50 MCQ on Chemical bonding
MCQ on Chemical bonding
– In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on Chemical bonding
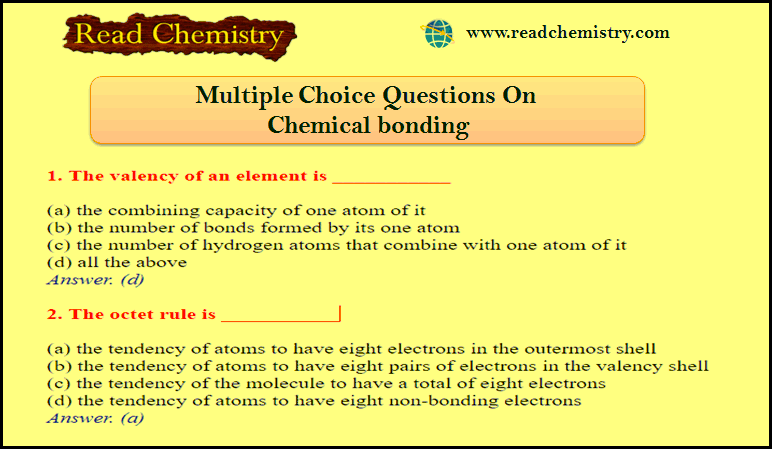
1. The valency of an element is ___________
(a) the combining capacity of one atom of it
(b) the number of bonds formed by its one atom(
c) the number of hydrogen atoms that combine with one atom of it(
d) all the above
Answer. (d)
2. The octet rule is ___________
(a) the tendency of atoms to have eight electrons in the outermost shell
(b) the tendency of atoms to have eight pairs of electrons in the valency shell
(c) the tendency of the molecule to have a total of eight electrons
(d) the tendency of atoms to have eight non-bonding electrons
Answer. (a)
3. An ionic bond is formed between ___________
(a) two metal atoms
(b) two non-metal atoms
(c) one metal atom and one non-metal atom
(d) one metal atom and one metalloid atom
Answer. (c)
4. Factors governing the formation of an ionic bond are ___________
(a) low ionization energy of metal and high electron affinity of non-metal atom
(b) high ionization energy of metal and high electron affinity of non-metal atom
(c) low ionization energy of metal atom and low electron affinity of non-metal atom
(d) high ionization energy of metal and low electron affinity of non-metal atom
Answer. (a)
5. The lattice energy is the amount of energy that ___________
(a) is released when one cation combines with one anion
(b) is released when one mole of cations combine with one mole of anions
(c) is released when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from its cations and anions
(d) is absorbed when one mole of an ionic compound is formed from its cation and anions
Answer. (c)
6. The most favourable conditions for the formation of an ionic compound is ___________
(a) low charge on ions, small cation and small anion
(b) high charge on ions, large cation and large anion
(c) high charge on ions, small cation and large anion
(d) low charge on ions, large cation and small anion
Answer. (c)
7. Ionic compounds are generally ___________
(a) solids having large melting points and good conductors of electricity
(b) gases having low melting points and poor conductors of electricity
(c) solids having low melting points and good conductors of electricity
(d) solids having high melting points and bad conductors of electricity
Answer. (a)
8. A covalent bond involves ___________
(a) sharing of electrons between a metal and a non-metal atom
(b) sharing of electrons between two metal atoms
(c) sharing of electrons between two atoms having similar electronegativity
(d) sharing of electrons between two atoms having a large difference in electronegativity
Answer. (c)
9. The total number of electron pairs in a nitrogen molecule is ___________
(a) 2
(b) 3
(c) 5
(d) 7
Answer. (d)
10. The covalent compounds are soluble in ___________
(a) all acids
(b) all bases
(c) all solvents
(d) non-polar solvents
Answer. (d)
11. The compounds which contain both ionic and covalent bonds are ___________
(a) CHCl3 and CCl4
(b) KCl and AlCl3
(c) KCN and NaOH
(d) H2and CH4
Answer. (c)
12. A co-ordinate bond is formed by ___________
(a) complete transfer of electrons
(b) sharing of electrons contributed by both the atoms
(c) sharing of electrons contributed by one atom only
(d) none of these
Answer. (c)
13. The types of bonds present in sulphuric acid molecules are ___________
(a) only covalent
(b) ionic and covalent
(c) co-ordinate and covalent
(d) co-ordinate, covalent and ionic
Answer. (d)
14. The common feature among the species O3, SO42–, H3O+and AlCl3 is that ___________
(a) they contain only ionic bonds
(b) they contain only covalent bonds
(c) they contain co-ordinate bond
(d) they contain covalent and ionic bonds
Answer. (c)
15. The species CO, CN– and N2 are ___________
(a) isoelectronic
(b) having co-ordinate bond
(c) having low bond energies
(d) having polar bonds
Answer. (a)
16. The polarity of a covalent bond is due to ___________
