Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry focuses on the structure, properties, and reactions of carbon-containing compounds. It’s essential in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and biochemistry, exploring mechanisms, functional groups, and synthesis of complex molecules.
-
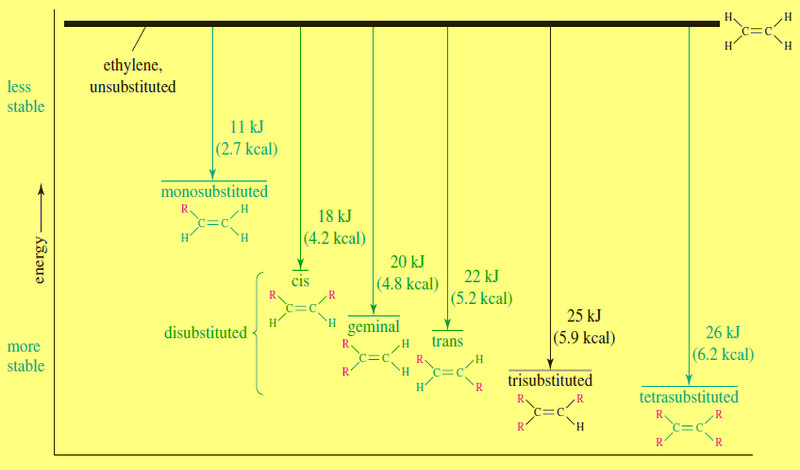
Stability of Alkenes
Stability of Alkenes – In making alkenes, we often find that the major product is the most stable alkene. –…
Read More » -
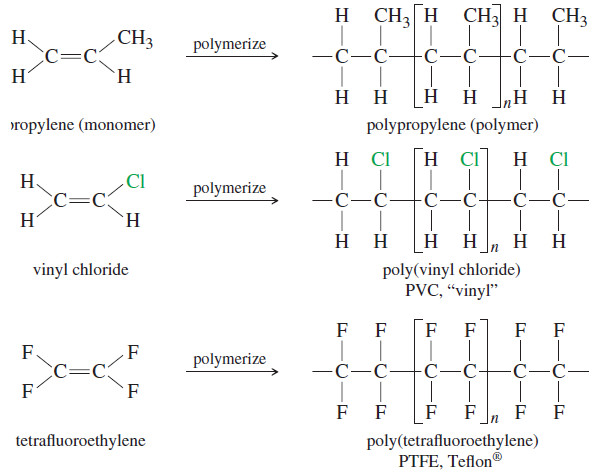
Commercial Importance of Alkenes
Commercial Importance of Alkenes – Because the carbon–carbon double bond is readily converted to other functional groups, alkenes are important…
Read More » -
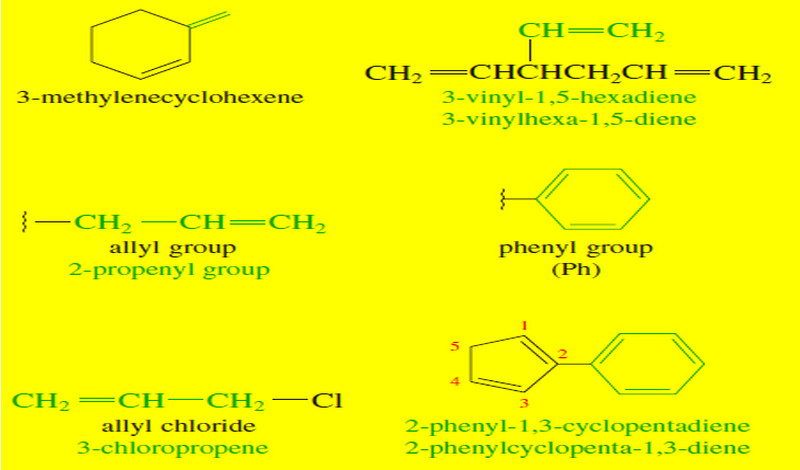
Nomenclature of Alkenes
Nomenclature of Alkenes – Simple alkenes are named much like alkanes, using the root name of the longest chain containing…
Read More » -
