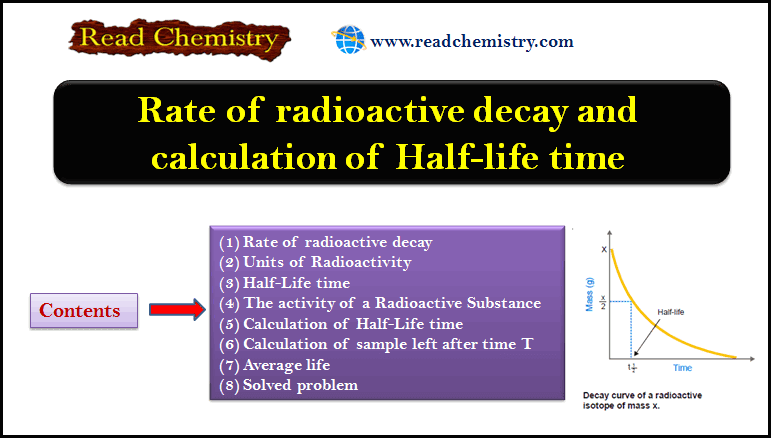
MCQ on the First law of Thermodynamics
MCQ on the First Law of Thermodynamics
– In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on the First law of Thermodynamics
1. The first law of thermodynamics is_______
(a) the total energy of an isolated system remains constant though it may change from one form to another.
(b) total energy of a system and surroundings remains constant
(c) whenever energy of one type disappears, equivalent amount of another type is produced
(d) all of the above
Answer. (d)
2. The study of the flow of heat or any other form of energy into or out of a system undergoing physical or chemical change is called_______
(a) thermochemistry
(b) thermokinetics
(c) thermodynamics
(d) thermochemical studies
Answer. (c)
3. Thermodynamics is applicable to_______
(a) microscopic systems only
(b) macroscopic systems only
(c) homogeneous systems only
(d) heterogeneous systems only
Answer. (b)
4. Which is not true about thermodynamics?
(a) it ignores the internal structure of atoms and molecules
(b) it involves the matter in bulk
(c) it is concerned only with the initial and final states of the system
(d) it is not applicable to macroscopic systems
Answer. (d)
5. A system that can transfer neither matter nor energy to and from its surroundings is called_______
(a) a closed system
(b) an isolated system
(c) an open system
(d) a homogeneous system
Answer. (b)
6. A thermos flask is an example of_______
(a) isolated system
(b) closed system
(c) open system
(d) heterogeneous system
Answer. (a)
7. A closed system is one which cannot transfer matter but transfer _______ to and from its surrounding_______
(a) heat
(b) work
(c) radiations
(d) all of these
Answer. (d)
8. A gas contained in a cylinder filled with a piston constitutes_______
(a) an open system
(b) a heterogeneous system
(c) a closed system
(d) an isolated system
Answer. (c)
9. A system that can transfer both energy and matter to and from its surroundings is called_______
(a) an isolated system
(b) a closed system
(c) an open system
(d) a heterogeneous system
Answer. (c)
10. Zinc granules reacting with dilute hydrochloric acid in an open beaker constitutes_______
(a) an isolated system
(b) an open system
(c) a closed system
(d) a heterogeneous system
Answer. (b)
11. A system in which no thermal energy passes into or out of the system is called_______
(a) adiabatic system
(b) an open system
(c) a reversible system
(d) a closed system
Answer. (a)
12. An intensive property does not depend upon_______
(a) nature of the substance
(b) quantity of matter
(c) external temperature
(d) atmospheric pressure
Answer. (b)
13. Which out of the following is not an intensive property?
(a) pressure
(b) concentration
(c) density
(d) volume
Answer. (d)
14. A property that depends upon the quantity of matter is called an extensive property. Which of the following is not an extensive property?