(a) lesser electronegativity difference between two atoms
(b) greater electronegativity difference between two atoms
(c) lesser bond energy
(d) greater bond energy
Answer. (b)
17. A CO2 molecule contains two polar bonds but the net dipole moment is zero. It is because ___________
(a) the molecule has symmetrical linear geometry
(b) the molecule is non-linear
(c) the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is too large
(d) the electronegativity difference between the two atoms is too small
Answer. (a)
18. Among BeF2, BF3, NH3 and CCl4, the molecule with net dipole moment is ___________
(a) BeF2
(b) BF3
(c) NH3
(d) CCl4
Answer. (c)
19. The common feature among the molecules HF, H2O, HCl and NH3 is ___________
(a) intramolecular H-bonding
(b) intermolecular H-bonding
(c) that they contain no polar bonds
(d) that their dipole moment is zero
Answer. (b)
20. Methanol is soluble in water due to ___________
(a) covalent bond nature
(b) ionic bond nature
(c) hydrogen bonding
(d) its poisonous nature
Answer. (c)
21. Among H2O, H2S, H2Se and H2Te, the substance with highest boiling point is ___________
(a) H2O; due to hydrogen bonding
(b) H2S; due to large size of S atom
(c) H2Se; due to large electronegativity difference
(d) H2Te; due to largest size of Te atom
22. In ice crystal, the H2O molecules are held together in a ___________
(a) planar structure
(b) linear structure
(c) tetrahedral three dimensional structure
(d) none of these
Answer. (c)
23. The density of ice (solid) is lesser than that of water (liquid) because it has ___________
(a) open cage like structure with no empty spaces
(b) open cage like structure with large empty spaces
(c) intermolecular H-bonding
(d) intramolecular H-bonding
Answer. (b)
24. The density of water is maximum at ___________
(a) 273 K
(b) 277 K
(c) 281 K
(d) 285 K
Answer. (b)
25. Among BeCl2, CHCl3, CCl4 and PCl5, the octet rule is not observed in ___________
(a) BeCl2only
(b) PCl5only
(c) BeCl2and PCl5
(d) CHCl3and CCl4
Answer. (c)
26. An example of electron deficient compound among BF3, CF4, PF5and SF6 is ___________
(a) BF3
(b) CF4
(c) PF5
(d) SF6
Answer. (a)
27. The transition metals show variable valency because of ___________
(a) the availability of vacant d-orbitals
(b) their tendency to form complex ions
(c) their ability to form coloured ions
(d) none of these
Answer. (a)
28. The electrical conductivity of metals is due to ___________
(a) mobile protons is the nucleus
(b) mobile nucleus in the nucleus
(c) mobile electrons in outer vacant spaces
(d) none of these
Answer. (c)
29. According to VSEPR theory, ___________
(a) the lone pairs only decide the structure of the molecule
(b) the bond pairs only decide the structure of the molecule
(c) the lone pairs and bond pairs both decide the structure of the molecule
(d) none of these
Answer. (c)
30. In which of the following, the central atom is surrounded by four electron pairs ___________
(a) H2O
(b) NH3
(c) CH4
(d) All
Answer. (d)
31. The molecule among CCl4, PCl3, SF4 and NH3that does not contain lone pairs of electrons around the central atom is ___________
(a) CCl4
(b) PCl3
(c) SF4
(d) NH3
Answer. (a)
32. Which of the following are isostructrual ___________
(a) SO2 and CO2
(b) SO2 and H2O
(c) BCl3 and CHCl3
(d) NH3 and CH4
Answer. (b)
33. The molecular shapes of H2O, NH3 and CH4 are ___________
(a) similar with 2, 1 and 0 lone pairs of electrons respectively
(b) similar with 0, 1 and 2 lone pairs of electrons respectively
(c) different with 0, 1 and 2 lone pairs of electrons respectively
(d) different with 2, 1 and 0 lone pairs of electrons respectively
Answer. (d)
34. The molecule of NH3 is ___________
(a) tetrahedral with bond angle 109° 28′
(b) pyramidal with bond angle 107° 20′
(c) trigonal with bond angle 120°
(d) linear with bond angle 180°
Answer. (b)
35. The NH4+and SO42– ions have ___________
(a) tetrahedral geometry
(b) triangular geometry
(c) pyramidal geometry
(d) square planar geometry
Answer. (a)