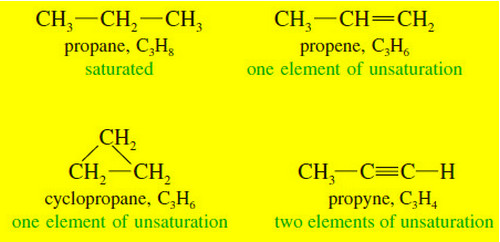
Elements of Unsaturation
Elements of Unsaturation (1) Elements of Unsaturation in Hydrocarbons – Alkenes are said to be unsaturated because they are capable…
Read More » -
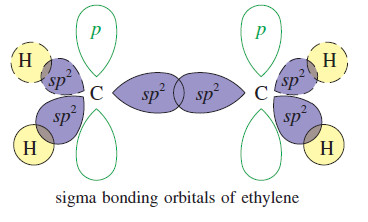
The Orbital Description of the Alkene Double Bond
The Orbital Description of the Alkene Double Bond – In a Lewis structure, the double bond of an alkene is…
Read More » -
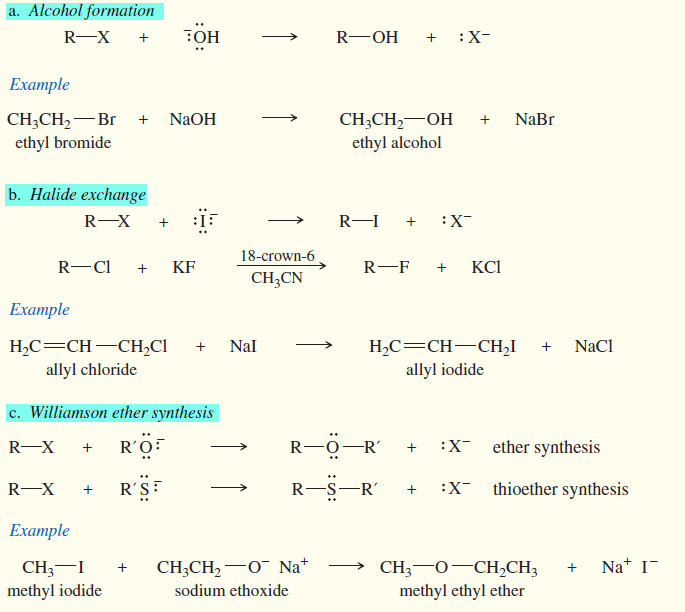
Reactions of Alkyl Halides
In this subject we will discuss the Reactions of Alkyl Halides with chemical equations and examples Introduction to Alkyl Halides…
Read More » -
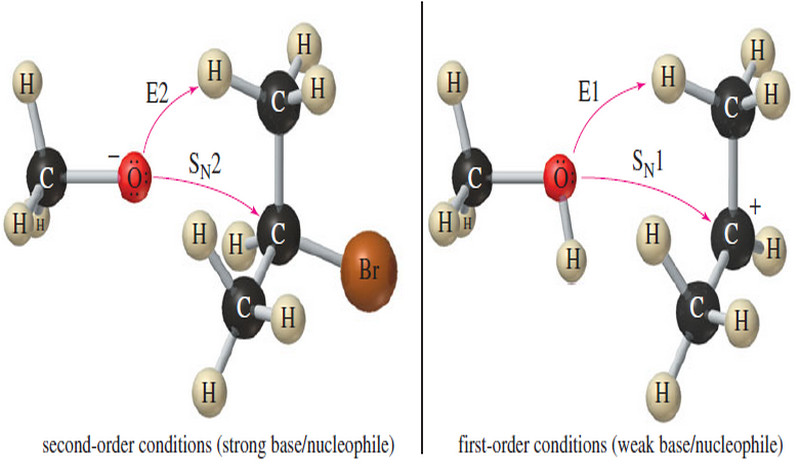
Predicting SN1 SN2 E1 E2 reactions
Predicting the mechanisms: SN1, SN2, E1, E2 reactions – In this subject we will learn how to predict the the…
Read More » -
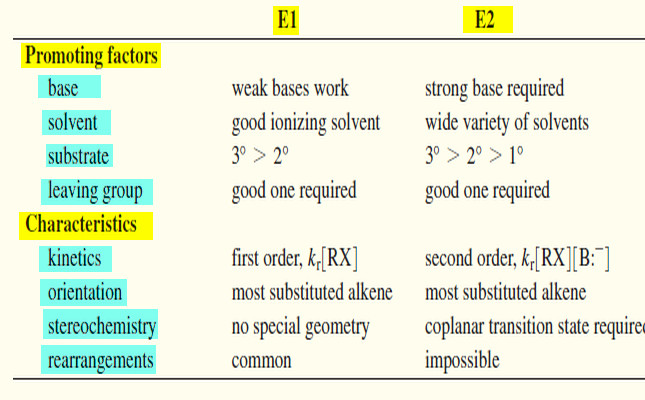
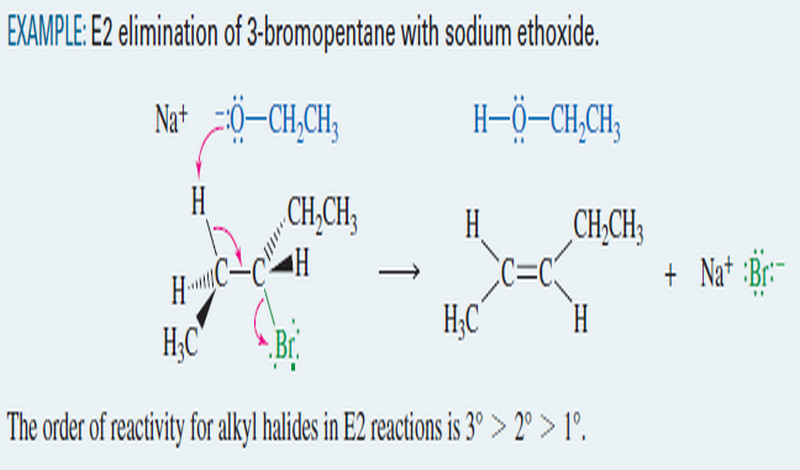
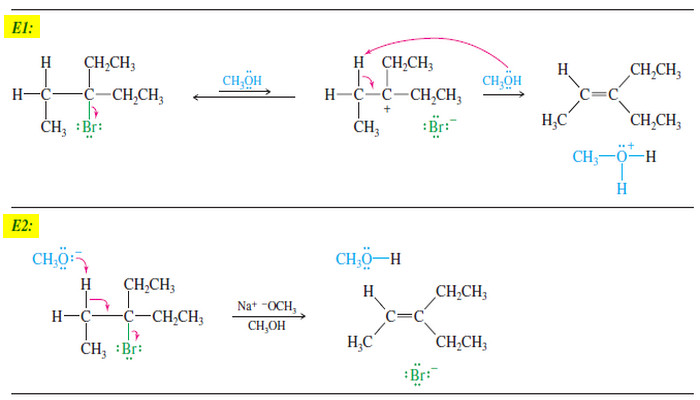
Comparison of E1 and E2 reactions
Comparison of E1 and E2 Elimination Mechanisms – Let’s summarize the major points to remember about the E1 and E2…
Read More » -
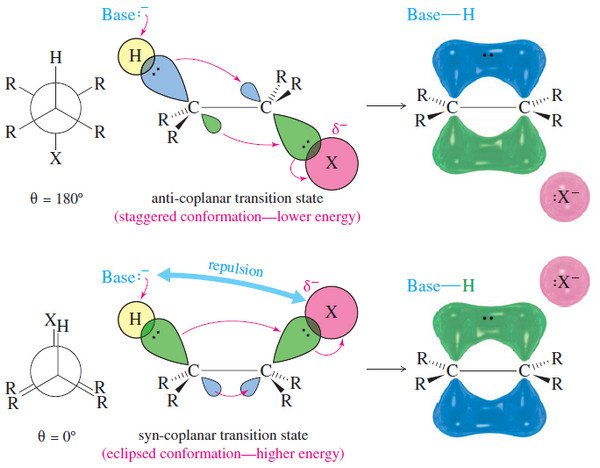
Stereochemistry of the E2 Reaction
Stereochemistry of the E2 Reaction – In this subject Stereochemistry of the E2 Reaction will be discussed – Like the…
Read More » -
E2 Reaction : Second-Order Elimination
Second-Order Elimination: The E2 Reaction – Eliminations can also take place under second-order conditions with a strong base present. –…
Read More » -
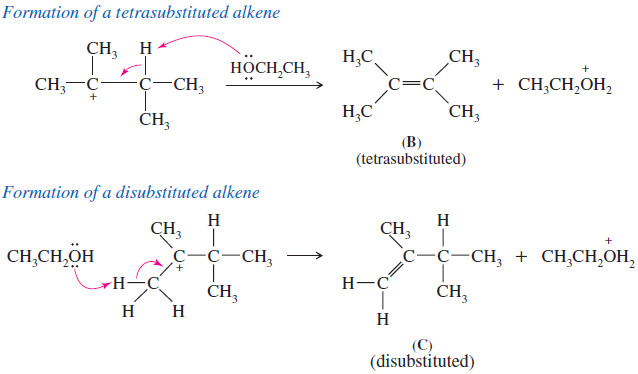
Zaitsev’s Rule : Positional Orientation of Elimination
Positional Orientation of Elimination: Zaitsev’s Rule – In this subject , Positional Orientation of Elimination: Zaitsev’s Rule will be discussed…
Read More » -
E1 Reaction : First-Order Elimination
First-Order Elimination : The E1 Reaction – An elimination involves the loss of two atoms or groups from the substrate,…
