Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry focuses on the structure, properties, and reactions of carbon-containing compounds. It’s essential in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and biochemistry, exploring mechanisms, functional groups, and synthesis of complex molecules.
-
Reaction of Alcohols with Phosphorus Halides
Reaction of Alcohols with Phosphorus Halides – Reaction of Alcohols with Phosphorus Halides gives alkyl halides. – Several phosphorus halides…
Read More » -
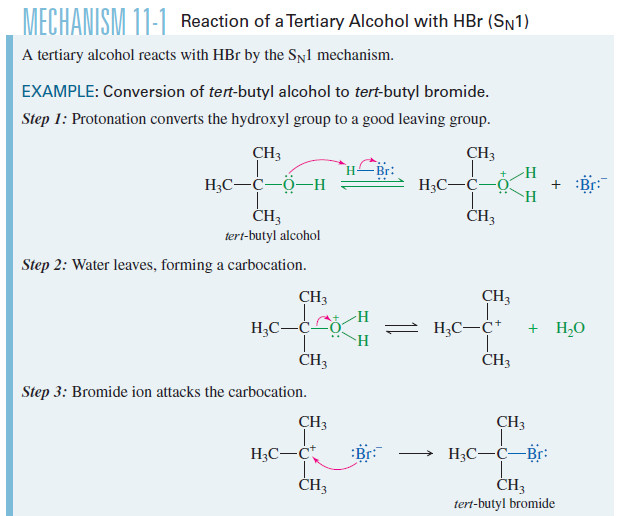
Reactions of Alcohols with Hydrohalic Acids
– In this topic the Reactions of Alcohols with Hydrohalic Acids such as HBr , HCl are discussed Reactions of…
Read More » -
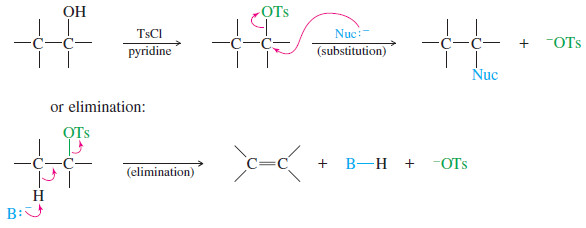
Alcohols as Nucleophiles and Electrophiles
Alcohols as Nucleophiles and Electrophiles; Formation of Tosylates – One reason alcohols are such versatile chemical intermediates is that they…
