Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry focuses on the structure, properties, and reactions of carbon-containing compounds. It’s essential in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and biochemistry, exploring mechanisms, functional groups, and synthesis of complex molecules.
-
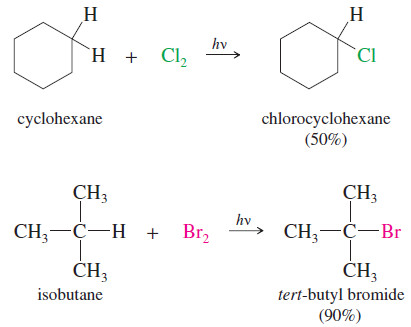
Preparation of alkyl halides
Preparation of alkyl halides – Most Methods of preparation of alkyl halides exploit the chemistry of functional groups we have…
Read More » -
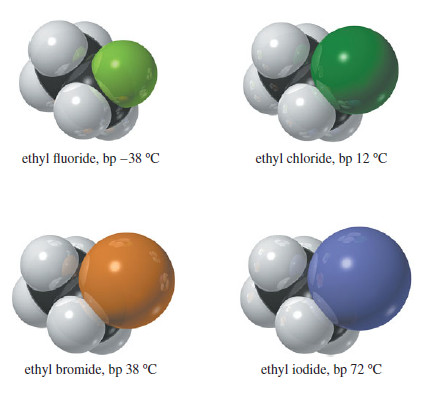
Physical Properties of Alkyl Halides
Physical Properties of Alkyl Halides will be discussed such as dipole moment, London force, Dipole–dipole attractions, densities of common alkyl…
Read More » -
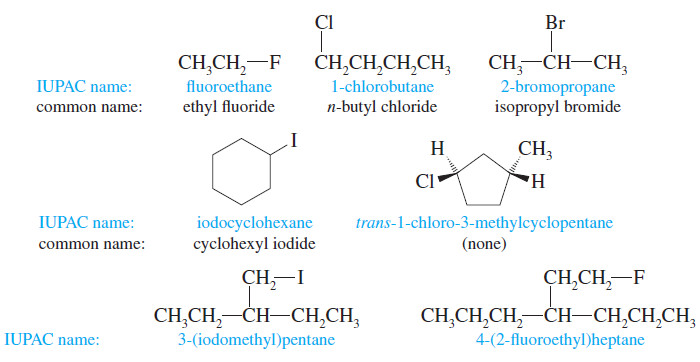
Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
Introduction to Alkyl Halides – In this subject , we consider Nomenclature of alkyl halides. – Our study of organic…
Read More » -
Essential terms in Stereochemistry
Essential terms in Stereochemistry stereochemistry – stereochemistry is The study of the three-dimensional structure of molecules. – It is the…
Read More » -
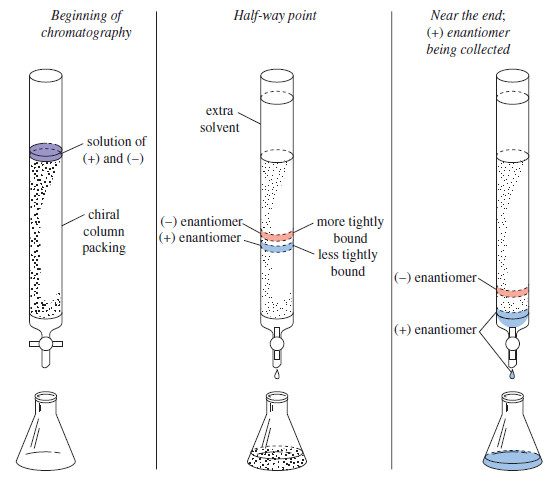
Resolution of Enantiomers
Resolution of Enantiomers – Pure enantiomers of optically active compounds are often obtained by isolation from biological sources. – Most…
Read More » -
Physical Properties of Diastereomers
What is Diastereomers? – We have defined stereoisomers as isomers whose atoms are bonded together in the same order but…
Read More » -
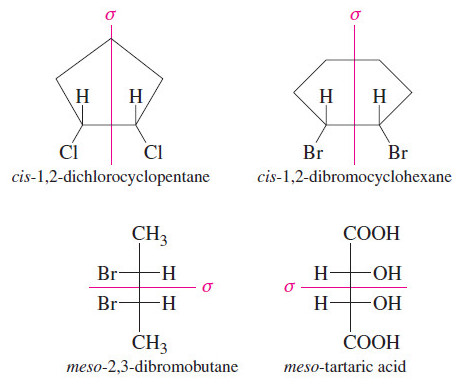
Meso Compounds
Meso Compounds – Compounds that are achiral even though they have asymmetric carbon atoms are called meso compounds. – The…
Read More » -
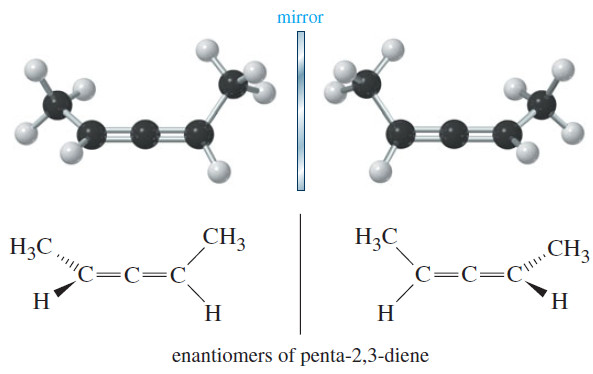
Chiral Compounds without Asymmetric Atom
Chiral Compounds without Asymmetric Atoms – Most chiral organic compounds have at least one asymmetric carbon atom. – Some compounds…
Read More » -
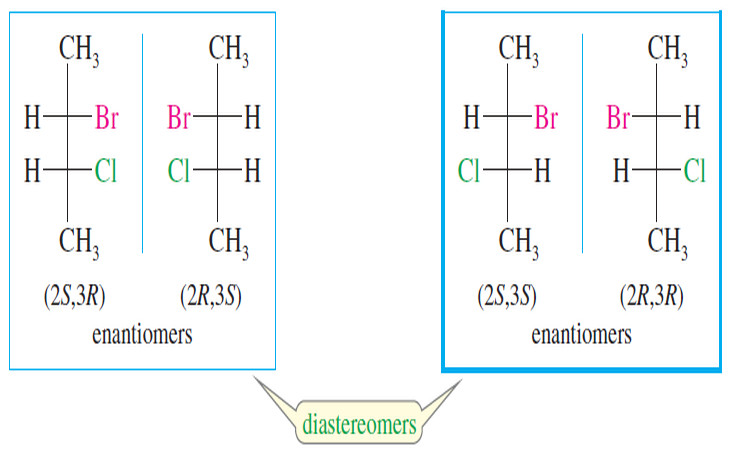
What is Diastereomers?
