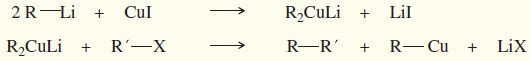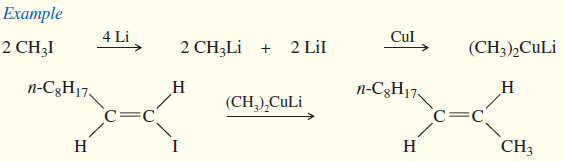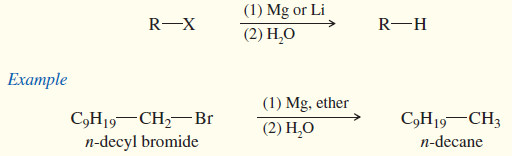Reactions of Alkyl Halides
In this subject we will discuss the Reactions of Alkyl Halides with chemical equations and examples
Introduction to Alkyl Halides
– Our study of organic chemistry is organized into families of compounds classified by their functional groups.
– We use alkyl halides to introduce substitution and elimination, two of the most important types of reactions in organic chemistry.
– Stereochemistry will play a major role in our study of these reactions.
– Many other reactions show similarities to substitution and elimination, and the techniques introduced will be used throughout our study of organic reactions.
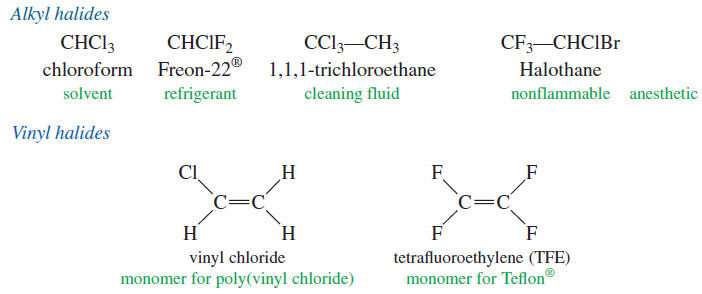
– There are three major classes of halogenated organic compounds: the alkyl halides, the vinyl halides, and the aryl halides.
– An alkyl halide simply has a halogen atom bonded to one of the sp3 hybrid carbon atoms of an alkyl group.
– A vinyl halide has a halogen atom bonded to one of the sp2 hybrid carbon atoms of an alkene.
– An aryl halide has a halogen atom bonded to one of the sp2 hybrid carbon atoms of an aromatic ring.
– The chemistry of vinyl halides and aryl halides is different from that of alkyl halides because their bonding and hybridization are different.
– The structures of some representative alkyl halides, vinyl halides, and aryl halides are shown here, with their most common names and uses.
Reactions of Alkyl Halides
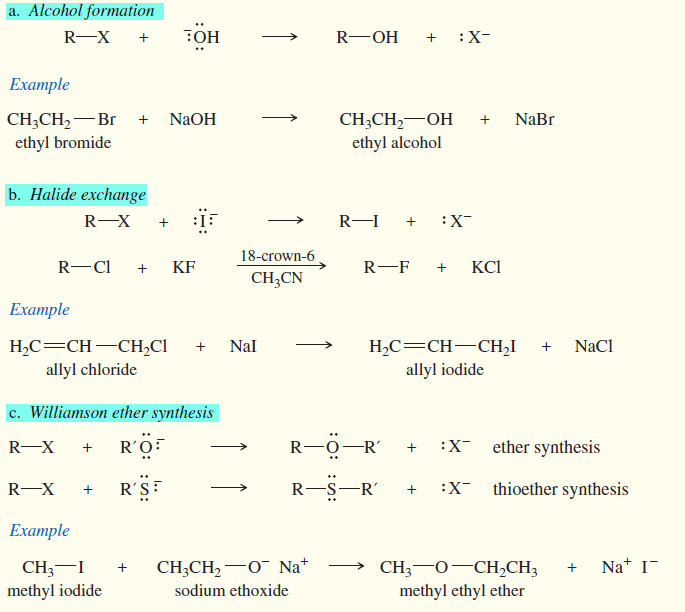
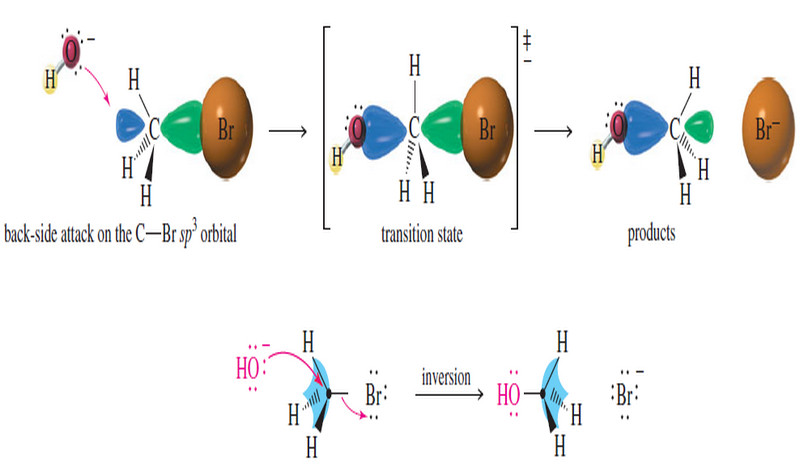
(1) Nucleophilic substitutions of Alkyl Halides
It includes as follow:
(a) Alcohol formation
(b) Halide exchange
(c) Williamson ether synthesis
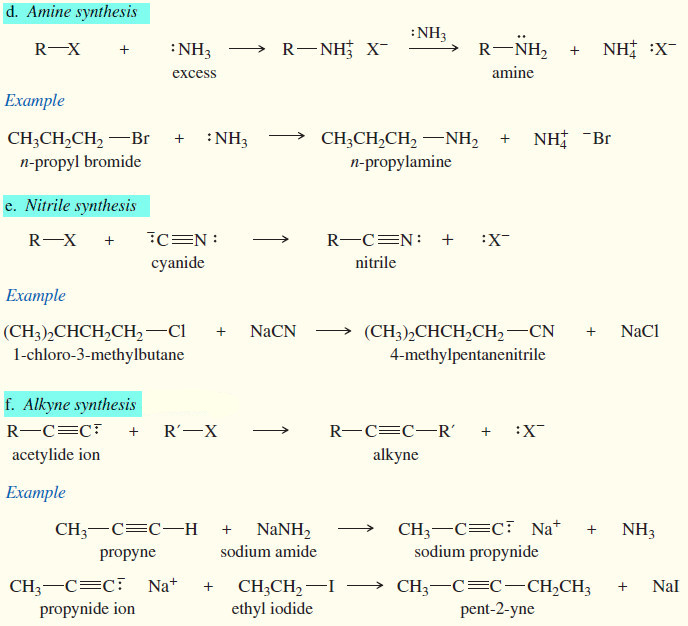
(d) Amine synthesis
(e) Nitrile synthesis
(f) Alkyne synthesis
Now we will indicate the equations for Reactions of Alkyl Halides
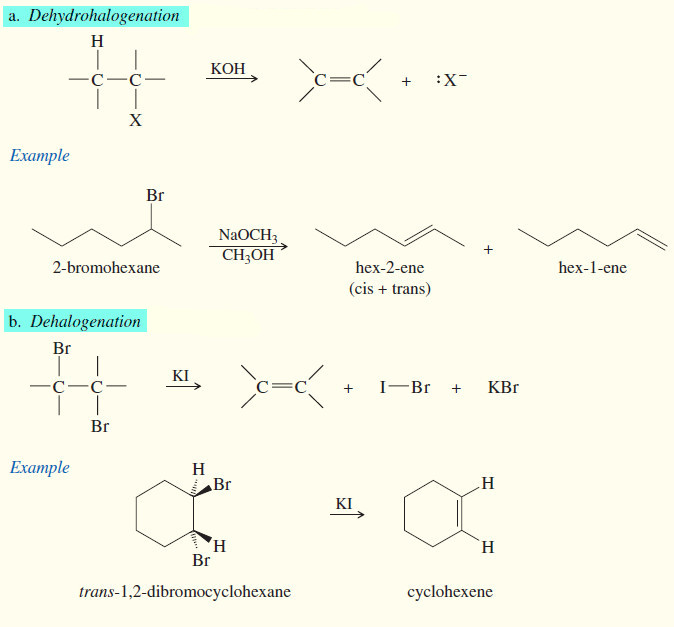
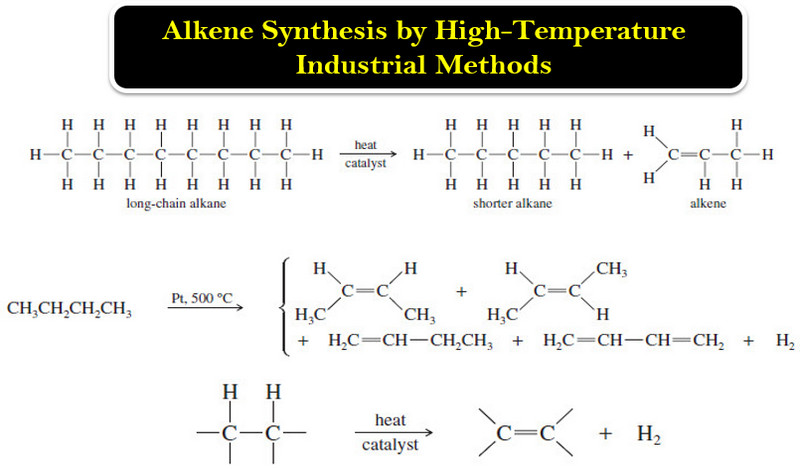
(2) Eliminations reactions of Alkyl Halides
(a) Dehydrohalogenation
(b) Dehalogenation
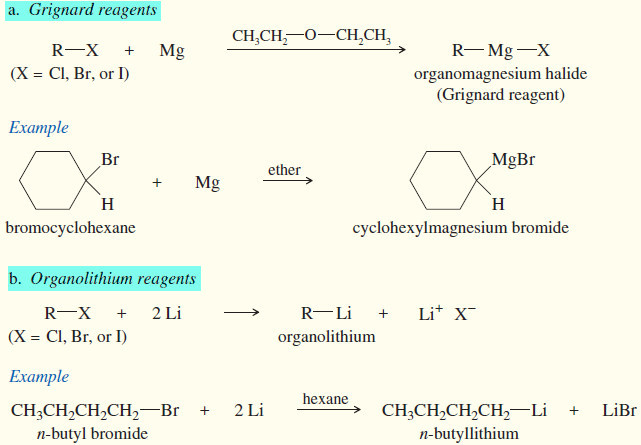
(3) Formation of organometallic reagents
(a) Grignard reagents
(b) Organolithium reagents