Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry focuses on the structure, properties, and reactions of carbon-containing compounds. It’s essential in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and biochemistry, exploring mechanisms, functional groups, and synthesis of complex molecules.
-
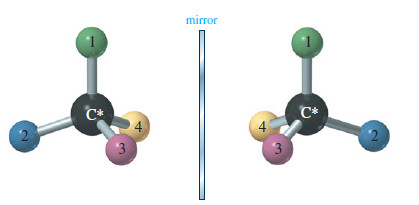
Chirality in Organic Chemistry
What is Chirality? – What is the difference between your left hand and your right hand? They look similar, yet…
Read More » -
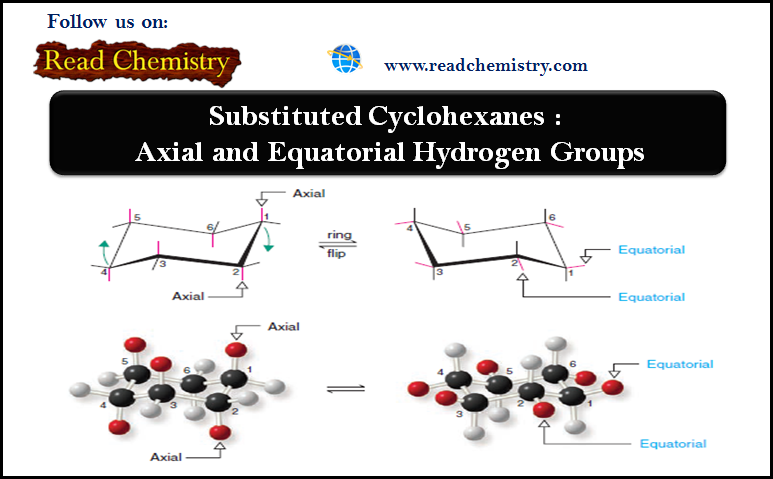
Cyclohexane: Axial and Equatorial Bonds in Cyclohexane
– In this subject, we will discuss the Substituted Cyclohexane: Axial and Equatorial Hydrogen Groups Substituted Cyclohexane: Axial and Equatorial…
Read More » -
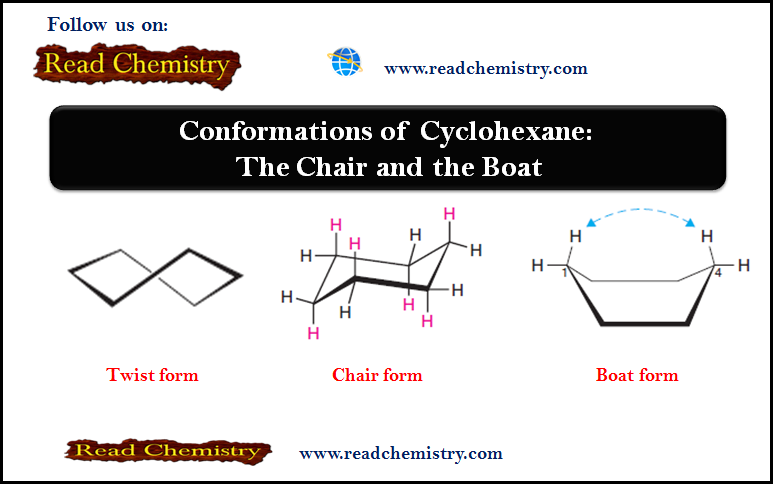
Conformations of Cyclohexane: The Chair and the Boat
– In this subject, we will discuss Conformations of Cyclohexane: The Chair and the Boat Conformations of Cyclohexane: The Chair…
Read More » -
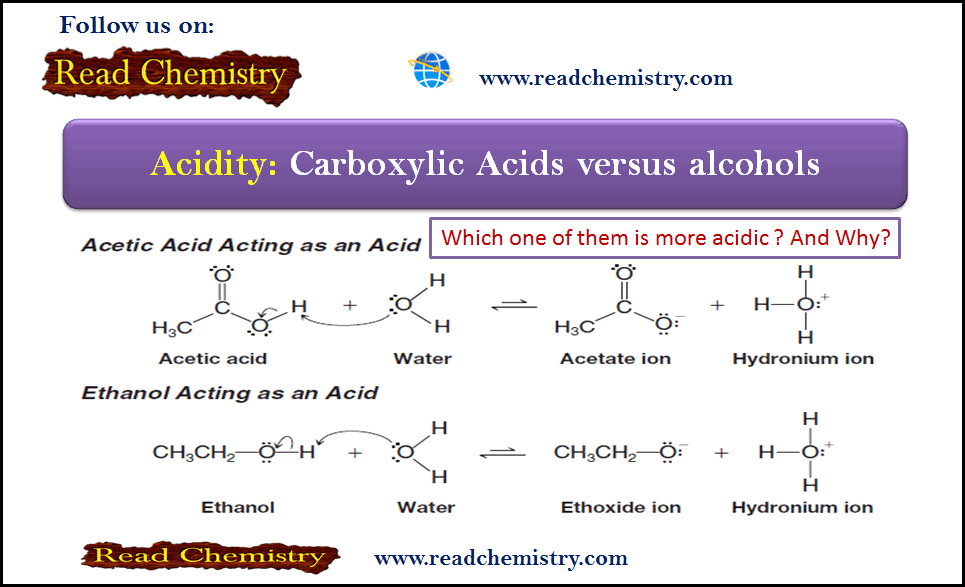
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols
– In this subject, we will discuss the Acidity Differences between Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids Acidity of Carboxylic Acids and…
Read More » -
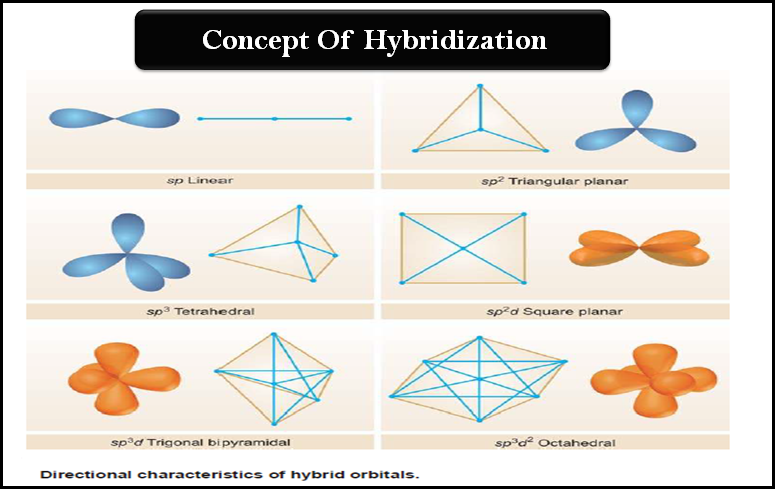
Hybridization: Definition, Types, Rules, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Hybridization: Definition, Types, Rules, and Examples – While the formation of simple…
Read More » -
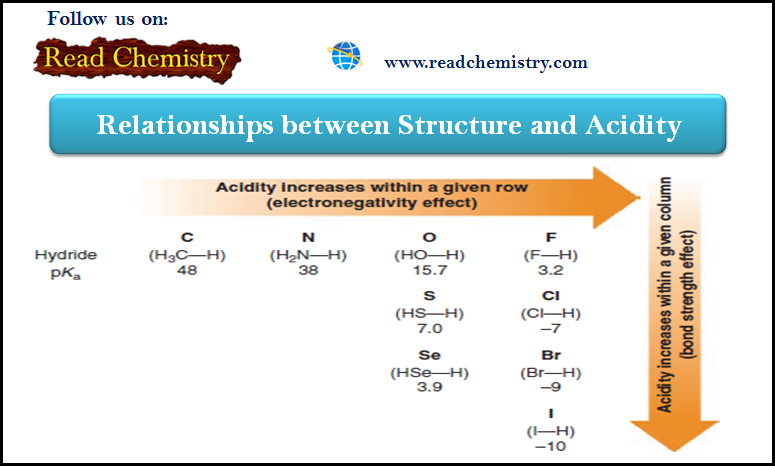
Acidity: The relationship between Structure and Acidity
– In this subject, we will discuss the Relationships between Structure and Acidity. – The strength of a Brønsted–Lowry acid…
Read More » -
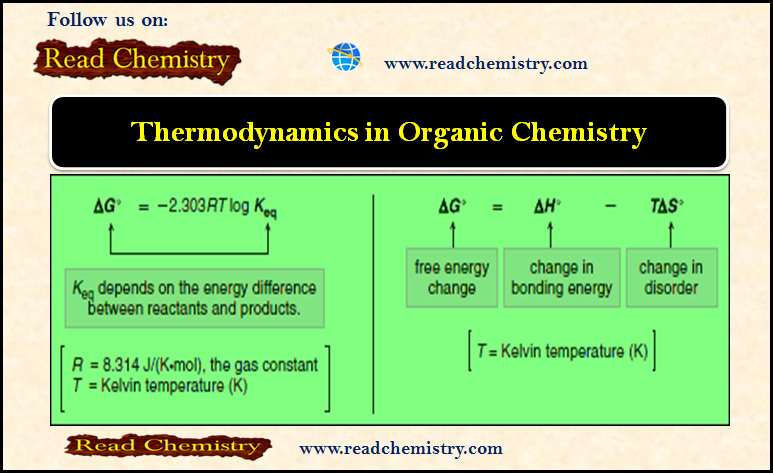
Thermodynamics of Organic Compounds
– In this subject, we will discuss the Thermodynamics of Organic Compounds Thermodynamics of Organic Compounds – For a reaction…
Read More » -
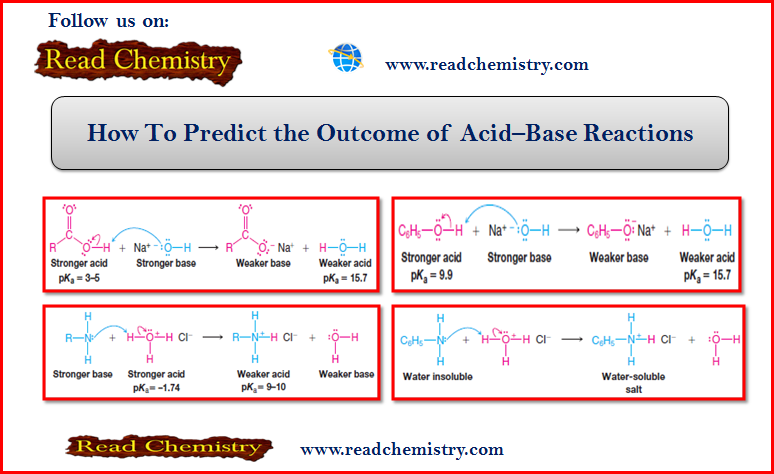
How to Predict the Outcome of acid-base reaction
– In this subject, we will discuss How to Predict the Outcome of acid-base reaction. How To Predict the Outcome…
Read More » -
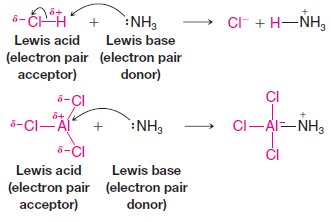
Lewis Acids and Lewis Bases
– In this subject, we will discuss the Lewis acid-base theory and Lewis Acids and Lewis Bases Lewis Acids and…
Read More » -
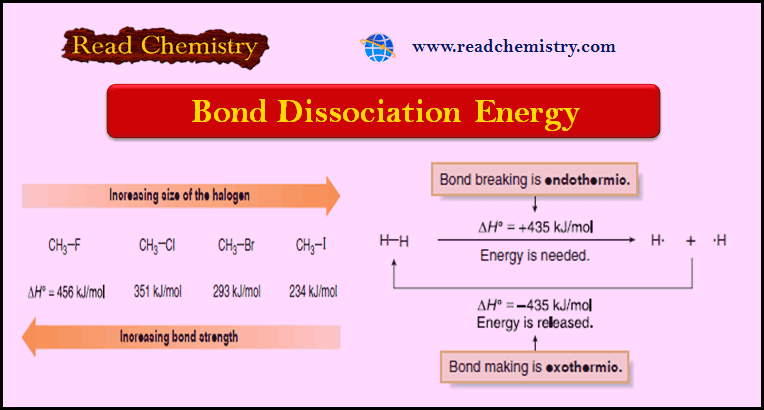
Bond Dissociation Energy: Definition, Equation, Problems
– In this subject, we will discuss the Bond Dissociation Energy: Definition, Equation, Problems Bond Dissociation Energy – Bond breaking…
Read More » -
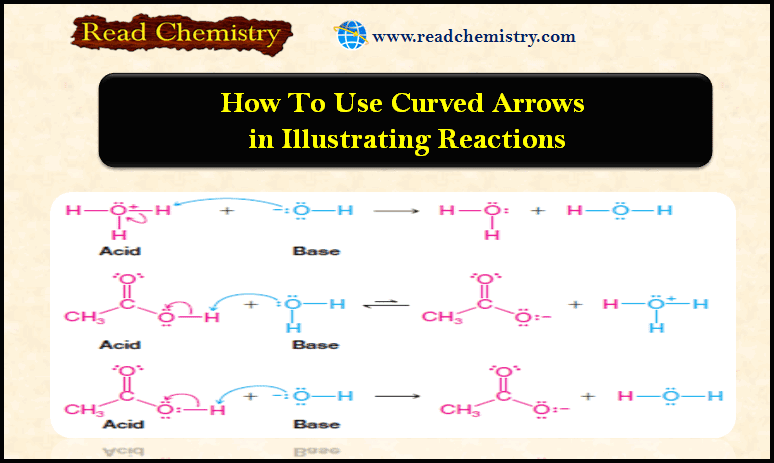
How to use Curved Arrows in illustrating Reactions
– In this subject, we will discuss How to use Curved Arrows in illustrating Reactions. How to use Curved Arrows…
Read More » -
How to interpret IR spectrum without Knowledge of the structure
– In this subject, we will discuss How to interpret an IR spectrum without any Knowledge of the structure How…
Read More » -
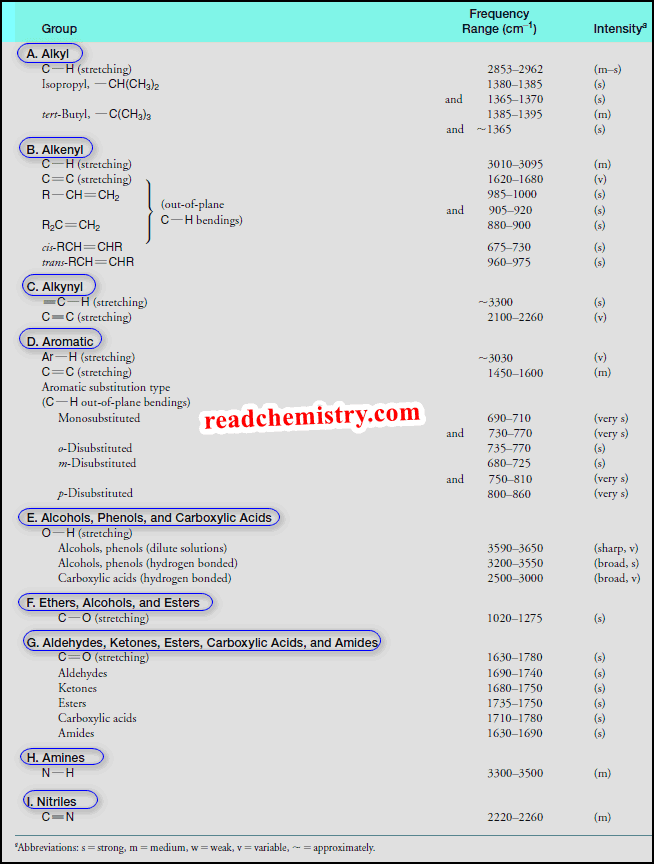
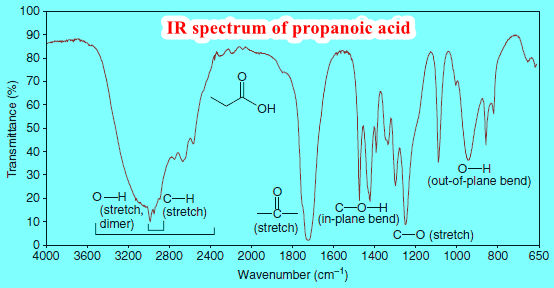
Interpreting IR Spectra
Interpreting IR Spectra – IR spectra contain a wealth of information about the structures of compounds. – We show some…
Read More » -
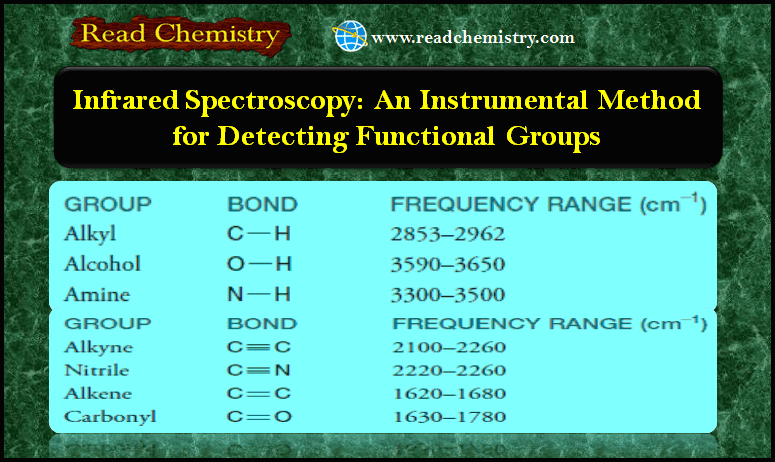
Infrared Spectroscopy: Instrumental Method for Detecting Functional Groups
– In this subject, we will discuss Infrared Spectroscopy: Instrumental Method for Detecting Functional Groups. Infrared Spectroscopy – Infrared spectroscopy…
Read More » -
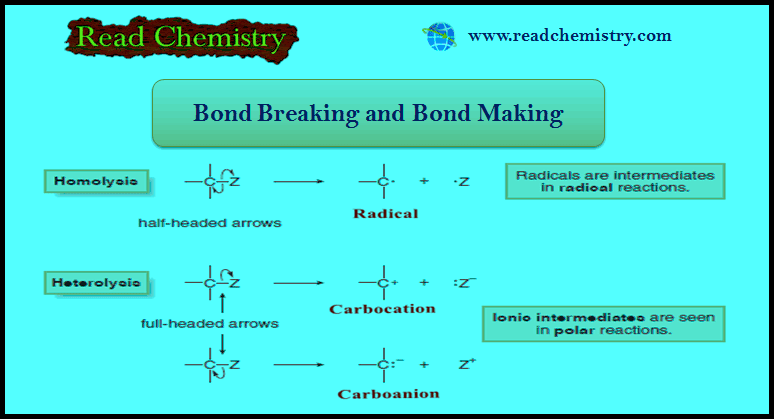
Bond Breaking and Bond Making in Organic Compounds
– In this subject, we will discuss bond Breaking and Bond Making in Organic Compounds. Bond Breaking and Bond Making …
Read More » -
Safety in the laboratory
– In this subject, we will discuss the Safety in the laboratory Safety in The Laboratory – There is necessarily…
Read More » -
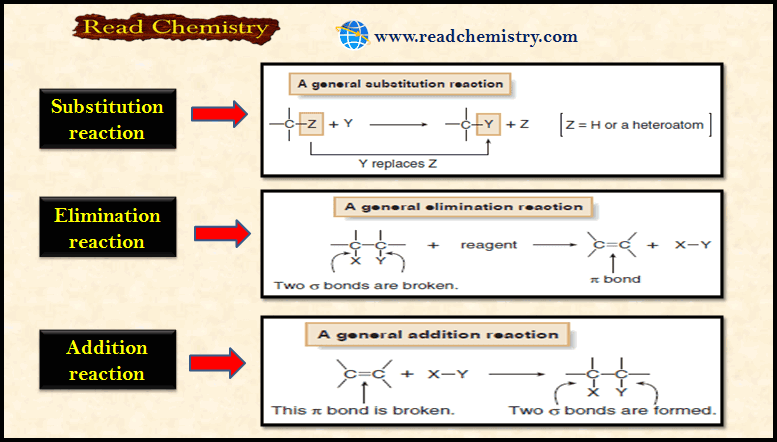
Types of Organic Reactions
– In this subject, we will discuss the general Types of Organic Reactions Types of Organic Reactions – Like other…
Read More » -
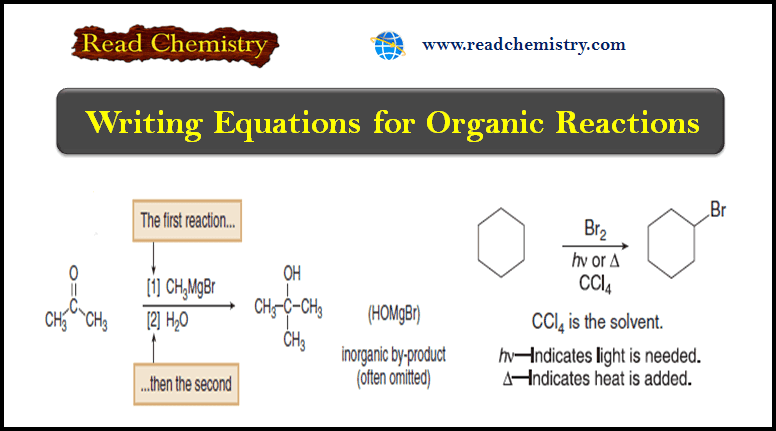
Writing Equations for Organic Reactions
– In this subject, we will discuss Writing Equations for Organic Reactions. Writing Equations for Organic Reactions (1) Like other…
Read More » -
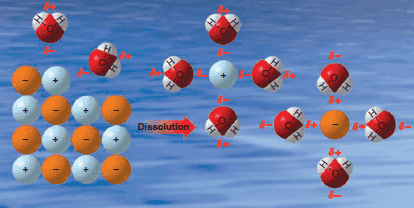
Solubility of Organic Compounds
Solubility of Organic Compounds – Intermolecular forces are of primary importance in explaining the solubility of substances. – Dissolution of…
Read More » -
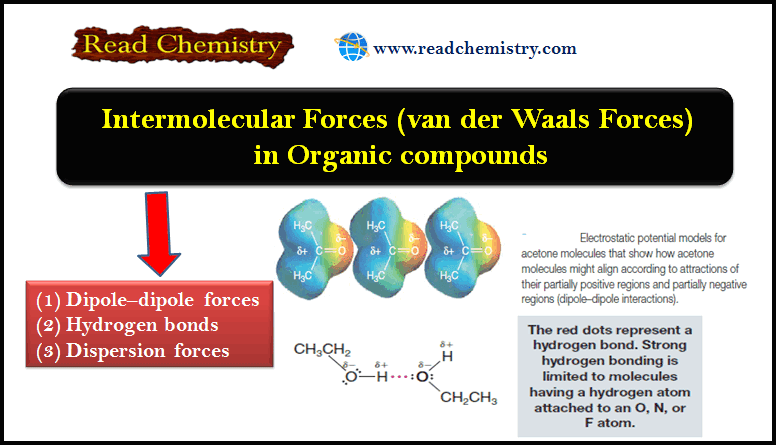
Intermolecular Forces in Organic compounds
– In this subject, we will discuss the Intermolecular Forces in Organic compounds Intermolecular Forces in Organic Compounds – The…
Read More »