(a) mass
(b) volume
(c) density
(d) internal energy
Answer. (c)
15. Which of the following sets of properties constitute intensive properties?
(a) temperature, pressure and volume
(b) mass, density and volume
(c) density, pressure and temperature
(d) internal energy, density and pressure
Answer. (c)
16. A system in which state variables have constant values throughout the system is called in a state of_______
(a) equilibrium
(b) non-equilibrium
(c) isothermal equilibrium
(d) none of these
Answer. (a)
17. In an adiabatic process _______ can flow into or out of the system.
(a) no heat
(b) heat
(c) matter
(d) no matter
Answer. (a)
18. Which of the following conditions holds good for an adiabatic process?
(a) dq < 0
(b) dq > 0
(c) dq = 0
(d) dq = α
Answer. (c)
19. An isobaric process takes place at constant _______.
(a) temperature
(b) pressure
(c) volume
(d) concentration
Answer. (b)
20. Which is true for an isobaric process?
(a) dp > 0
(b) dp < 0
(c) dp = α
(d) dp = 0
Answer. (d)
21. An isochoric process takes place at constant_______.
(a) volume
(b) temperature
(c) pressure
(d) concentration
Answer. (a)
22. For a cyclic process, the change in internal energy of the system is_______
(a) always positive
(b) always negative
(c) equal to zero
(d) equal to infinity
Answer. (c)
23. Which out of the following is incorrect?
(a) heat flow into the system is +ve
(b) heat flow out of the system is –ve
(c) work done on the system is –ve
(d) none of these
Answer. (c)
24. The units erg, joule and calorie are interconvertible, which of the following is incorrect?
(a) 107 ergs = 1 Joule
(b) 4.184 J = 1 cal
(c) 1 Joule = 0.2390 cal
(d) 1 erg = 4.184 cal
Answer. (d)
25. A gas expands from 10 litres to 20 litres against a constant external pressure of 10 atm. The pressurevolume work done by the system is_______
(a) 100 lit atm
(b) –100 lit atm
(c) 10 lit atm
(d) –10 lit atm
Answer. (b)
26. Which out of the following is incorrect, for an ideal gas?
(a) P V = n R T
(b)V = n RT / P
(c) P= n RT / V
(d) all are correct
Answer. (d)
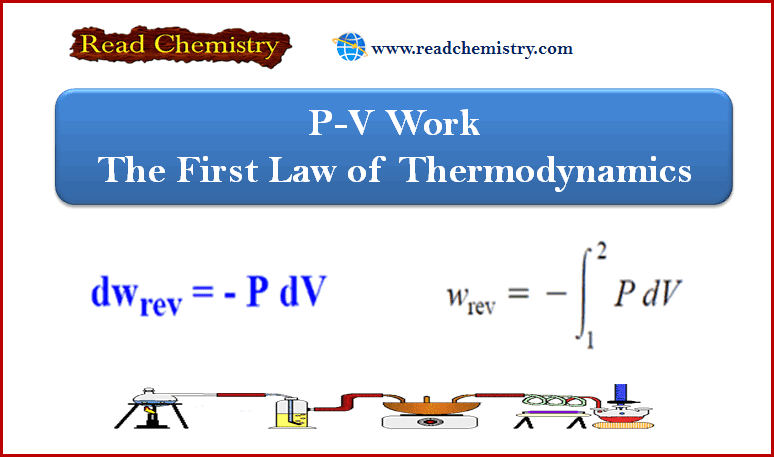
27. The work done in the reversible expansion of a gas from the initial state A to final state B is_______
(a) maximum
(b) minimum
(c) equal to zero
(d) equal to infinity
Answer. (a)
28. The mathematical relation for the first law of thermodynamics is_______
(a) ΔE = q – w
(b) ΔE = 0 for a cyclic process
(c) ΔE = q for an isochoric process
(d) all of these
Answer. (d)
29. For an adiabatic process, according to first law of thermodynamics, _______
(a) ΔE = –w
(b) ΔE = w
(c) ΔE = q – w
(d) none of these
Answer. (a)
30. The change in internal energy for an isobaric process is given by_______
(a) ΔE = q + p Δv
(b) ΔE = q – p Δv
(c) ΔE = q
(d) ΔE = p Δv
Answer. (b)
