogeneous…
Read More » -
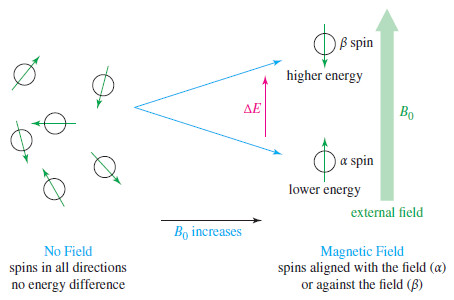
NMR – Theory of Magnetic Nuclear Resonance
Introduction to NMR – Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination. –…
Read More » -
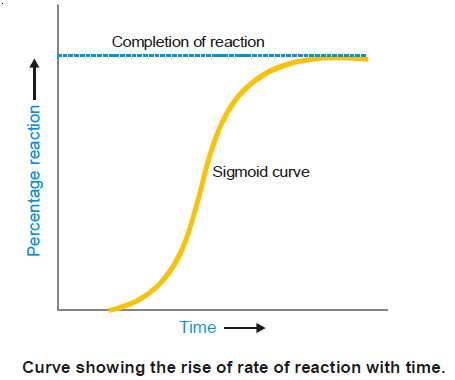
Characteristics of Catalytic Reactions
– In this topic, we will discuss general Characteristics of Catalytic Reactions and Promoters. General Characteristics of Catalytic Reactions –…
Read More » -
Catalysis: Types of Catalysis
– In this topic, we will discuss the Catalysis and The types of catalysis : Homogeneous catalysis – Heterogenous catalysis.…
Read More » -
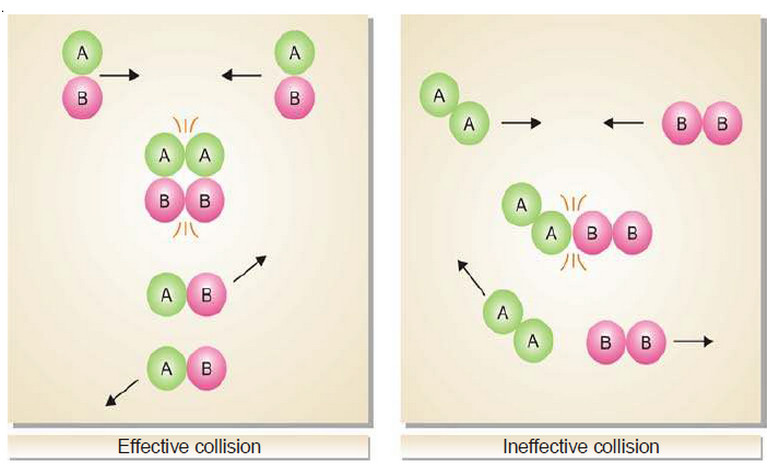
Collision theory of Reaction rates
Collision theory of Reaction rates – According to collision theory, a chemical reaction takes place only by collisions between the…
Read More » -
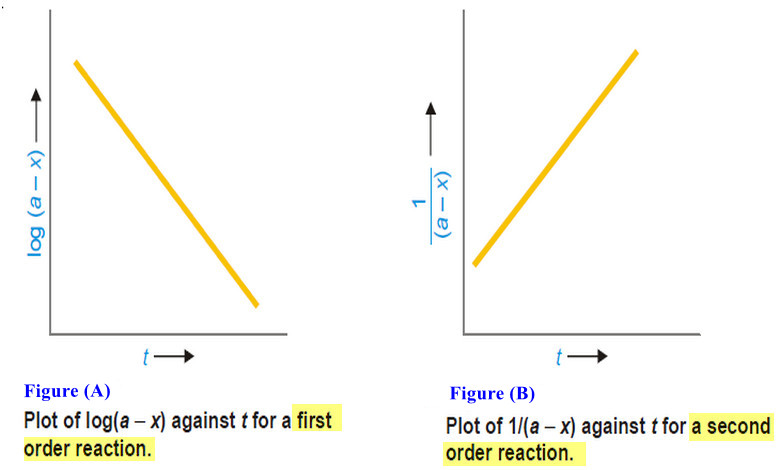
How to determine the order of reaction?