Read More » -
Biological Oxidation of Alcohols
– In this topic, the Biological Oxidation of Alcohols and their effect on the humans and animals will be discussed…
Read More » -
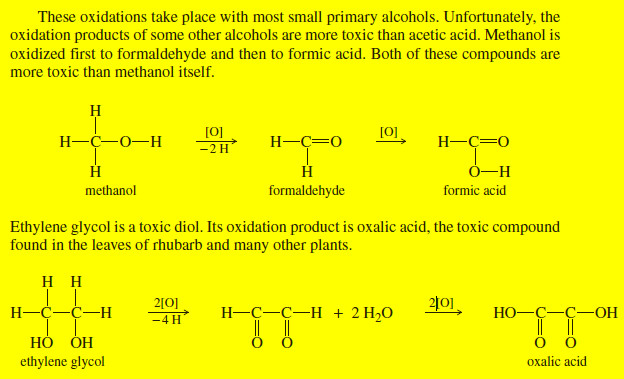
Additional Methods for Oxidizing Alcohols
Additional Methods for Oxidizing Alcohols – Many other reagents and procedures have been developed for oxidizing alcohols. – Some are…
Read More » -
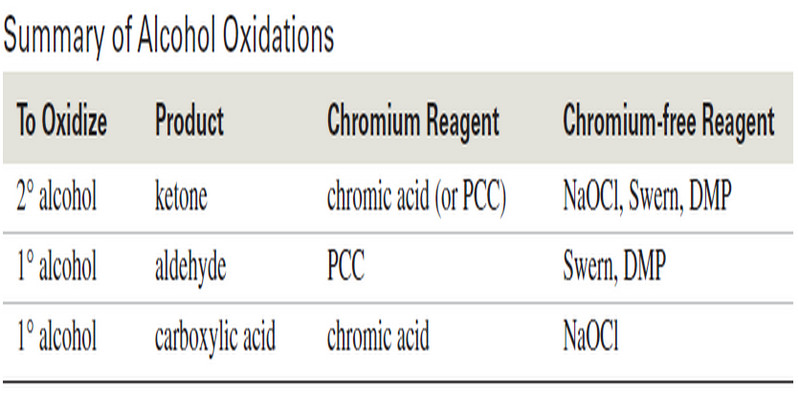
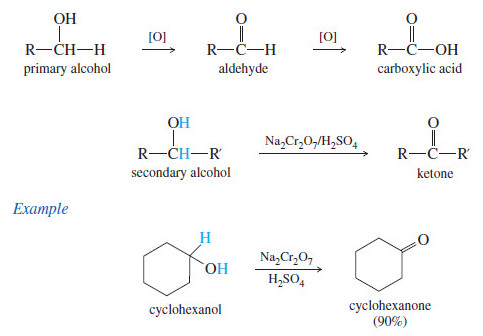
Oxidation of Alcohols
Oxidation of Alcohols – Primary and secondary alcohols are easily oxidized (Oxidation of Alcohols) by a variety of reagents, including…
Read More » -
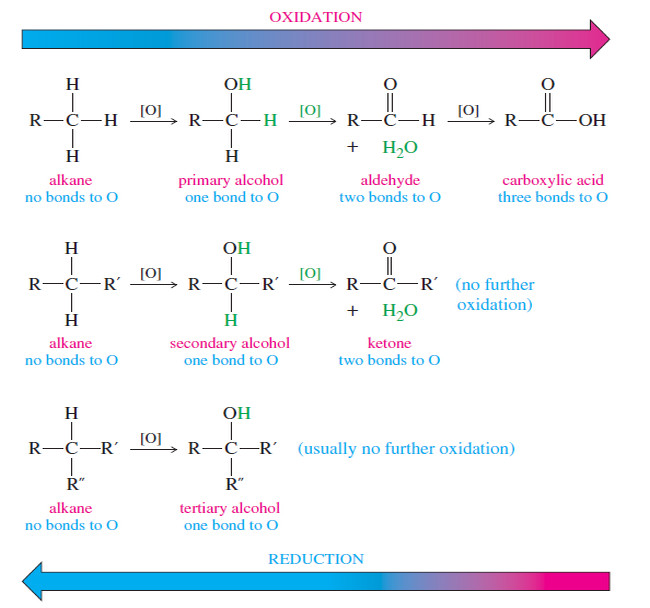
Oxidation states of Alcohols and Related Functional Groups
Oxidation states of Alcohols and Related Functional Groups – Oxidation states of Alcohols leads to ketones, aldehydes, and carboxylic acids.…
Read More » -
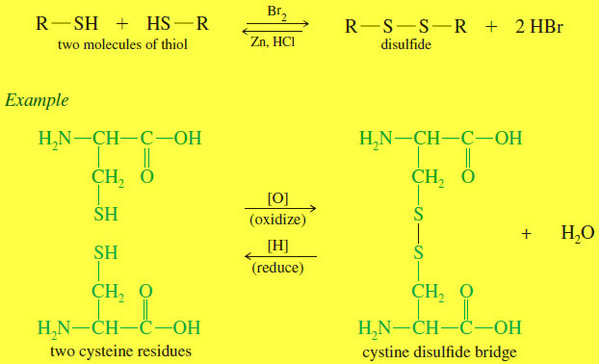
Thiols (Mercaptans)
What is Thiols? – Thiols are sulfur analogues of alcohols, with an -SH group in place of the alcohol -OH…
Read More » -
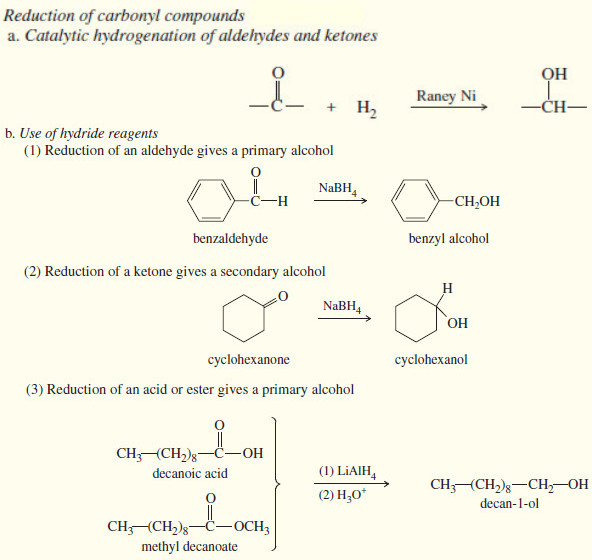
Reduction of the Carbonyl group : Synthesis of Alcohols
Reduction of the Carbonyl group : Synthesis of 1° and 2° Alcohols – Grignard reagents convert carbonyl group to alcohols…
Read More » -
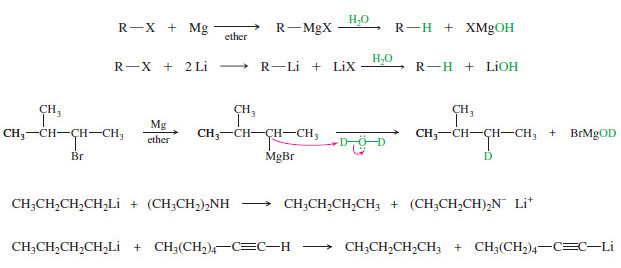
Side Reactions of Organometallic Reagents
Side Reactions of Organometallic Reagents: Reduction of Alkyl Halides – Organometallic Reagents: Grignard and organolithium reagents are strong nucleophiles and…
Read More » -
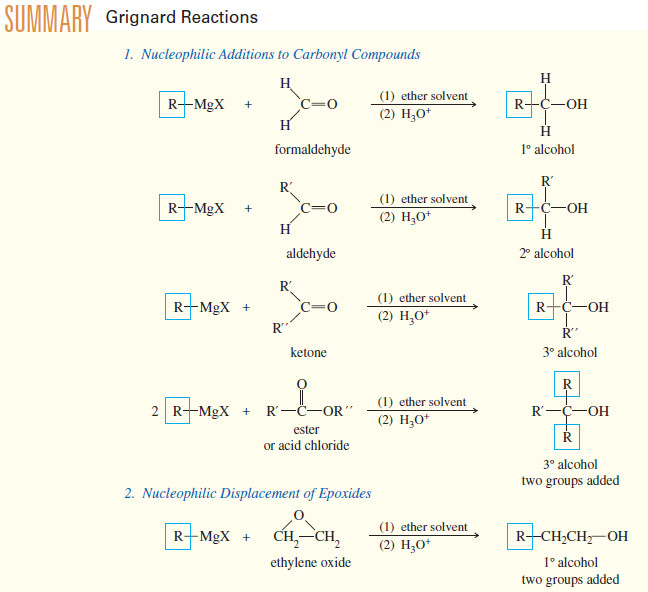
Addition of Grignard Reagents to Carbonyl Compounds
Addition of Organometallic Reagents to Carbonyl Compounds – Because they resemble carbanions, Grignard reagents and organolithium reagents are strong nucleophiles…
Read More » -
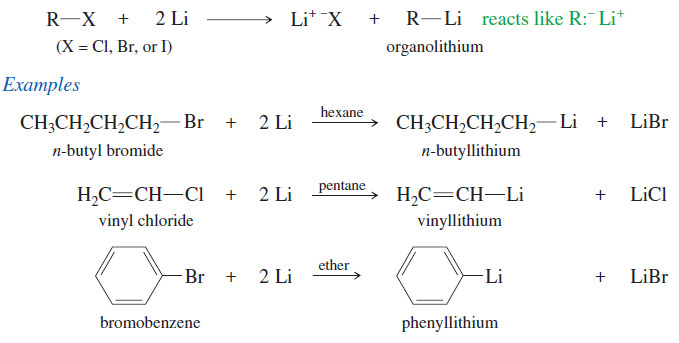
