-
Organic Chemistry
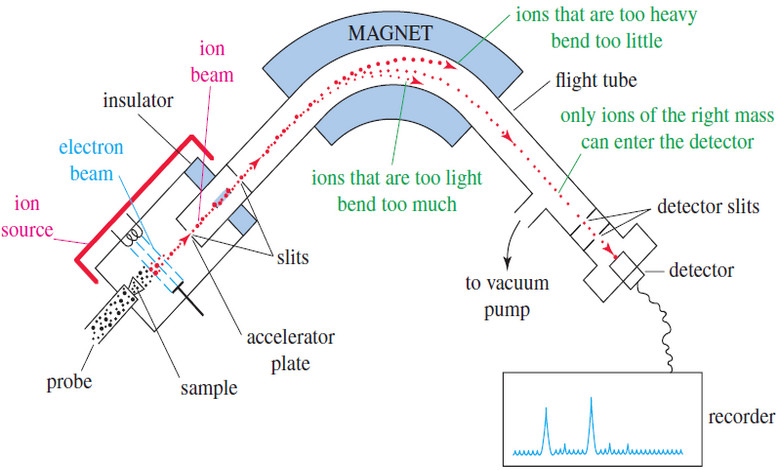
Mass Spectrometry : Introduction
Mass spectrometry (MS) provides the molecular weight and valuable information about the molecular formula, using a very small sample. Introduction…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
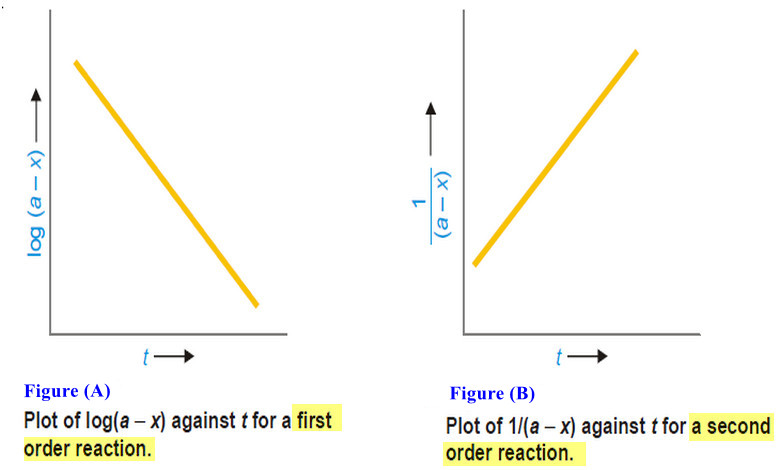
How to determine the order of reaction?
Determination of the order of reaction – There are at least four different methods to determine the order of reaction…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
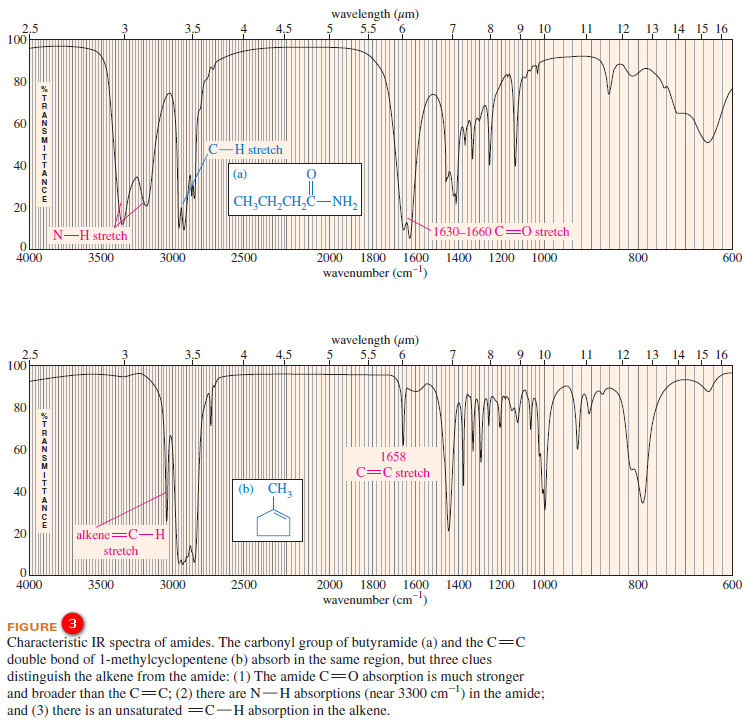
Characteristic Absorptions of Carbonyl Compounds
– In this subject, we will talk about Characteristic Absorptions of Carbonyl Compounds such as Ketones, Aldehydes, Amines, and Acids.…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
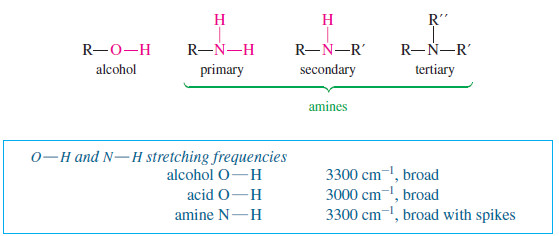
