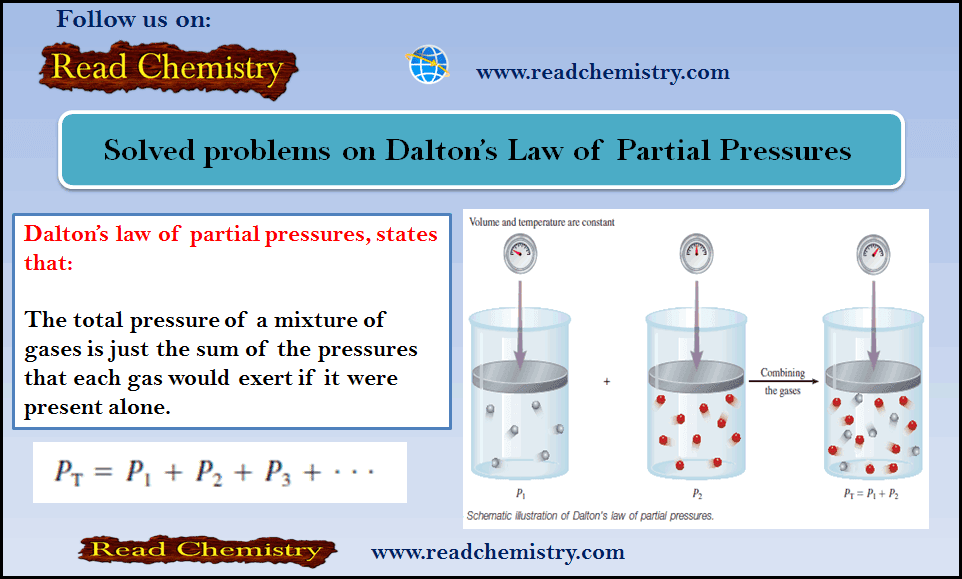
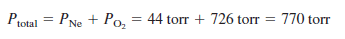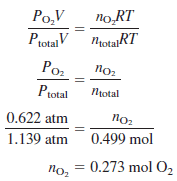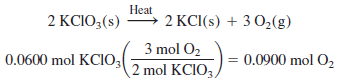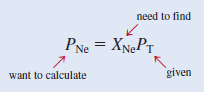– Before you solve these problems, you can read this subject for Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures (Statement, Mathematical, Importance, Application).
– Let us understand Dalton’s law by solving these problems.
Solved Problems on Dalton’s Law
Problem (1) on Dalton’s Law
A mixture of oxygen and neon contains oxygen at a pressure of 726 torr and neon at a pressure of 44 torr. What is the pressure of the mixture?
Solution:
Problem (2) on Dalton’s Law
Calculate the total number of moles in a 10.5L sample of gas at 292 K, containing O2 at 0.622 atm and N2 at 0.517 atm. Also, calculate the number of moles of present.
Solution:
– The total pressure of the gas mixture is
– The total number of moles is
– The number of moles of O2 is:
– We can calculate the number of moles of oxygen another way.
– Because the oxygen and the gas mixture are both at the same temperature and have the same volume, the numbers of moles are proportional to the pressures:
Problem (3)
Oxygen gas is collected over water in an apparatus such as that shown in Figure 12.8 at a barometric pressure of 759 torr at 23 oC
(a) What is the pressure of the water vapor?
(b) What is the pressure of the oxygen gas?
Solution
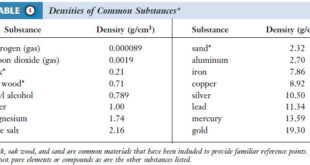
(a) The water vapor pressure at 23 oC is 21.1 torr, (from Table above)
(b) The pressure of the oxygen gas is:
Problem (4)
What volume of oxygen, collected over water, will be obtained at 23 oC and 762 torr barometric pressure from the thermal decomposition of 0.0600 mol of KClO3
Solution:
– Since we have the number of moles of oxygen, we must use the partial pressure of oxygen, which is the barometric pressure minus the water vapor pressure (from the Table above):
Problem (5)
A mixture of gases contains 4.46 moles of neon (Ne), 0.74 mole of argon (Ar), and 2.15 moles of xenon (Xe). Calculate the partial pressures of the gases if the total pressure is 2.00 atm at a certain temperature.
Strategy:
– What is the relationship between the partial pressure of a gas and the total gas pressure? How do we calculate the mole fraction of a gas?
Solution:
– The partial pressure of Ne ( PNe ) is equal to the product of its mole fraction ( XNe ) and the total pressure ( PT )
– we calculate the mole fraction of Ne as follows:
– Therefore:
Check:
– Make sure that the sum of the partial pressures is equal to the given total pressure; that is,
(1.21 + 0.20 + 0.586) atm = 2.00 atm.
Problem (6)
Oxygen gas generated by the decomposition of potassium chlorate is collected as shown in Figure (1). The volume of oxygen collected at 24 °C and atmospheric pressure of 762 mmHg is 128 mL. Calculate the mass (in grams) of oxygen gas obtained. The pressure of the water vapor at 24°C is 22.4 mmHg.
Strategy:
– To solve for the mass of O2 generated, we must first calculate the partial pressure of O2 in the mixture.
– What gas law do we need? How do we convert the pressure of O2 gas to the mass of O2 in grams?
Solution:
– From Dalton’s law of partial pressures we know that:

– From the ideal gas equation, we write:
– where m and µ are the mass of O2 collected and the molar mass of O2, respectively.
– Rearranging the equation we obtain
Check:
The density of the oxygen gas is (0.164 g/0.128 L), or 1.28 g/L, which is a reasonable value for gases under atmospheric conditions.
Reference:
- Chemistry / Raymond Chang, Williams College /(10th edition).
- Fundamentals of Chemistry / David E.Goldberg/(5th edition).
 Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry