– In this topic, we will discuss The Gels : Defination, Types, and Properties.
What are Gels?
– A gel is a jelly-like colloidal system in which a liquid is dispersed in a solid medium.
– For example, when a warm sol of gelatin is cooled, it sets to a semisolid mass which is a gel.
– The process of a gel formation is known as Gelation.
Explanation:
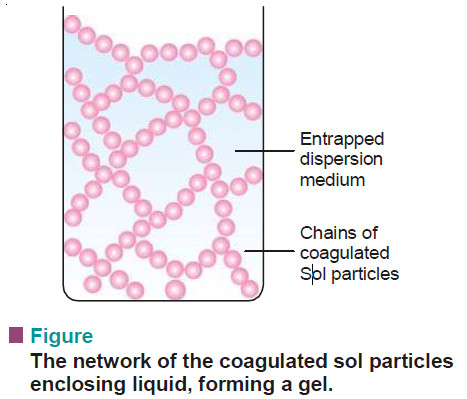
– Gelation may be thought of as partial coagulation of a sol.
– The coagulating sol particles first unite to form long thread-like chains.
– These chains are then interlocked to form a solid framework.
– The liquid dispersion medium gets trapped in the cavities of this framework.
– The resulting semisolid porous mass has a gel structure.
– A sponge soaked in water is an illustration of gel structure.
Types of Gels
– Gels may be classified into two types :
(a) Elastic gels
– They are those which posses the property of elasticity.
– They change their shape on applying force and return to original shape when the force is removed.
– Gelatin, starch and soaps are examples of substances which form elastic gels.
– Elastic gels are obtained by cooling fairly concentrated lyophilic sols.
– The linkages between the molecules (particles) are due to electrical attraction and are not rigid.
(b) Non-elastic gels
– They are those which are rigid e.g., silica gel.
– These are prepared by appropriate chemical action.
– Thus silica gel is produced by adding concentrated hydrochloric acid to sodium silicate solution of the correct concentration.
– The resulting molecules of silicic acid polymerise to form silica gel.
– It has a network linked by covalent bonds which give a strong and rigid structure.
Properties of Gels
(1) Hydration
– A completely dehydrated elastic gel can be regenerated by addition of water.
– But once a nonelastic gel is freed from moisture, addition of water will not bring about gelation.
(2) Swelling
– Partially dehydrate elastic gels imbibe water when immersed in the solvent.
– This causes increase in the volume of the gel and process is called Swelling.
(3) Syneresis
– Many inorganic gels on standing undergo shrinkage which is accompanied by exudation of solvent. This process is termed Syneresis.
(4) Thixotropy
– Some gels are semisolid when at rest but revert to liquid sol on agitation.
– This reversible sol-gel transformation is referred to as Thixotropy.
– Iron oxide and silver oxide gels exhibit this property.
– The modern thixotropic paints are also an example.
 Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry