Collision theory of Reaction rates
Collision theory of Reaction rates
– According to collision theory, a chemical reaction takes place only by collisions between the reacting molecules. However, not all collisions are effective.
– Only a small fraction of the collisions produce a reaction.
– The two main conditions for a collision between the reacting molecules to be productive are:
(1) The colliding molecules must possess sufficient kinetic energy to cause a reaction.
(2) The reacting molecules must collide with proper orientation.
– Now let us have a closer look at these two postulates of the collision theory.
(1) The molecules must collide with sufficient kinetic energy
– Let us consider a reaction:
A – A + B – B → 2A – B
– A chemical reaction occurs by breaking bonds between the atoms of the reacting molecules and forming new bonds in the product molecules.
– The energy for the breaking of bonds comes from the kinetic energy possessed by the reacting molecules before the collision.
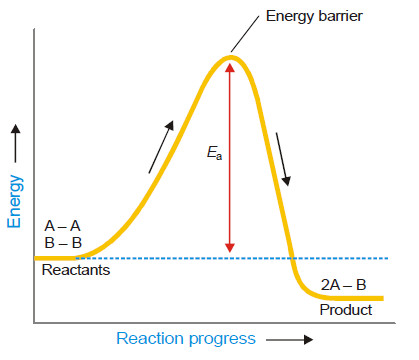
– The followimg Figure shows the energy of molecules A2 and B2 as the reaction A2 + B2 → 2AB progresses.
– The previous Figure also shows the activation energy, Ea, which is the minimum energy necessary to cause a reaction between the colliding molecules.
– Only the molecules that collide with a kinetic energy greater than Ea, are able to get over the barrier and react.
– The molecules colliding with kinetic energies less than Ea fail to surmount the barrier.
– The collisions between them are unproductive and the molecules simply bounce off one another.
(2) The molecules must collide with the correct orientation
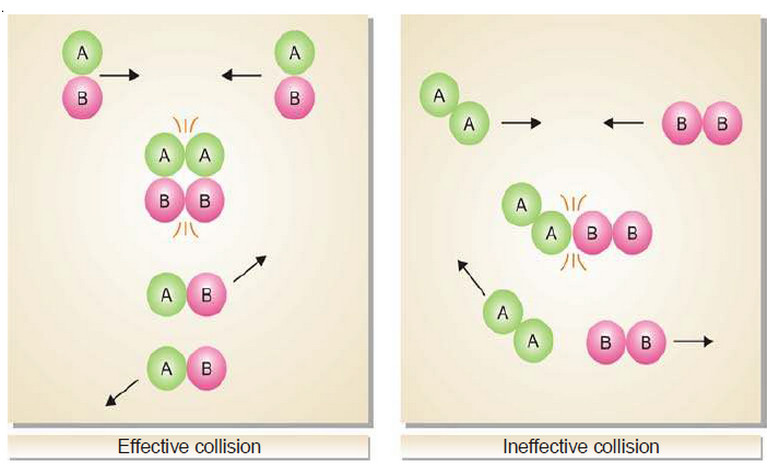
– The reactant molecules must collide with favorable orientation (relative position).
– The correct orientation is that which ensures direct contact between the atoms involved in the breaking and forming of bonds.
– From the above discussion, it is clear that: Only the molecules colliding with kinetic energy greater than Ea and with correct orientation can cause a reaction.
– The following figure shows the Orientations of reacting molecules A and B which lead to an effective and ineffective collision.
Collision Theory and Reaction Rate Expression
– Taking into account the two postulates of the collision theory, the reaction rate for the elementary process.
A + B ⎯⎯→ C + D
is given by the expression:
rate = f × p × z
– where:
f = fraction of molecules that possess sufficient energy to react
p = probable fraction of collisions with effective orientations
z = collision frequency.