Read More » -
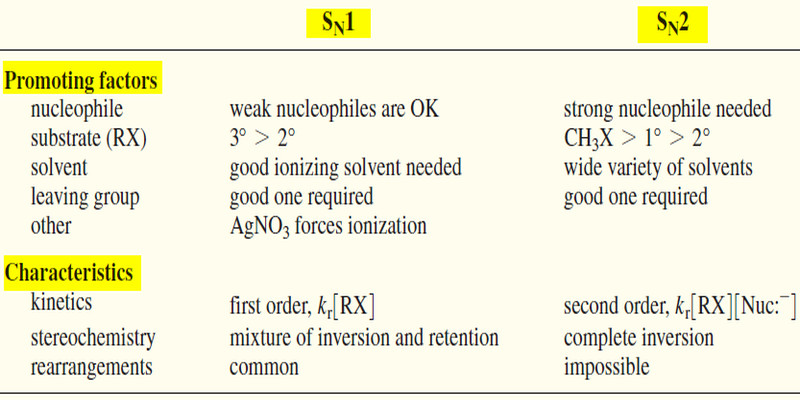
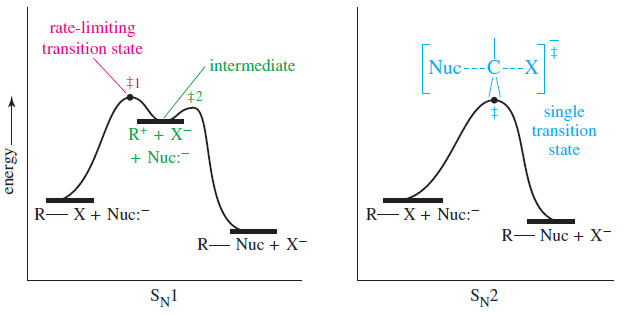
Comparison of SN1 and SN2 Reactions
Comparison of SN1 and SN2 Reactions Let’s compare what we know about the SN1 and SN2 Reactions and reactions, the…
Read More » -
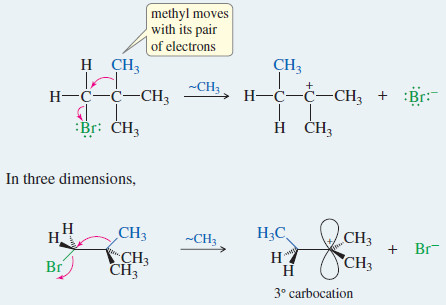
Rearrangements in the SN1 Reactions
Rearrangements in the SN1 Reactions – Carbocations frequently undergo structural changes, called rearrangements, to form more stable ions. – A…
Read More » -
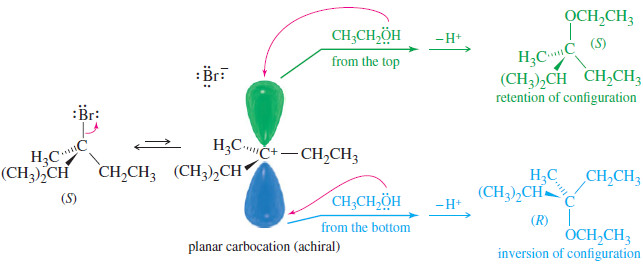
Stereochemistry of the SN1 Reactions
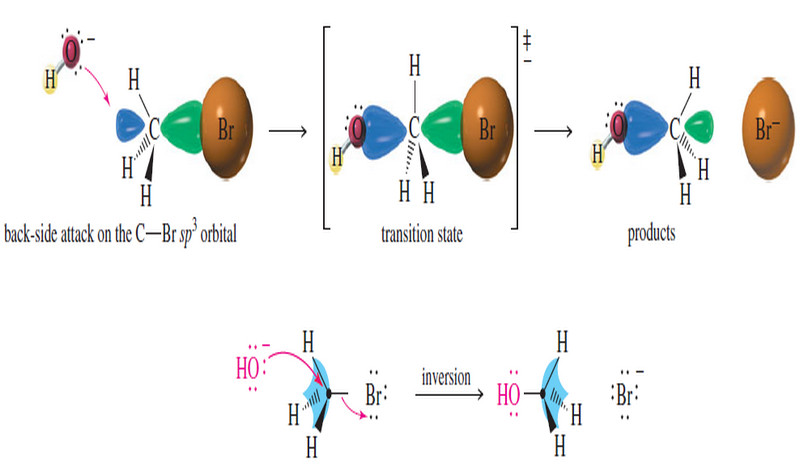
Stereochemistry of the SN1 Reaction – The SN2 reaction is stereospecific: the nucleophile attacks from the back side of the…
Read More » -
SN1 Reaction – Nucleophilic Substitution reaction
SN1 Reaction: First-Order Nucleophilic Substitution – When tert-butyl bromide is placed in boiling methanol, methyl tert butyl ether can be…