Organometallic Reagents for Alcohol Synthesis
Organometallic Reagents for Alcohol Synthesis – Organometallic compounds contain covalent bonds between carbon atoms and metal atoms. – And Organometallic…
Read More » -
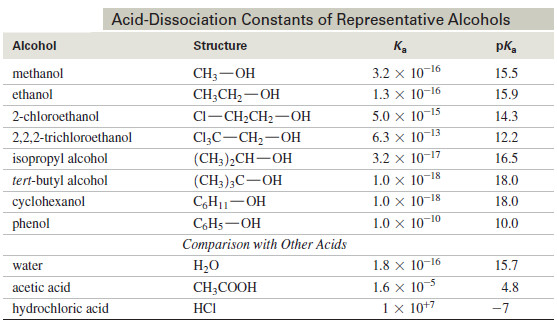
Acidity of Alcohols and Phenols
Acidity of Alcohols and Phenols – we will talk here about some Acidity of Alcohols and Phenols. – Like the…
Read More » -
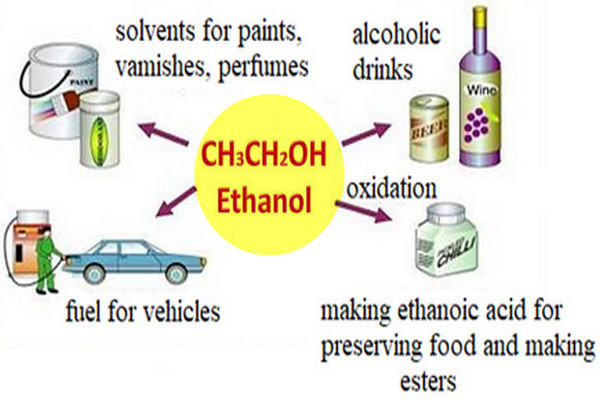
Commercially Important Alcohols
we will talk about some Commercially Important Alcohols such as: Methanol , Ethanol , isopropyl alcohol (1) Commercially Important Alcohols:…
Read More » -
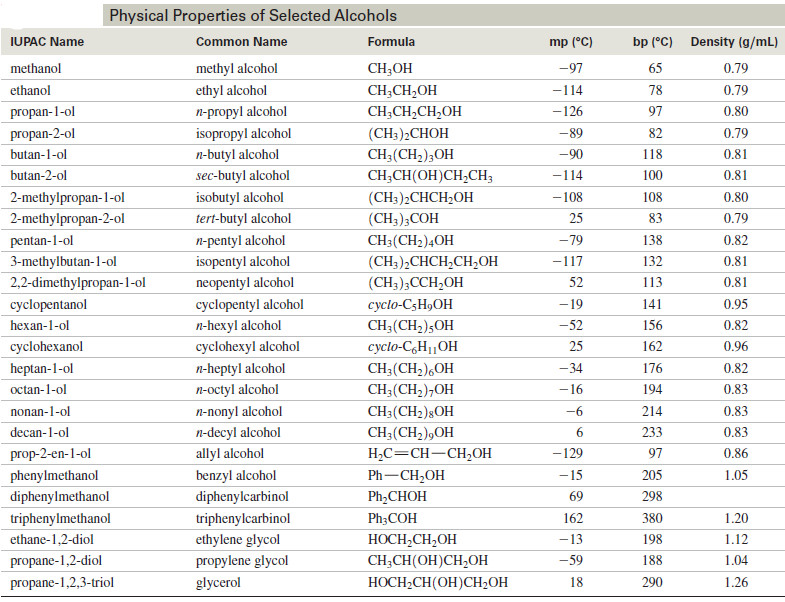
Physical Properties of Alcohols
We will discuss here Physical Properties of Alcohols: (A) Boiling Points of Alcohols (B) Solubility Properties of Alcohols Physical Properties…
Read More » -
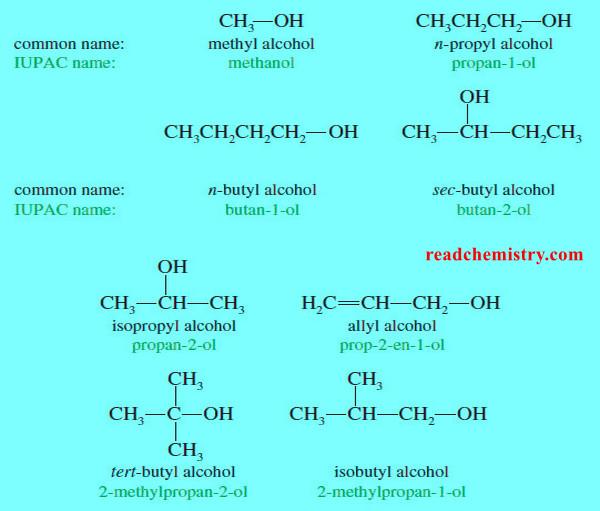
Nomenclature of Alcohols and Phenols
In this subject we will talk about Nomenclature of Alcohols and Phenols (1) Nomenclature of Alcohols: IUPAC Names – The…
Read More » -
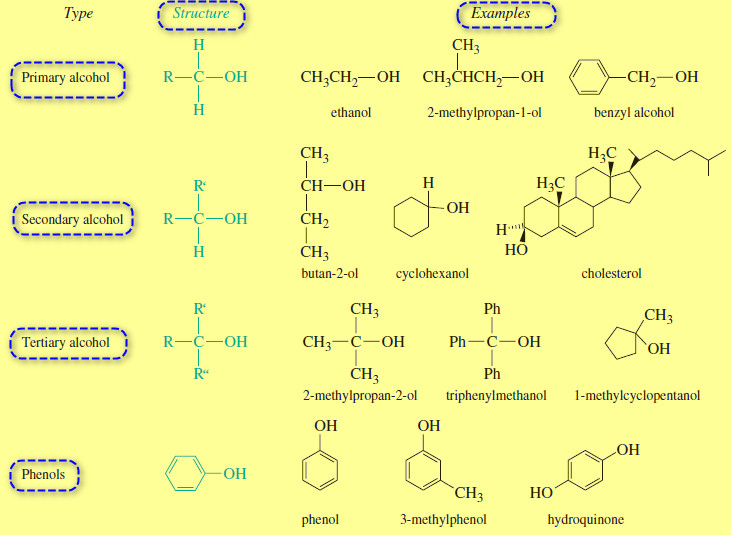
Structure and Classification of Alcohols
– In this subject we will talk about Structure and Classification of Alcohols. What are Alcohols? – Alcohols are organic…
Read More » -
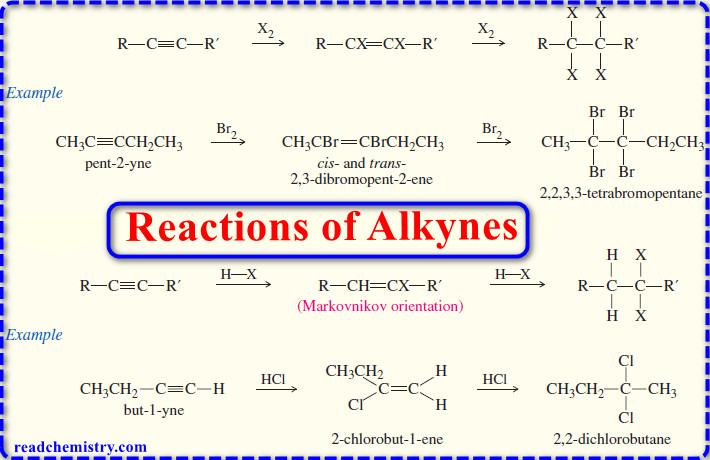
Reactions of Alkynes
Reactions of Alkynes – Many of the reactions of alkynes are similar to the corresponding reactions of alkenes because both…
Read More » -
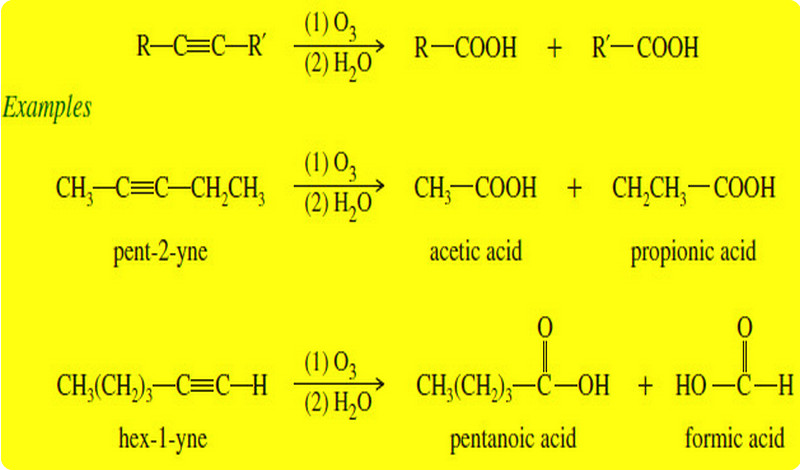
Oxidation of Alkynes
Before we discuss Oxidation of Alkynes we will talk about triple bond of Alkynes What are Alkynes? – Alkynes are…
Read More » -
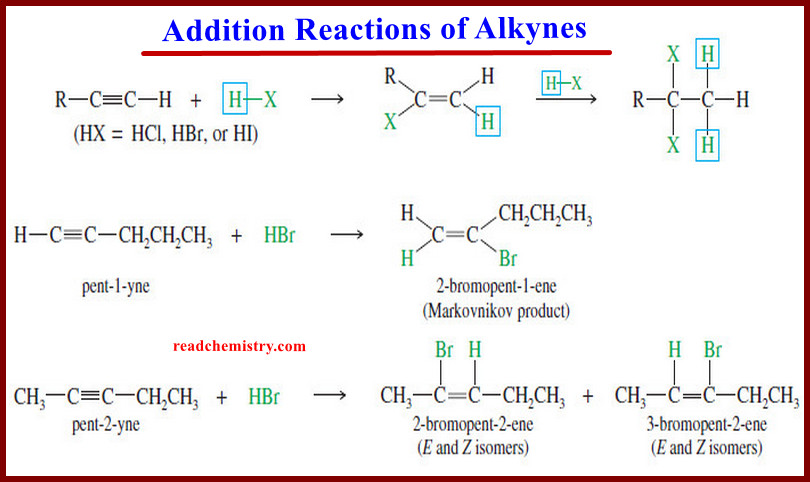
Addition Reactions of Alkynes
Addition Reactions of Alkynes – Many of the reactions of alkynes are similar to the corresponding reactions of alkenes because…
Read More »