General Chemistry
General Chemistry introduces basic chemical concepts, including atomic structure, bonding, reactions, stoichiometry, states of matter, and periodic trends. It lays the groundwork for advanced study in all chemistry branches.
-
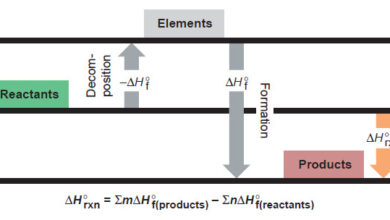
Standard Heats of Reaction (ΔH°rxn)
In this subject, we talk about Standard Heats of Reaction (ΔH°rxn) Standard Heats of Reaction (ΔH°rxn) – In this subject,…
Read More » -
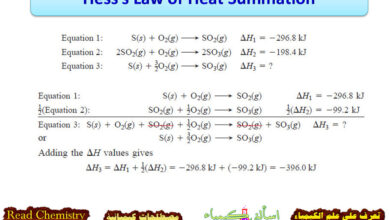
Hess’s Law of Heat Summation
In this subject, we will discuss Hess’s Law of Heat Summation Hess’s Law of Heat Summation – Many reactions are…
Read More » -
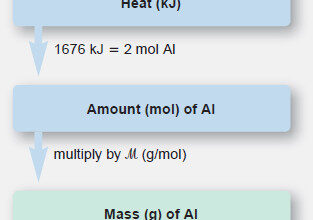
Stoichiometry of Thermochemical Equation
Stoichiometry of Thermochemical Equation – A thermochemical equation is a balanced equation that includes the heat of reaction (ΔHrxn). –…
Read More » -
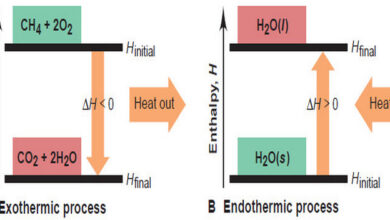
Enthalpy: Heats of Reaction and Chemical Change
In this subject, we will discuss the Enthalpy: Heats of Reaction and Chemical Change. Enthalpy: Heats of Reaction and Chemical…
Read More » -
Forms of Energy and Their Interconversion
Forms of Energy and Their Interconversion – we discussed before the facts that all energy is either potential or kinetic…
Read More » -
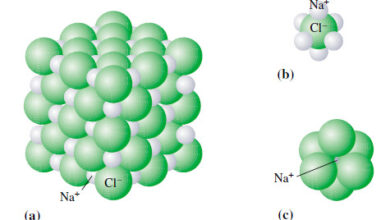
Ions and ionic compounds
– In this topic, we will discuss definition of The Ions and ionic compounds Ions and ionic compounds – So…
Read More » -
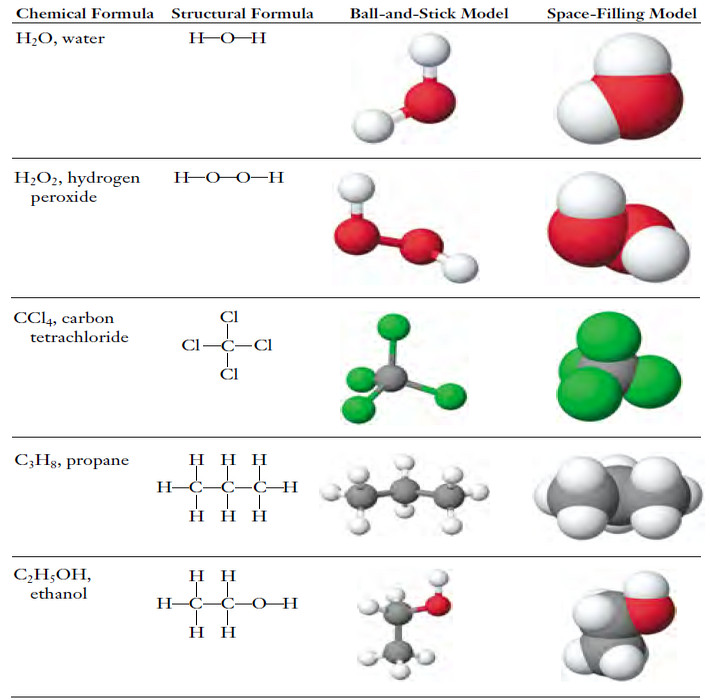
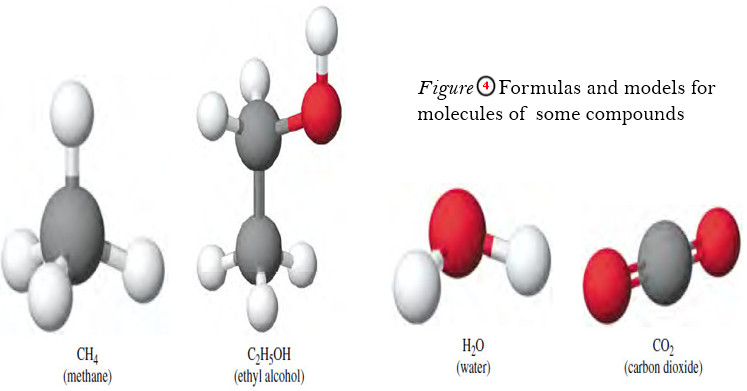
Chemical Formula – Structural Formula
Chemical Formula – The chemical formula for a substance shows its chemical composition. – This represents the elements present as…
Read More » -
Atoms and Molecules
Democritus’s ideas about atoms – The Greek philosopher Democritus (470–400 BC) suggested that all matter is composed of tiny, discrete,…
Read More » -
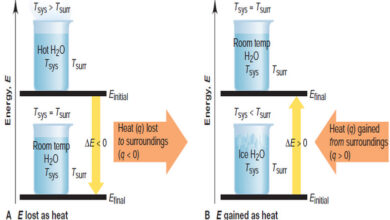
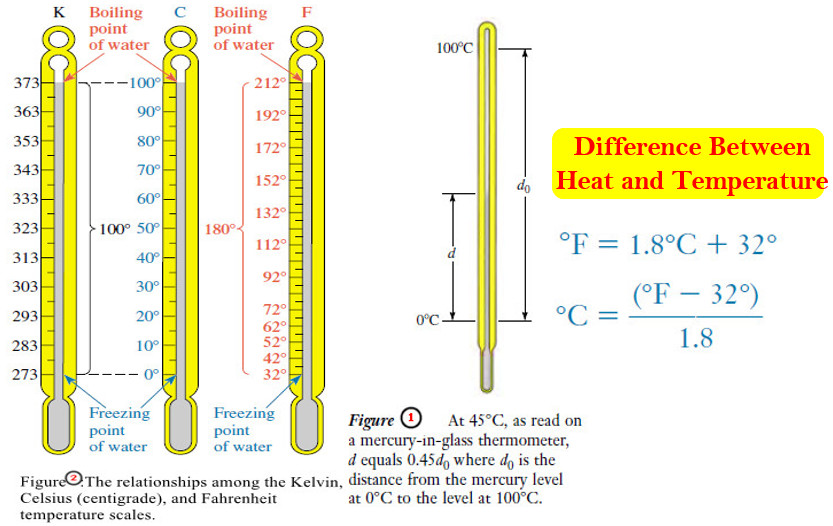
Heat and Temperature
Difference Between Heat and Temperature – Heat is one form of energy. – Many forms of energy can be interconverted…
Read More » -
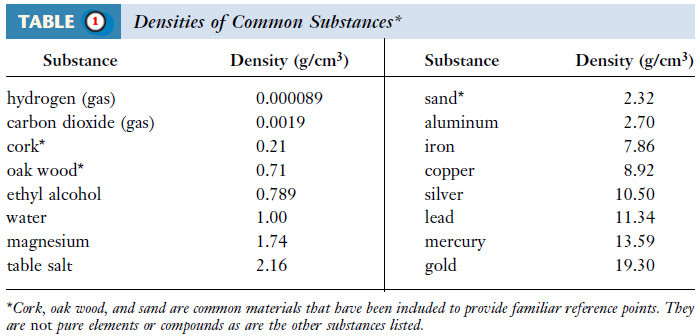
Density and Specific gravity: Definition, Solved problems
– In this topic, we will discuss The Density and Specific gravity: Definition and Solved problems. Definition of Density –…
Read More » -
Physical and Chemical properties of Matter
– In this topic, we will discuss The Physical and Chemical properties of Matter and The Physical and Chemical Changes.…
Read More » -
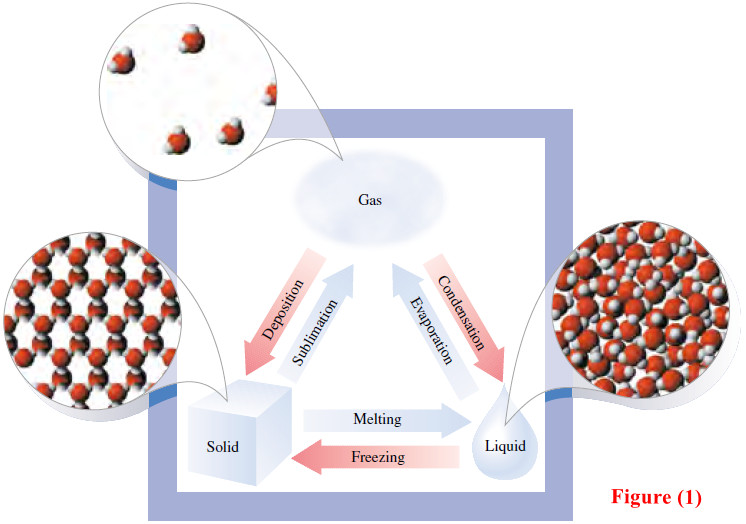
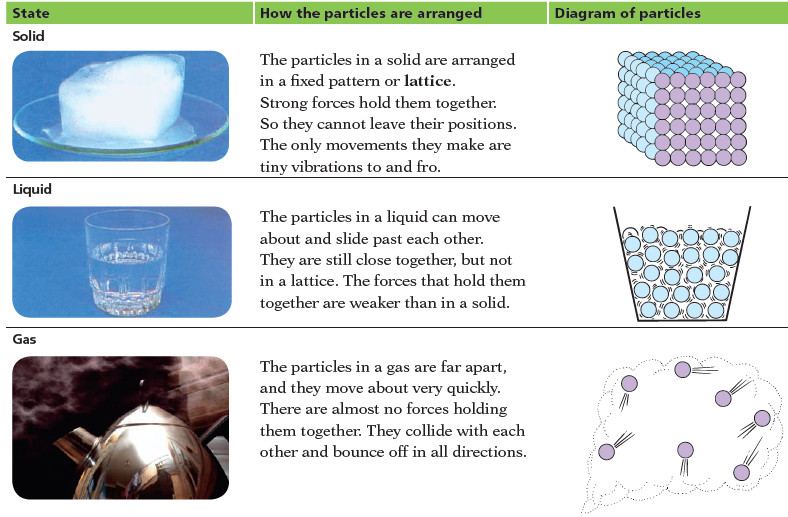
Solids, liquids, and gases.
What’s the difference between Solids, liquids, and gases? – It is easy to tell the difference between solids, liquids and…
Read More » -
Matter and Energy
Definition of Matter and Energy What is Matter? – Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. – Mass…
Read More » -
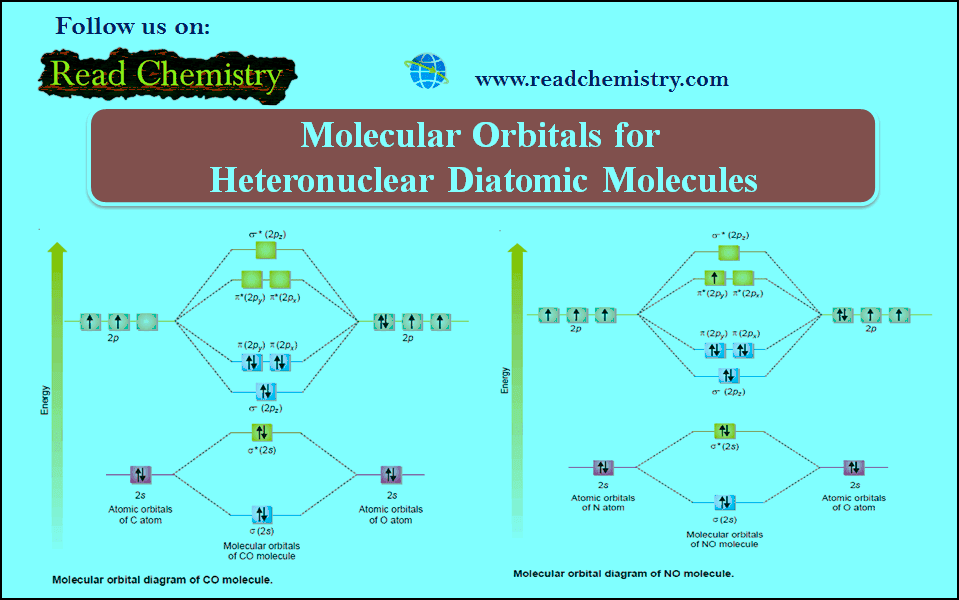
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties…
Read More » -
Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules
Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties…
Read More » -
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory – In this subject, you will find 46 questions and answers MCQ on…
Read More » -
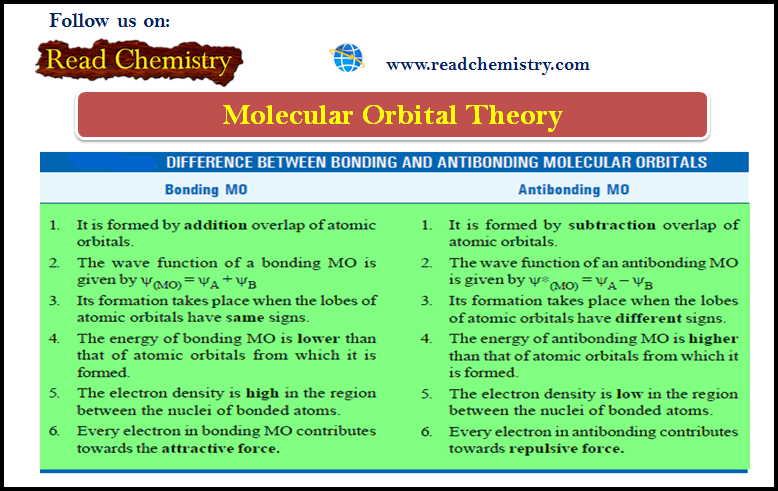
Molecular Orbital Theory
