Physical Chemistry blends chemistry with physics, studying matter’s behavior using concepts like thermodynamics, kinetics, quantum mechanics, and spectroscopy. It explains how and why chemical reactions occur at the molecular level.
Physical Chemistry
-
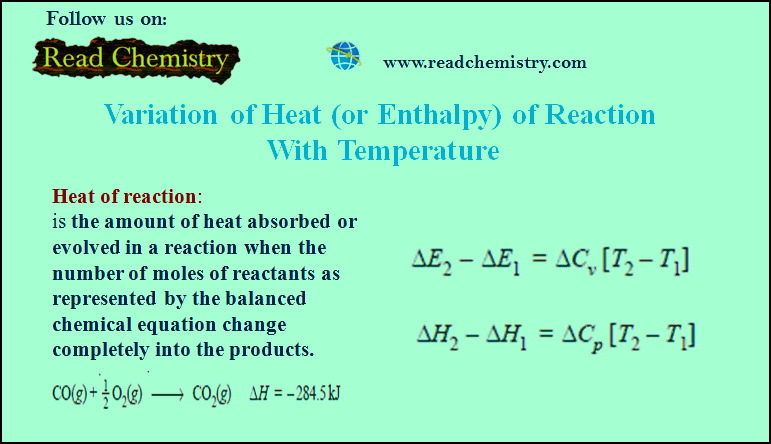
Variation of heat of reaction with temperature
– In this subject, the Variation of heat of reaction with temperature will be discussed. Heat of Reaction or Enthalpy…
Read More » -
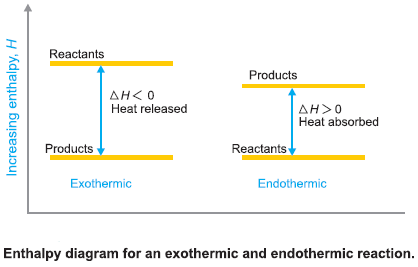
Enthalpy of Reaction
– For reactions involving solids and liquids only the change in volume (ΔV) is very small and the term P…
Read More » -
MCQ on the First law of Thermodynamics
MCQ on the First Law of Thermodynamics – In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on…
Read More » -
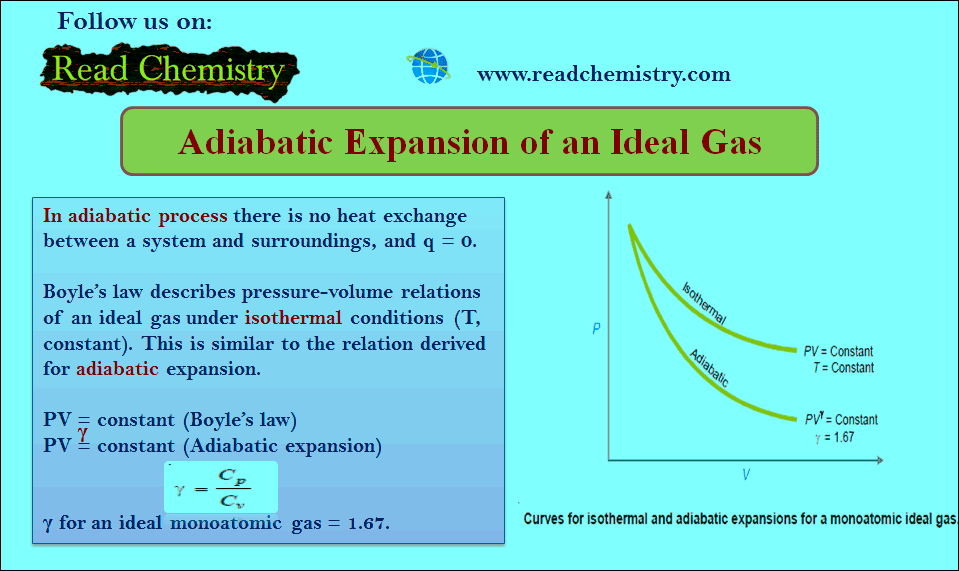
Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas
Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas – A process carried in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated so that…
Read More » -
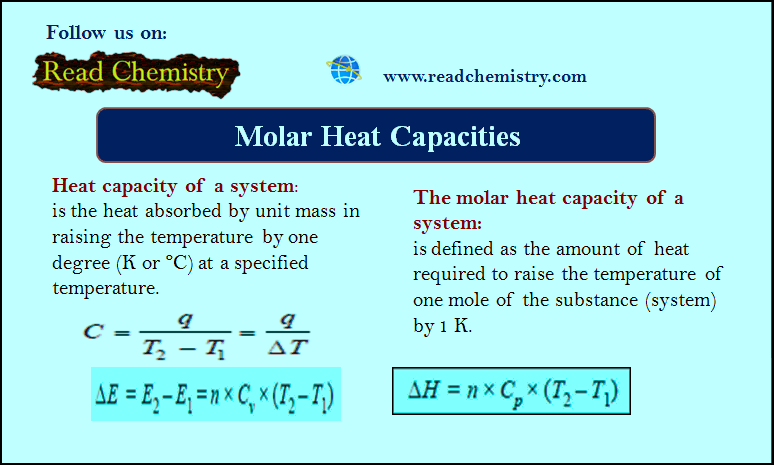
Heat Capacity – Molar Heat Capacity
Molar Heat Capacity – By heat capacity of a system, we mean the capacity to absorb heat and store energy.…
Read More » -
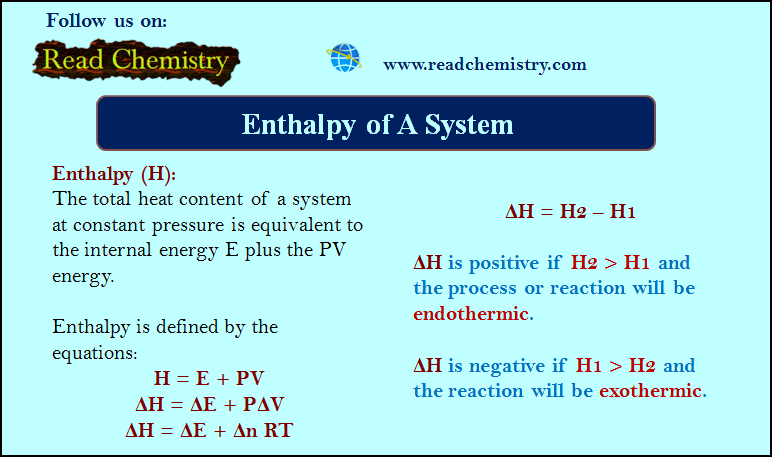
Enthalpy of A System
– Enthalpy (H) is the total heat content of a system at constant pressure and is equivalent to the internal…
Read More » -
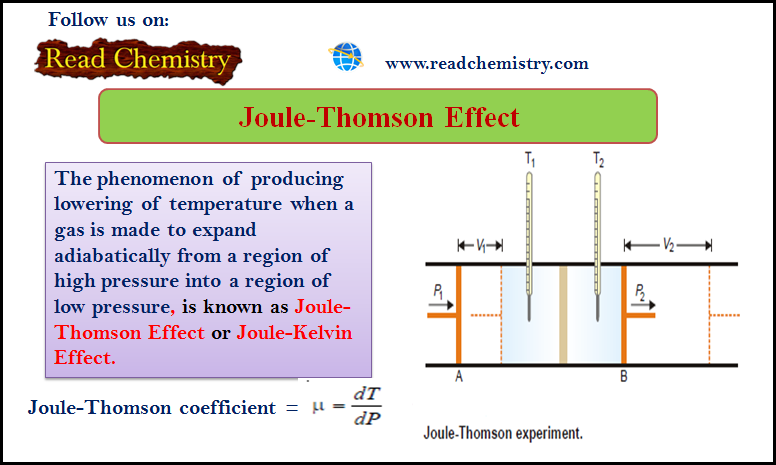
Joule-Thomson Effect
– The phenomenon of producing a lowering of temperature when a gas is made to expand adiabatically from a region…
Read More » -
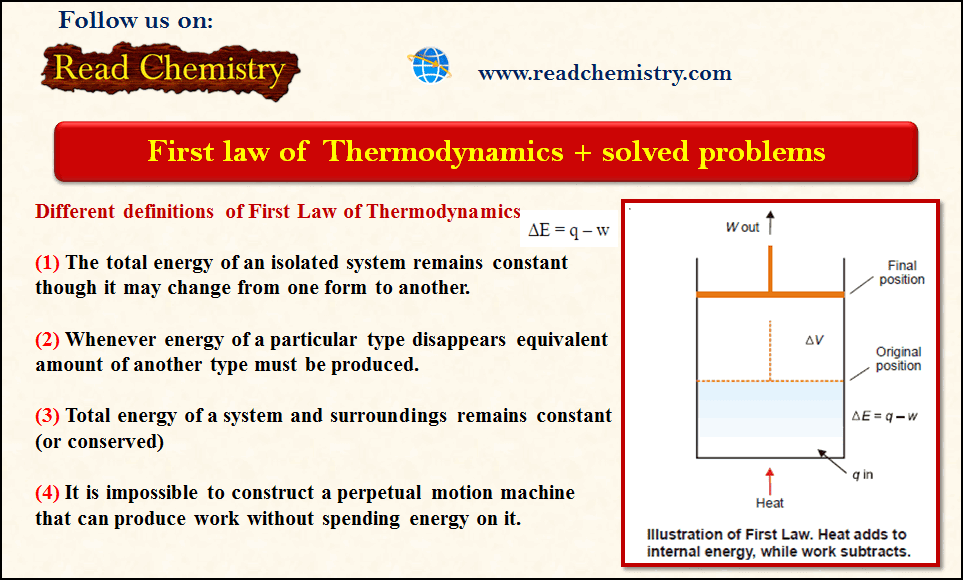
The First Law of Thermodynamics + Solved Problems