Read More » -
Stereochemistry of the SN2 Reaction
Stereochemistry of the SN2 Reaction – As we have seen, the reaction SN2 requires attack by a nucleophile on the…
Read More » -
Reactivity of the Substrate in SN2 Reactions
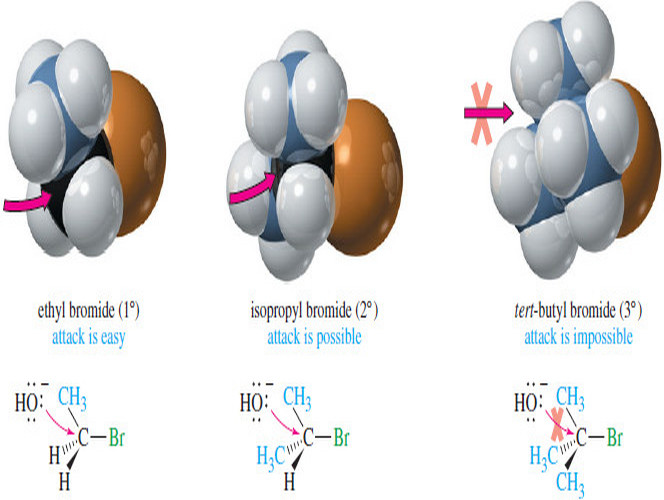
Reactivity of the Substrate in SN2 Reactions – We will often refer to the alkyl halide as the substrate: literally,…
Read More » -
Factors Affecting SN2 Reactions: Strength of the Nucleophile
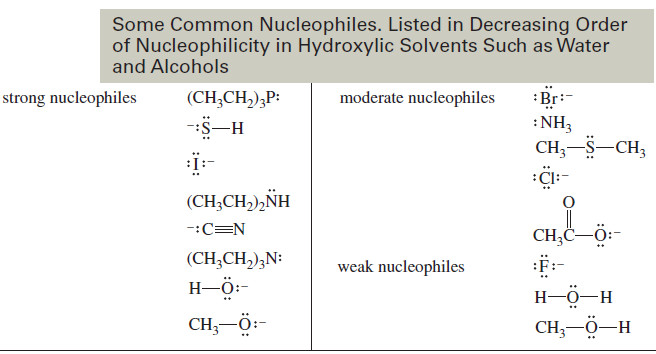
Factors Affecting SN2 Reactions: Strength of the Nucleophile – we will discuss Factors Affecting SN2 Reactions especially Strength of the…
Read More » -
SN2 reaction of Alkyl halides
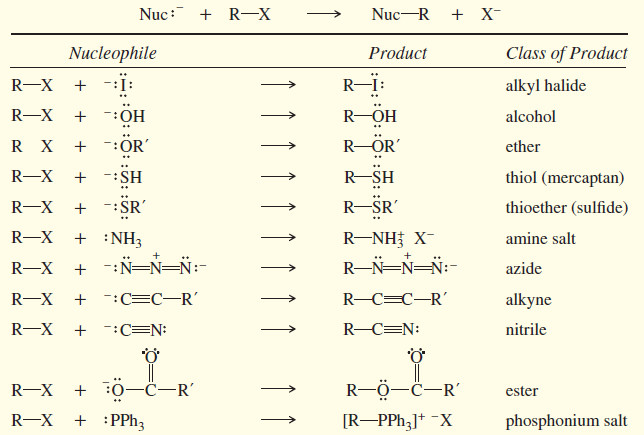
In this subject Second-Order Nucleophilic Substitution: The SN2 Reaction of Alkyl halides will be discussed Reactions of Alkyl Halides: Substitution…
Read More »