Molecular Orbital Theory – The molecular orbital theory proposed by Hund and Mulliken in 1932 explains the formation of a…
Read More » -
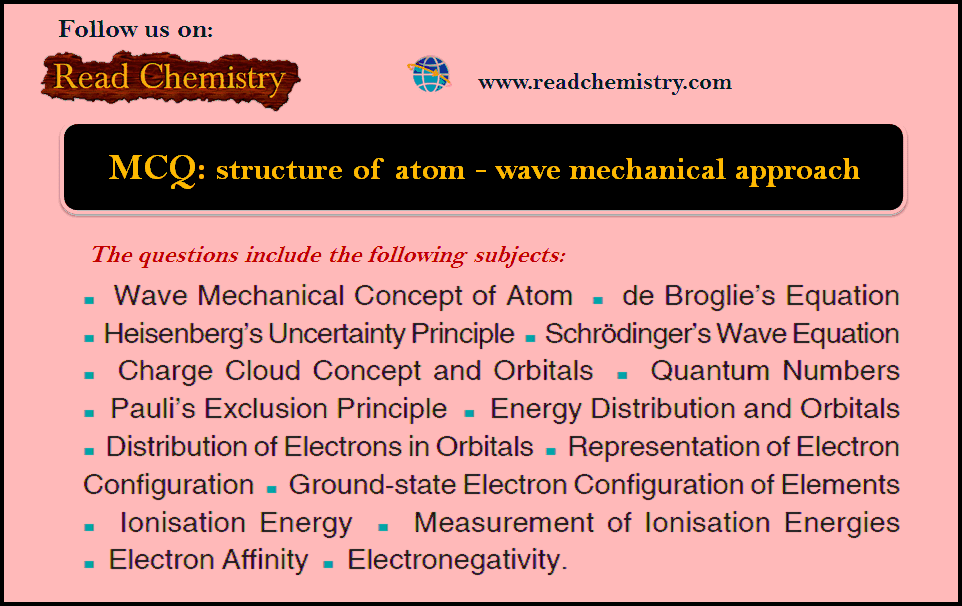
MCQ on Chapter: structure of atom – wave mechanical approach
MCQ on the structure of the atom – In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on…
Read More » -
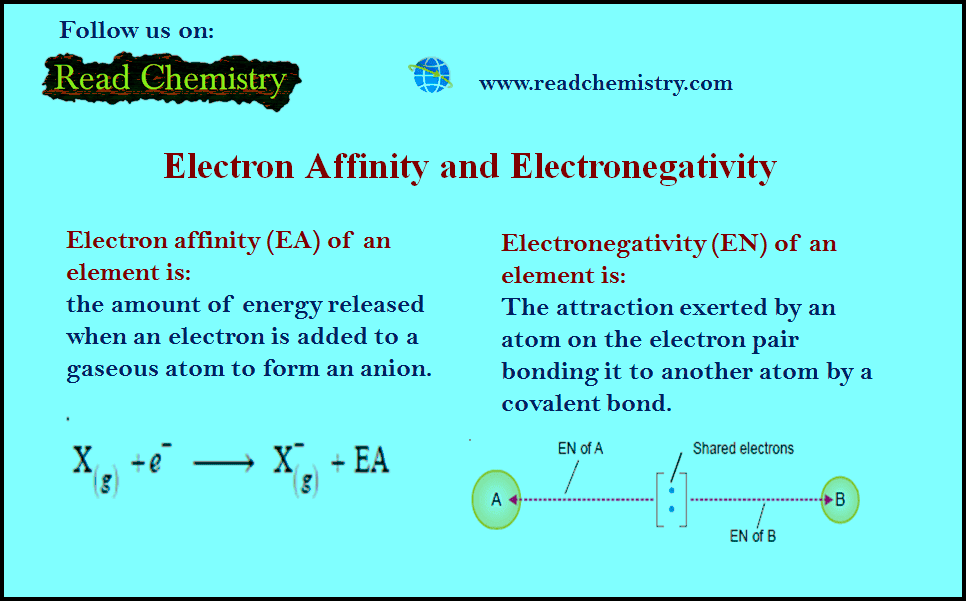
Electronegativity and Electron Affinity
– In this subject, we will discuss the difference Between Electronegativity and Electron Affinity Electron Affinity – A neutral atom…
Read More » -
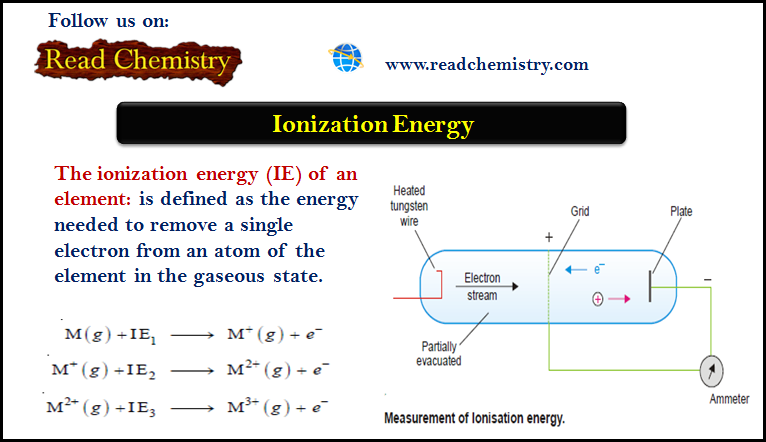
Ionization Energy (Definition – Trends – Measurement)
– The ionization energy (IE) of an element is defined as the energy needed to remove a single electron from…
Read More »