NMR – Essential Terms in NMR spectroscopy
– In this topic, we will discuss some Essential Terms in NMR spectroscopy.
Essential Terms in NMR spectroscopy
accidentally equivalent nuclei
– Nuclei that are not chemically equivalent, yet absorb at nearly the same chemical shift and are not resolved.
– Nuclei that absorb at the same chemical shift cannot split each other, whether they are chemically equivalent or accidentally equivalent.
chemically equivalent atoms
– Atoms that cannot be distinguished chemically.
– The replacement test for chemically equivalent atoms gives identical compounds.
chemical shift
– The difference (in ppm) between the resonance frequency of the proton (or carbon nucleus) being observed and that of tetramethylsilane (TMS).
– Chemical shifts are usually given on the δ (delta) scale, in parts per million downfield from TMS.
complex splitting
– Splitting by two or more different kinds of protons with different coupling constants.
coupling constant (J)
– The distance (in hertz) between two adjacent peaks of a multiplet.
DEPT
– (Distortionless Enhanced Polarization Transfer) A method of running several 13C experiments with different pulse sequences so that the carbon atoms appear differently depending on whether they are bonded to 0, 1, 2, or 3 protons.
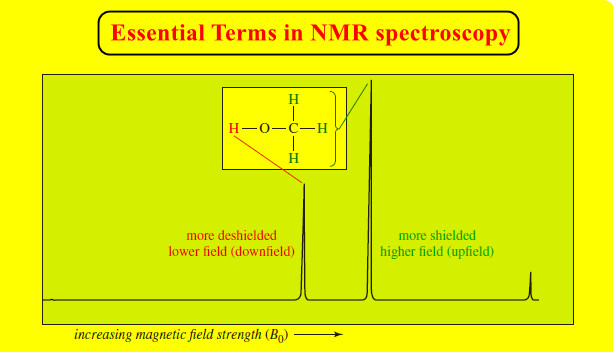
deshielded
– Bonded to a group that withdraws part of the electron density from around the nucleus.
– The absorptions of deshielded nuclei are moved downfield, resulting in larger chemical shifts.
diastereotopic atoms
– Nuclei that occupy diastereomeric positions.
– The replacement test for diastereotopic atoms gives diastereomers.
– Diastereotopic nuclei can be distinguished by NMR, and they can split each other unless they are accidentally = equivalent.
downfield
– At a lower value of the applied magnetic field, toward the left (higher values of ) on the NMR spectrum.
– The more deshielded a nucleus is, the farther downfield it absorbs.
Fourier transform spectroscopy
– Spectroscopy that involves collecting transients (containing all the different resonance frequencies) and converting the averaged transients into a spectrum using the mathematical Fourier transform.
transient
– (free induction decay, or FID): The signal that results when many nuclei are irradiated by a pulse of energy and precess at their resonance frequencies. (p.603)
gyromagnetic ratio (γ)
– A measure of the magnetic properties of a nucleus.
– The resonance frequency 1n2 is given by the equation
where Beff is the effective magnetic field at the nucleus.
– The gyromagnetic ratio of a proton is 26,753 sec-1 gauss-1.
– The gyromagnetic ratio of a 13C nucleus is 6728 sec-1 gauss-1
induced magnetic field
– The magnetic field set up by the motion of electrons in a molecule (or in a wire) in response to the application of an external magnetic field.
integration
– The measurement of the area under a peak, proportional to the number of protons giving rise to that peak.
magnetically coupled
– Nuclei that are close enough that their magnetic fields influence each other, resulting in spin-spinsplitting.
magnetic moment
– The magnitude of a nuclear magnetic field, characterized by the gyromagnetic ratio.
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
– The medical term for NMR imaging, avoiding the word nuclear.
– Use of field gradients in a large-bore magnet to scan two-dimensional slices of a patient’s body.
multiplet
– A group of peaks resulting from the spin-spin splitting of the signal from a single type of nucleus.
– A doublet has two peaks, a triplet has three peaks, a quartet has four peaks, etc.
N+1 rule
– A signal that is being split by N neighboring equivalent protons is split into a multiplet with N+1 individual peaks.
NMR
– (nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy) A form of spectroscopy that measures the absorption of radio frequency energy by nuclei in a magnetic field.
– The energy absorbed causes nuclear spin transitions.
carbon magnetic resonance
– (13C NMR ,CMR): NMR of the isotope of carbon.
proton magnetic resonance
– ( 1H NMR , PMR): NMR of protons.
off-resonance decoupling
– A technique used with 13C NMR in which only the protons directly bonded to a carbon atom cause spin-spin splitting.
relaxation time
– A measure of how slowly the nuclear spins return to their normal state after an RF pulse near their resonance frequency.
– Alternatively, the evening after a chemistry exam.
shielded
– Surrounded by electrons whose induced magnetic field opposes the externally applied magnetic field.
– The effective magnetic field at the shielded nucleus is less than the applied magnetic field.
spin decoupling
– Elimination of spin-spin splitting by constantly irradiating one type of nuclei at its resonance frequency.
spin-spin splitting
– (magnetic coupling) The interaction of the magnetic fields of two or more nuclei, usually through the bonds connecting them.
– Spin-spin splitting converts a single signal to a multiplet, a set of smaller peaks.
TMS
– Tetramethylsilane, an NMR standard whose absorption is defined as δ 0.00.
– At a higher value of the applied magnetic field, toward the right (lower values of δ) on the NMR spectrum.
– The more shielded a nucleus is, the farther upfield it absorbs.
References:
- Organic chemistry / L.G. Wade, Jr / 8th ed, 2013 / Pearson Education, Inc. USA.
- Fundamental of Organic Chemistry / John McMurry, Cornell University/ 8th ed, 2016 / Cengage Learningm, Inc. USA.
- Organic Chemistry / T.W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle , Scott A. Snyder / 11 ed, 2014/ John Wiley & Sons, Inc. USA.