– The first law of Thermodynamics states that The total energy of an isolated system remains constant though it may…
Read More » -
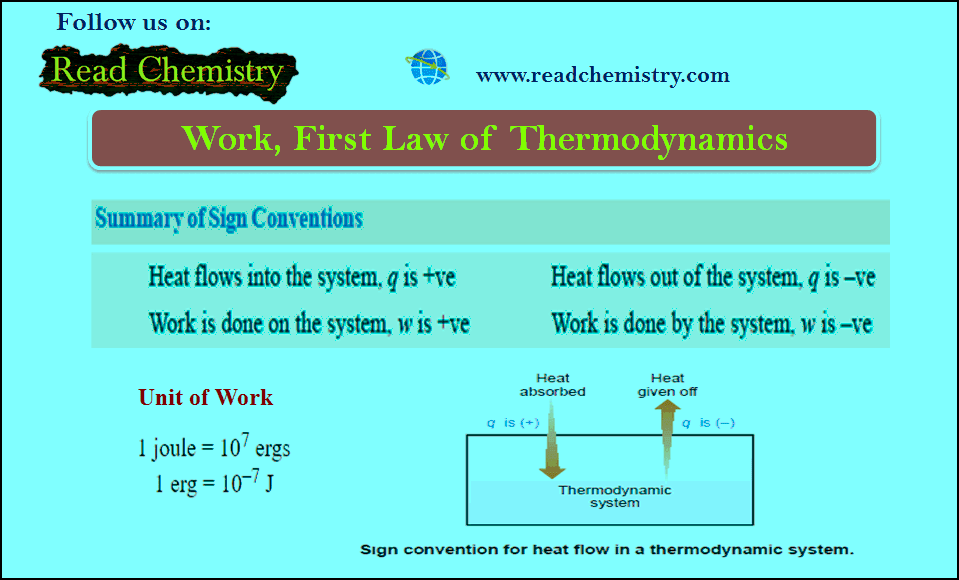
Work in Thermodynamics (Definition – Formula – Problems)
– In physics, mechanical work is defined as force multiplied by the distance through which the force acts. – In…
Read More » -
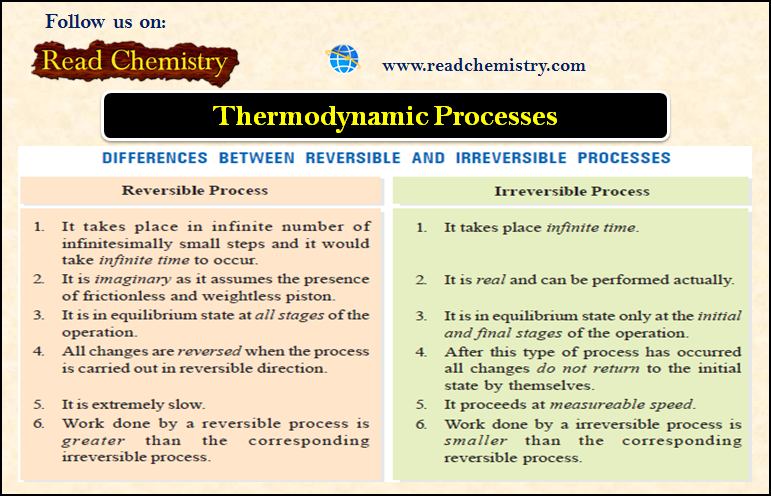
Thermodynamic Processes
– Thermodynamic Processes involve the change of conditions (temperature, pressure, and volume). Thermodynamic Processes – When a thermodynamic system changes…
Read More » -
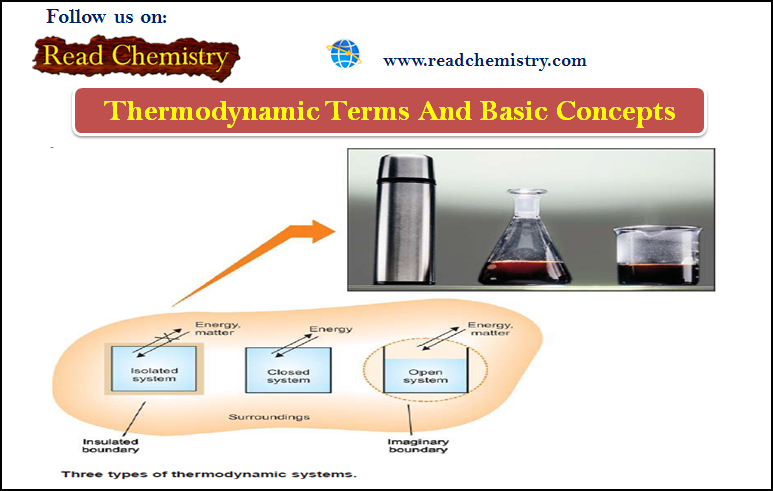
Thermodynamics – Basic terms and concepts in Thermodynamics
What is Thermodynamics? – Thermodynamics is The study of the flow of heat or any other form of energy into…
Read More » -
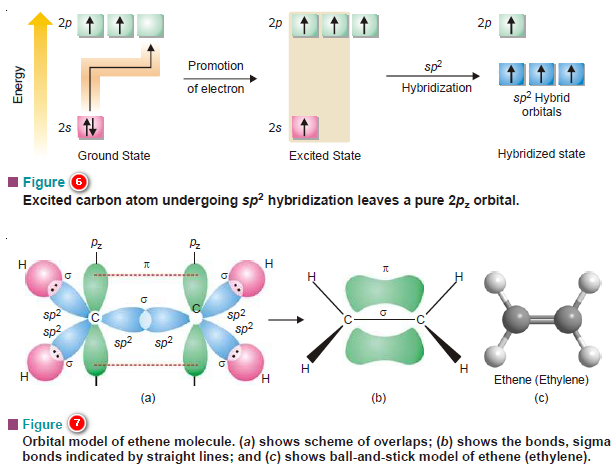
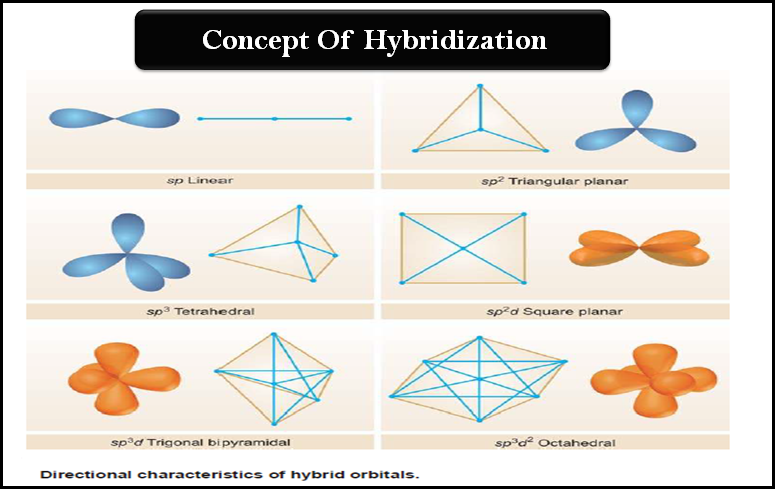
Hybridization and Shapes of Molecules
Hybridization and Shapes of Molecules – In the previous subject, we talked about the concept of Hybridization and the types…
Read More » -
Hybridization: Definition, Types, Rules, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Hybridization: Definition, Types, Rules, and Examples – While the formation of simple…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer The…
Read More » -
Fundamentals of Electrochemistry book by V.S. Bagotsky
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Fundamentals of Electrochemistry book by V.S. Bagotsky The Preface of…
Read More » -
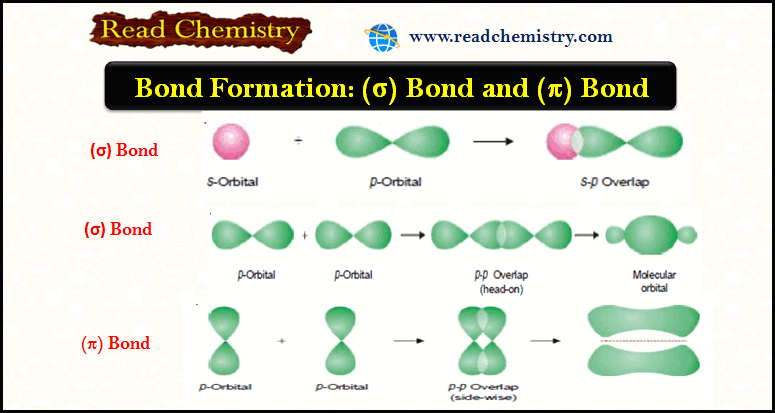
Bond Formation, (σ) Bond and (π) Bond
Bond Formation (Valence Bond Theory) – Bond formation between atoms to give chemical compounds can be interpreted admirably in terms…
Read More » -
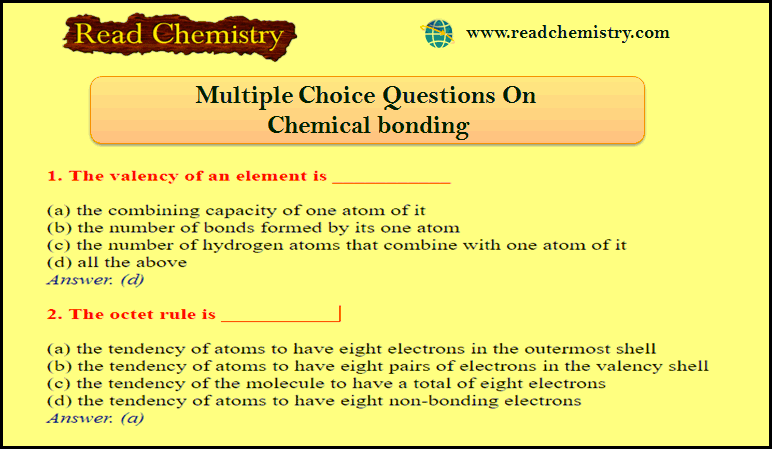
50 MCQ on Chemical bonding
MCQ on Chemical bonding – In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on Chemical bonding …
Read More » -
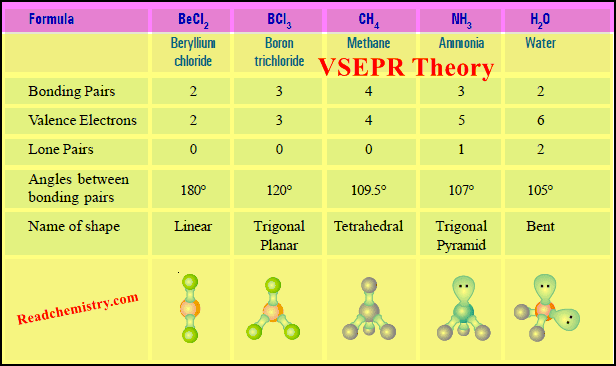
VSEPR Theory: Postulates, Predicting Shapes of Molecules
– In this subject, we will discuss the VSEPR Theory: definition, Postulates, limitations, and Predicting Shapes of Molecules. VSEPR Theory…
Read More » -
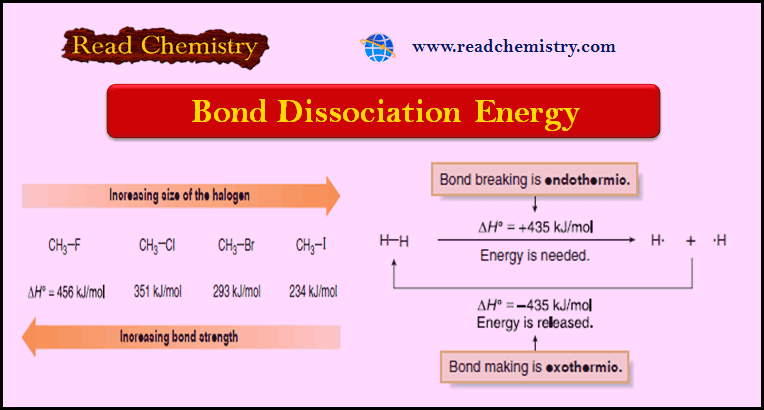
Bond Dissociation Energy: Definition, Equation, Problems
– In this subject, we will discuss the Bond Dissociation Energy: Definition, Equation, Problems Bond Dissociation Energy – Bond breaking…
Read More » -
Metallic Bonding: Definition, Properties, Examples, Explanation
– In this subject, we will discuss the Metallic Bonding: Definition, Properties, Examples, Explanation Metallic Bonding – The valence bonds…
Read More »