Determination of the order of reaction – There are at least four different methods to determine the order of reaction…
Read More » -
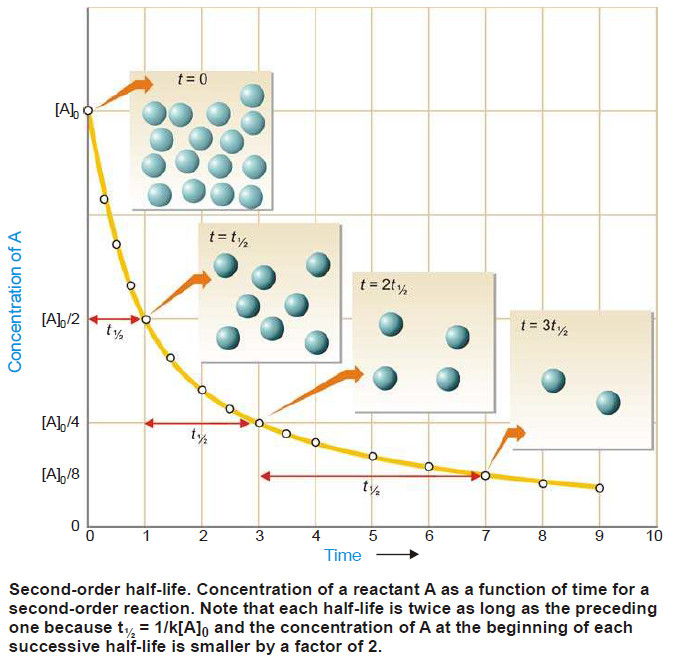
Second order reaction
Second order reaction – Let us take a second order reaction of the type 2A ⎯⎯→ products – Suppose the…
Read More » -
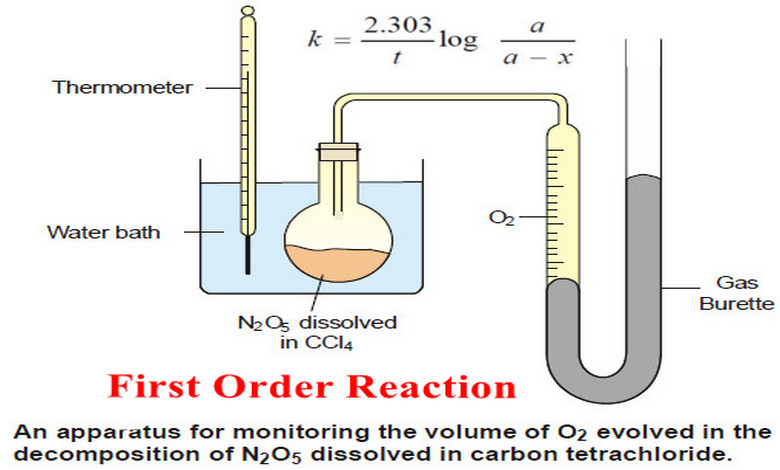
First Order Reaction -Examples and Solved problems
First order reaction – Let us consider a first order reaction: A → products – Suppose that at the beginning…
Read More » -
Molecular Vibrations : IR spectrum
– In this subject we talk about Molecular Vibrations as introduction to understand IR spectrum Molecular Vibrations – Before discussing…
Read More » -
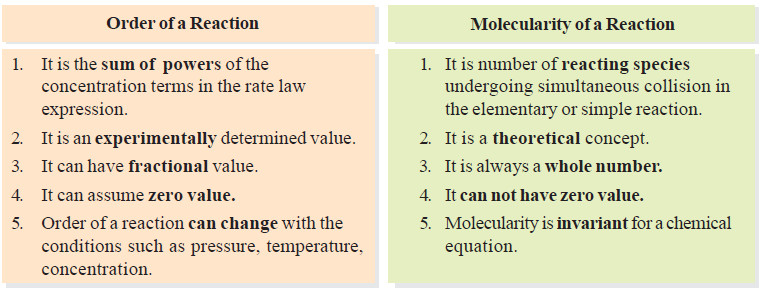
Molecularity of a reaction
– we will discuss the Molecularity of a reaction and the Differences Between Order and Molecularity. Molecularity of a reaction…
Read More » -
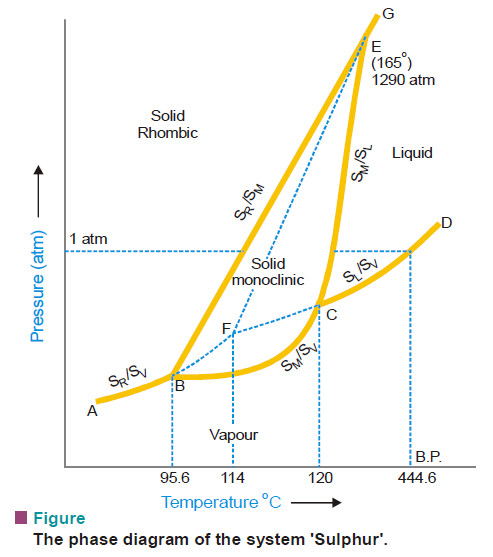
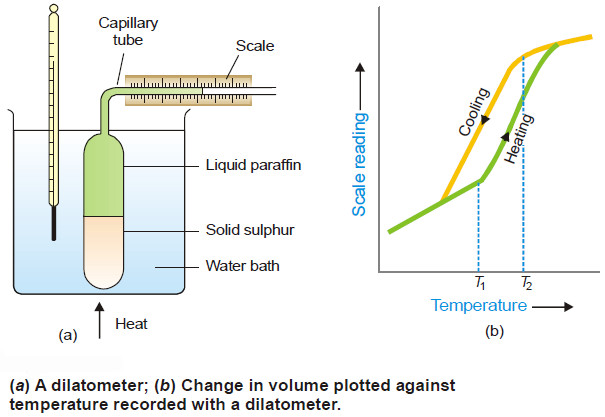
Sulphur system – Phase diagram of Sulphur
The Sulphur system – Sulphur system is a one-component, four-phase system. – The four phases are: (a) Two solid polymorphic…
Read More » -
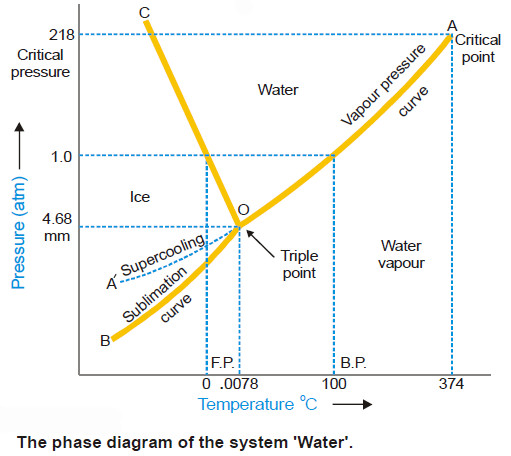
Water system, Phase diagram of Water
The Water system – Under normal conditions the Water system is a three-phase, one-component system. – The three phases involved…
Read More » -
Polymorphism – Allotropy
Polymorphism – The occurrence of the same substance in more than one crystalline forms is known as Polymorphism. – Polymorphism…
Read More » -
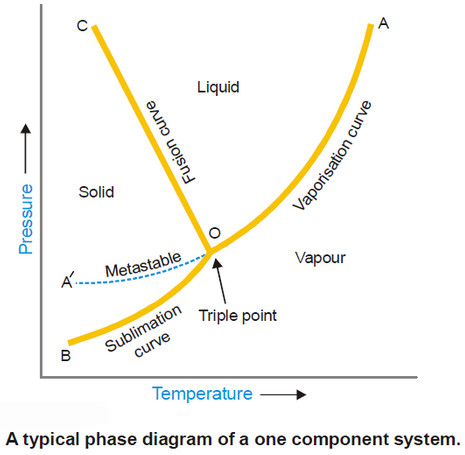
Phase diagram – Phase Rule
Phase Diagram – A phase diagram is a plot showing the conditions of pressure and temperature under which two or…
Read More »