36. Which is incorrect?
(a) all molecules with polar bonds have dipole moment
(b) all molecules with polar bonds may or may not have dipole moment
(c) the greater the difference in electronegativity between two atoms, greater is the polarity
(d) if the electronegativity difference between two atoms is greater than 1.7, the bond will be ionic
Answer. (a)
37. The favourable conditions for the formation of H–bonding are ___________
(a) high electronegativity and small size of the atom bonded to H–atom
(b) low electronegativity and large size of the atom bonded to H–atom
(c) high electronegativity and large size of the atom bonded to H–atom
(d) low electronegativity and small size of the atom bonded to H–atom
Answer. (a)
38. The strength of hydrogen bonding lies in between ___________
(a) covalent and ionic bond
(b) metallic and covalent bond
(c) van der Waal’s and covalent bond
(d) metallic and ionic bond
Answer. (d)
39. The bond angles in a trigonal bipyramid molecules are ___________
(a) 90°
(b) 120°
(c) 109.5°
(d) 120°, 90°
Answer. (d)
40. CO2has zero dipole moment whereas H2O has a dipole moment. It is because ___________
(a) H2O is linear while CO2 is a bent molecule
(b) of intermolecular H–bonding in H2O molecules
(c) CO2 is linear while H2O is a bent molecule
(d) CO2 is a gas while H2O is a liquid at room temperature
Answer. (c)
41. Which of the following does not obey the octet rule?
(a) PCl5
(b) H2O
(c) NH3
(d) CCl4
Answer. (a)
42. The total number of electrons that take part in forming bonds in O2 is ___________
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 8
Answer. (d)
43. CO is isoelectronic with ___________
(a) C2H2
(b) CN–
(c) O2+
(d) O2–
Answer. (b)
44. CO2 is isostructural with ___________
(a) H2O
(b) NO2
(c) H2S
(d) C2H2
Answer. (d)
45. In a bond between two atoms X and Y, the shared electron pair does not lie in the centre. The bond is ___________
(a) single bond
(b) non-polar bond
(c) polar bond
(d) co-ordinate bond
Answer. (c)
46. The maximum number of Hydrogen bonds formed by a water molecule is ___________
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Answer. (b)
47. Out of the following, intramolecular Hydrogen bonding exists in ___________
(a) water
(b) H2S
(c) 2-nitrophenol
(d) 4-nitrophenol
Answer. (c)
48. In a compound, hydrogen bonding exists but there is no effect on physical properties like m. pt., b. pt. etc. It shows the presence of ___________
(a) weak van der Waal’s forces
(b) intramolecular hydrogen bonding
(c) intermolecular hydrogen bonding
(d) resonance in the molecule
Answer. (b)
49. Which one of the following is the most polar ___________
(a) H — F
(b) H — Cl
(c) H — Br
(d) H — I
Answer. (a)
- Reference: Essentials of Physical Chemistry /Arun Bahl, B.S Bahl and G.D. Tuli / multicolor edition.

very good i love and i want to ask for paper ii