Radioactive Disintegration Series: Definition, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Radioactive Disintegration Series: Definition, Examples
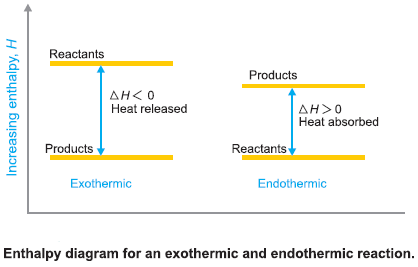
Radioactivity
– Several elements such as uranium and radium are unstable.
– Their atomic nucleus breaks off its own accord to form a smaller atomic nucleus of another element.
– The protons and neutrons in the unstable nucleus regroup to give the new nucleus.
– This causes the release of excess particles and energy from the original nucleus, which we call radiation.
– The elements whose atomic nucleus emits radiation are said to be radioactive.
– The spontaneous breaking down of the unstable atoms is termed radioactive disintegration or radioactive decay.
– The disintegration or decay of unstable atoms accompanied by emission of radiation is called Radioactivity
Radioactive Disintegration Series
– A radioactive element disintegrates by the emission of an α- or β- particle from the nucleus to form a new ‘daughter element’.
– This again disintegrates to give another ‘daughter element’.
– The process of disintegration and formation of a new element continues till a non-radioactive stable element is the product.
– The whole series of elements starting with the parent radioactive element to the stable end product is called a Radioactive Disintegration Series.
– Sometimes, it is referred to as a Radioactive Decay Series or simply a Radioactive Series.
– All the natural radioactive elements belong to one of the three series:
- The Uranium Series
- The Thorium Series
- The Actinium Series
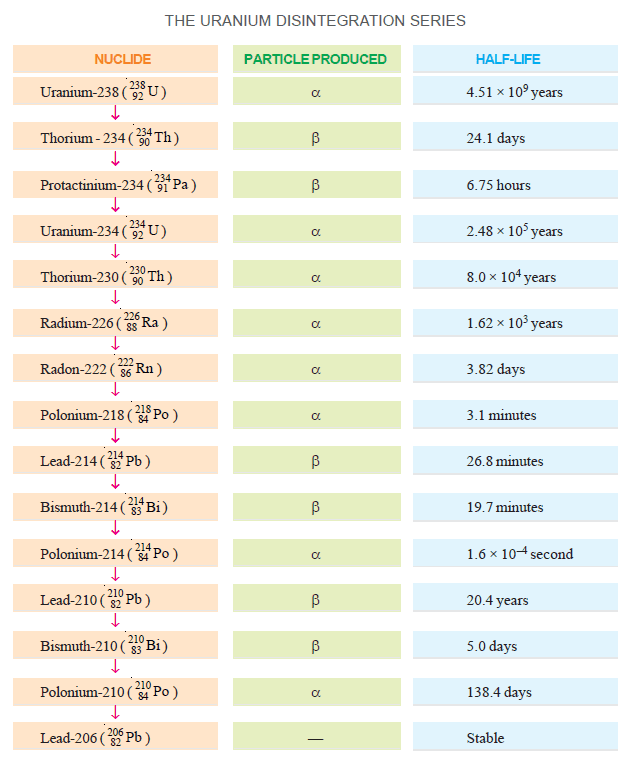
The Uranium Series
– It commences with the parent element uranium-238 and terminates with the stable element lead-206.
– It derives its name from uranium-238 which is the prominent member of the series and has the longest half-life.
– The Uranium series is illustrated in this Figure.
The Thorium Series
– It begins with the parent element thorium-232 and ends with lead-208 which is stable.
– This series gets its name from the prominent member thorium-232.
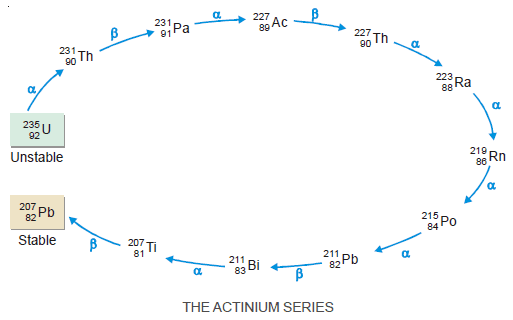
The Actinium Series
– It starts with the radioactive element uranium-235.
– The end product is the stable element lead-207.
– This series derives its name from the prominent member actinium-227.
The Neptunium Series
– This series consists of elements that do not occur naturally.
– It commences with neptunium-237 and terminates at bismuth-200.
– It derives its name from the prominent member neptunium-237.
Reference: Essentials of Physical Chemistry /Arun Bahl, B.S Bahl and G.D. Tuli / multicolor edition.