31. Which of the following properties is not a function of state?
(a) concentration
(b) internal energy
(c) enthalpy
(d) entropy
Answer. (a)
32. The change in enthalpy of a system is measured by measuring_______
(a) heat of the process at constant volume
(b) heat of the process at constant temperature
(c) heat of the process at constant pressure
(d) none of these
Answer. (c)
33. The enthalpy change, ΔH of a process is given by the relation_______
(a) ΔH = ΔE + p Δv
(b) ΔH = ΔE + Δn R T
(c) ΔH = ΔE + w
(d) all of these
Answer. (b)
34. The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one mole of the substance by 1 K is called_______
(a) heat capacity
(b) molar heat capacity
(c) molar heat
(d) molar capacity
Answer. (b)
35. Which of the following statements is not correct?
(a) heat is not a state function
(b) heat capacity is not a state function
(c) neither of these
(d) both
Answer. (c)
36. Heat capacity at constant pressure is the change in_______
(a) internal energy with temperature at constant volume
(b) internal energy with temperature at constant pressure
(c) enthalpy with temperature at constant volume
(d) enthalpy with temperature at constant pressure
Answer. (d)
37. Heat capacity at constant volume is the change in_______
(a) internal energy with temperature at constant volume
(b) internal energy with temperature at constant pressure
(c) enthalpy with temperature at constant volume
(d) enthalpy with temperature at constant pressure
Answer. (a)
38. Which of the following relations is true ?
(a) Cp > Cv
(b) Cv > Cp
(c) Cp = Cv
(d) Cp = Cv = 0
Answer. (a)
39. The heat capacity at constant pressure is related to heat capacity at constant volume by the relation_______
(a) Cp – R = Cv
(b) Cv – R = Cp
(c) Cp – Cv = R
(d) R – Cp = Cv
Answer. (c)
40. The phenomenon of lowering of temperature when a gas is made to expand adiabatically from a region of high pressure into a region of low pressure is known as_______
(a) First law of thermodynamics
(b) Second law of thermodynamics
(c) Le Chatlier’s principle
(d) Joule Thomson effect
Answer. (d)
41. Which of the following relations is applicable to adiabatic expansion of an ideal gas?
(a) T1 V1 γ–1 = T2 V2 γ–1
(b) P1 V1 γ = P2 V2 γ
(c) both
(d) none of these
Answer. (c)
42. In an adiabatic process _______ must change
(a) pressure
(b) volume
(c) concentration
(d) temperature
Answer. (d)
43. The enthalpy change of a reaction is independent of_______
(a) state of the reactants and products
(b) nature of the reactants and products
(c) initial and final enthalpy change of the reaction
(d) different intermediate reaction
Answer. (d)
44. Which of the following is not correct?
(a) H = E + P V
(b) H – E = P V
(c) H – E – P V = 0
(d) H = E – P V
Answer. (d)
45. When the total energy change in an isothermal cycle is zero, it represents_______
(a) a reversible cycle
(b) an adiabatic change
(c) a thermodynamic equilibrium
(d) an irreversible cycle
Answer. (a)
46. One mole of an ideal gas at 300 K is expanded isothermally from 1 litre volume to 10 litre volume. ΔE for this process is_______ (R = 2 cal K–1 mol–1)
(a) 300 cal
(b) 600 cal
(c) 1200 cal
(d) 0 cal
Answer. (d)
47. A system absorbs 100 kJ heat and performs 50 kJ work on the surroundings. The increase in internal energy of the system is_______
(a) 50 kJ
(b) 100 kJ
(c) 150 kJ
(d) 5000 kJ
Answer. (a)
48. For the reaction H2 + I2 → 2HI, ΔH is equal to_______
(a) ΔE + 2 R T
(b) ΔE – 2 R T
(c) ΔE
(d) ΔE + R T
Answer. (c)
49. The work done when 1 mole of a gas expands reversibly and isothermally from 5 atm to 1 atm at 300 K is_______
(a) – 4015 J
(b) +4015 J
(c) zero
(d) 150 J
Answer. (a)
50. Three moles of an ideal gas (Cv = 5 cal K–1 mol–1) at 10.0 atm and 0° are converted to 2.0 atm at 50°. The ΔE for the process is_______
(a) 150 cal
(b) 300 cal
(c) 750 cal
(d) 1500 cal
Answer. (c)
Reference: Essentials of Physical Chemistry /Arun Bahl, B.S Bahl and G.D. Tuli / multicolour edition.