Characteristic Absorptions of Alcohols and Amines
– In this topic, we will discuss the Characteristic Absorptions of Alcohols and Amines by examples. Characteristic Absorptions of Alcohols…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
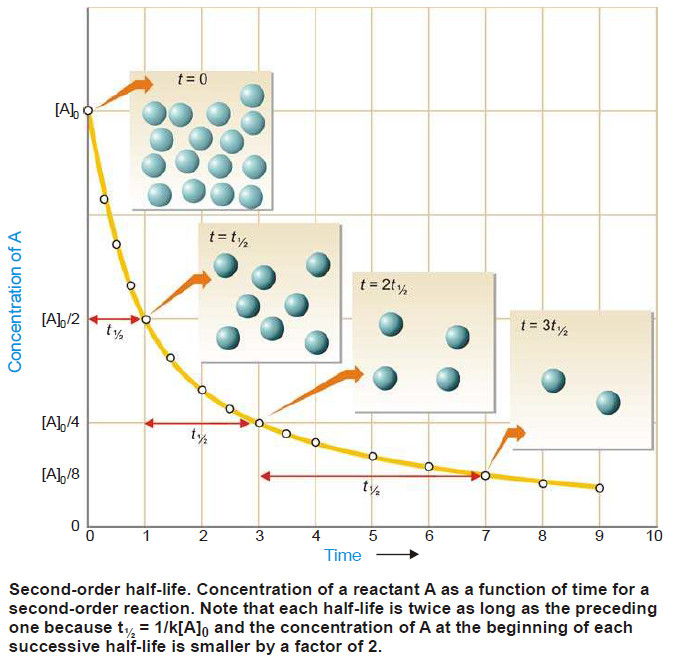
Second order reaction
Second order reaction – Let us take a second order reaction of the type 2A ⎯⎯→ products – Suppose the…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
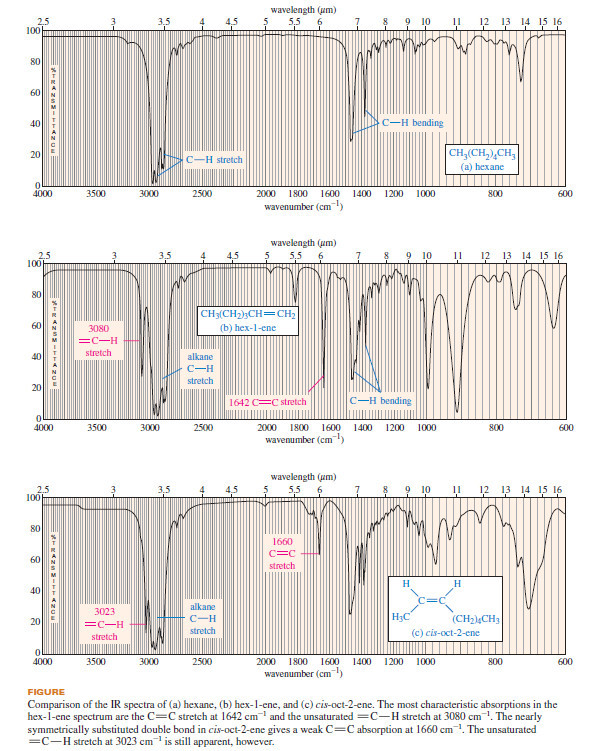
Hydrocarbons: Infrared Spectroscopy of Hydrocarbons
Infrared Spectroscopy of Hydrocarbons – Hydrocarbons contain only carbon–carbon bonds and carbon–hydrogen bonds. – An infrared spectrum does not provide…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
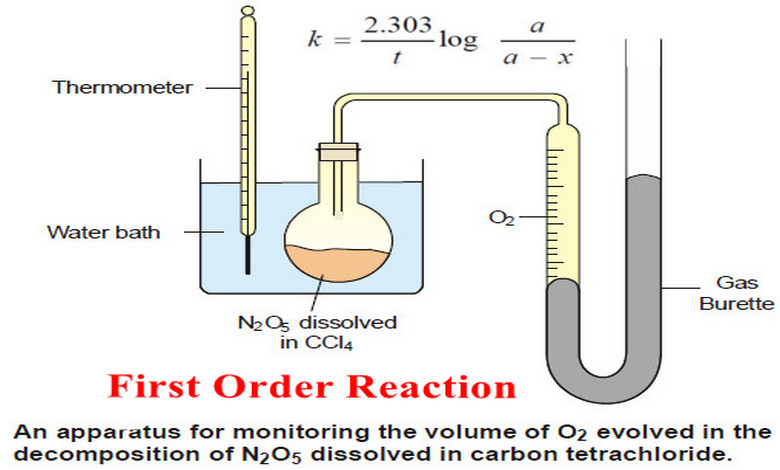
First Order Reaction -Examples and Solved problems
First order reaction – Let us consider a first order reaction: A → products – Suppose that at the beginning…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
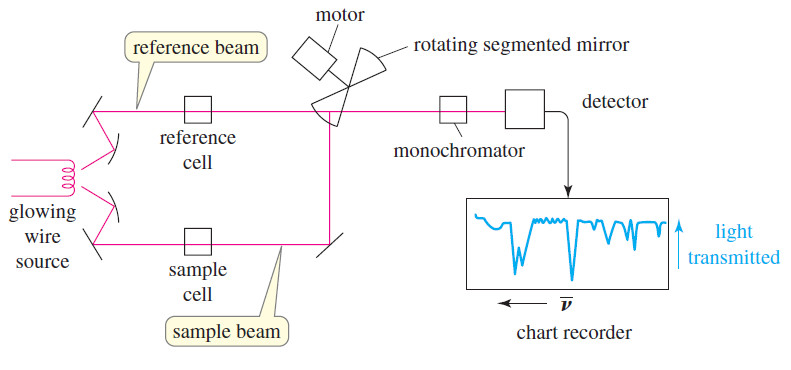
IR Spectrum – Measurement of the IR Spectrum
– In this subject, we talk about how to Measure the IR Spectrum. Measurement of the IR Spectrum – Infrared…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
Molecular Vibrations : IR spectrum
– In this subject we talk about Molecular Vibrations as introduction to understand IR spectrum Molecular Vibrations – Before discussing…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
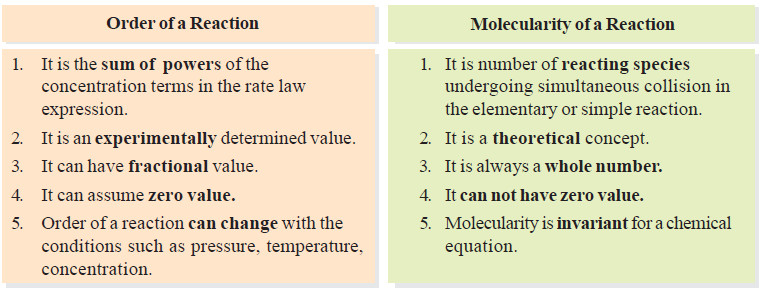
Molecularity of a reaction
– we will discuss the Molecularity of a reaction and the Differences Between Order and Molecularity. Molecularity of a reaction…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
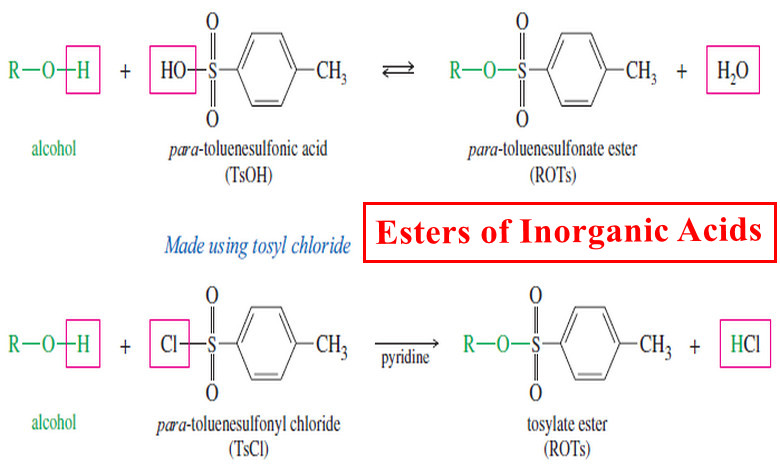
Inorganic Esters – Esters of Inorganic Acids
Esters of Inorganic Acids – In addition to forming esters with carboxylic acids, alcohols form inorganic esters with inorganic acids…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
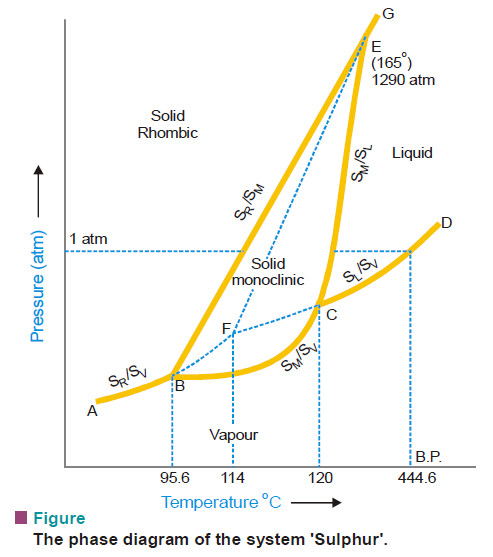
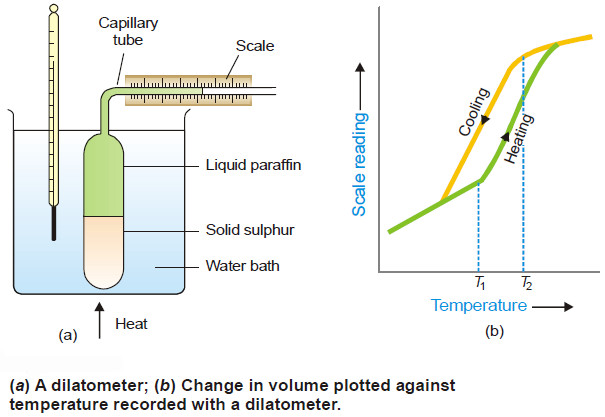
Sulphur system – Phase diagram of Sulphur
The Sulphur system – Sulphur system is a one-component, four-phase system. – The four phases are: (a) Two solid polymorphic…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
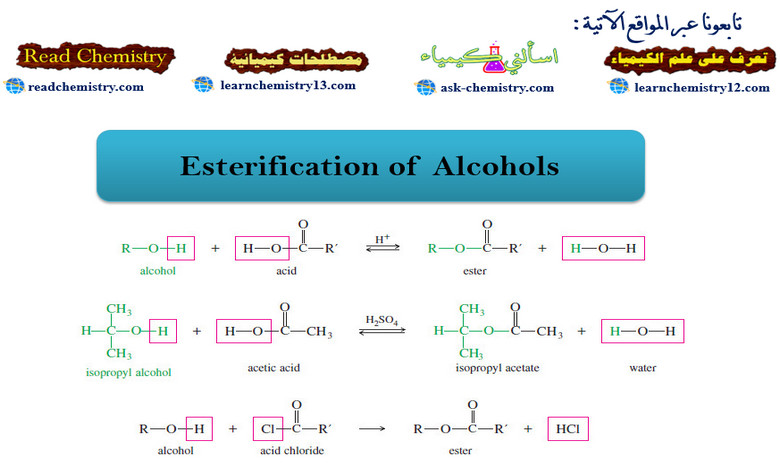
Esterification of Alcohols
– In this subject we will talk about the Esterification of Alcohols. What are Alcohols? – Alcohols are organic compounds…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
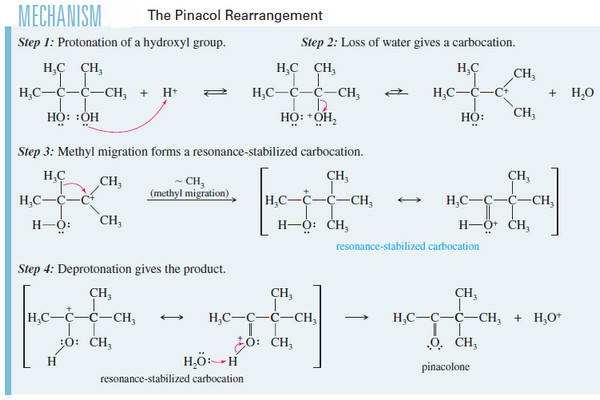
Reactions of Diols
Unique Reactions of Diols – Unique Reactions of Diols are: (1) The Pinacol Rearrangement (2) Periodic Acid Cleavage of Glycols…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
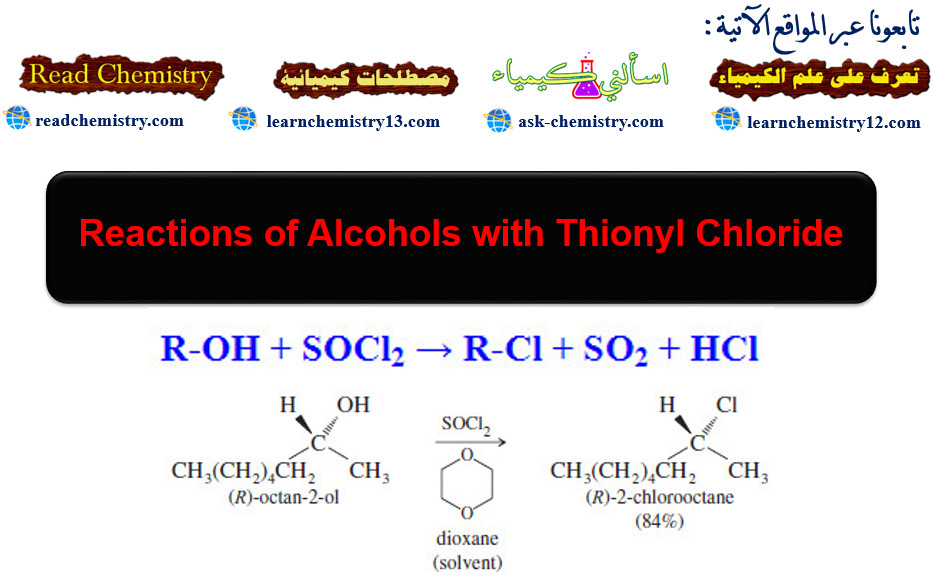
Reactions of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride
Reactions of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride – Reactions of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride give alkyl chloride. – Thionyl chloride (SOCl2)…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
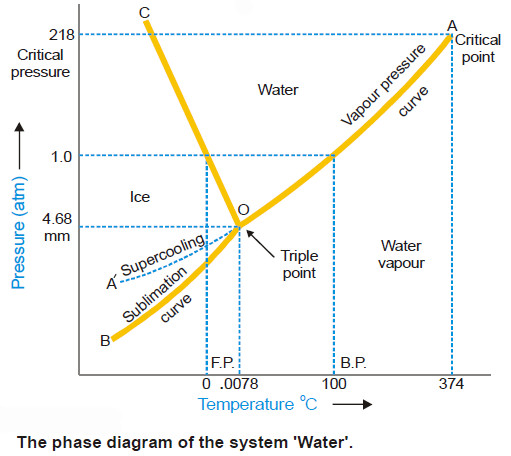
Water system, Phase diagram of Water
The Water system – Under normal conditions the Water system is a three-phase, one-component system. – The three phases involved…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
Reaction of Alcohols with Phosphorus Halides
Reaction of Alcohols with Phosphorus Halides – Reaction of Alcohols with Phosphorus Halides gives alkyl halides. – Several phosphorus halides…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
Polymorphism – Allotropy
Polymorphism – The occurrence of the same substance in more than one crystalline forms is known as Polymorphism. – Polymorphism…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
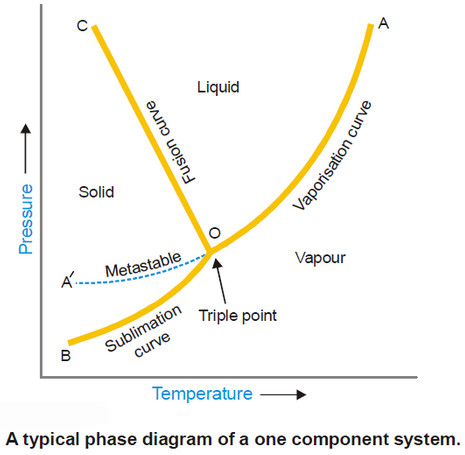
Phase diagram – Phase Rule
Phase Diagram – A phase diagram is a plot showing the conditions of pressure and temperature under which two or…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
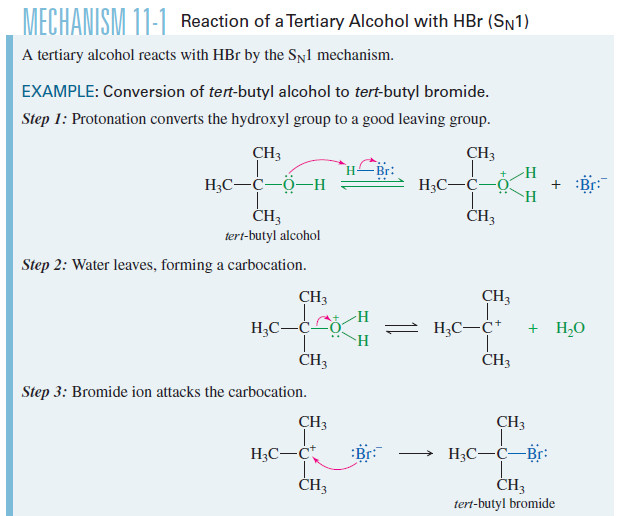
Reactions of Alcohols with Hydrohalic Acids
– In this topic the Reactions of Alcohols with Hydrohalic Acids such as HBr , HCl are discussed Reactions of…
Read More »