Diastereomers – We have defined stereoisomers as isomers whose atoms are bonded together in the same order but differ in…
Read More » -
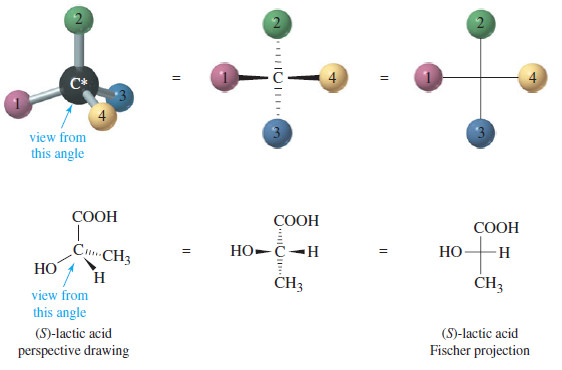
Drawing Fischer Projections
In this subject we will discuss How to draw Fischer projections Introduction to Fischer Projections – We have been using…
Read More » -
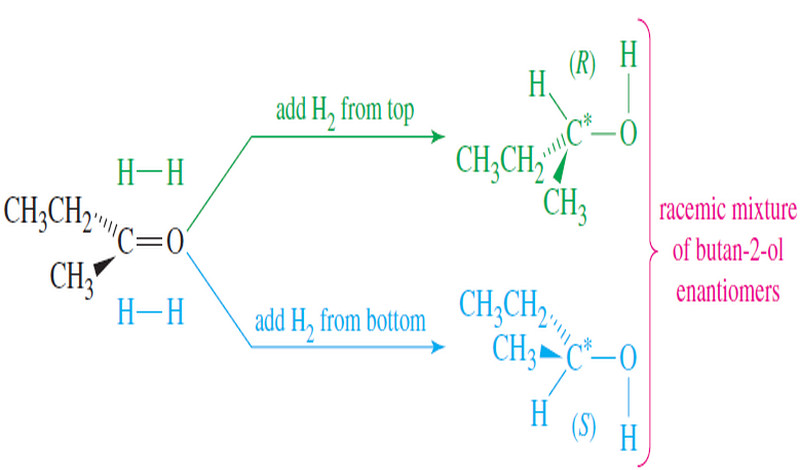
Racemic Mixtures
Racemic Mixtures – Suppose we had a mixture of equal amounts of (+)-butan-2-ol and (-)-butan-2-ol – The (+) isomer would…
Read More » -
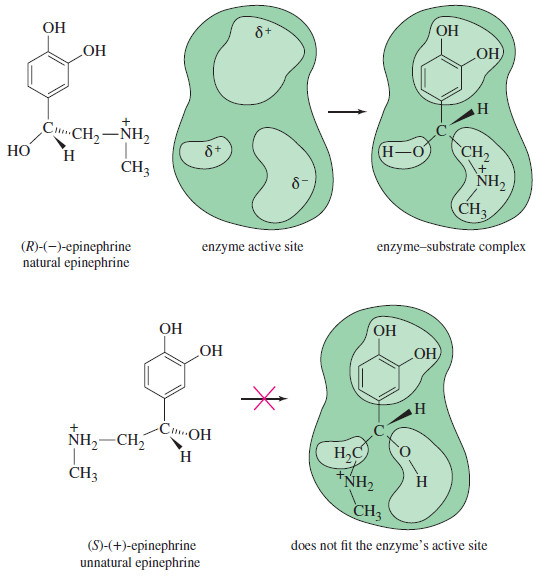
Biological Discrimination of Enantiomers
Biological Discrimination of Enantiomers – If the direction of rotation of polarized light were the only difference between enantiomers, one…
Read More » -
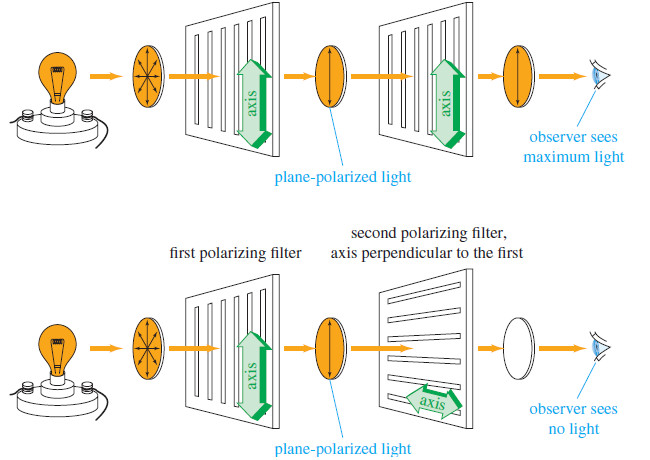
Optical Activity in Organic Compounds
– Rotation of the plane of polarized light is called optical activity, and substances that rotate the plane of polarized…
Read More » -
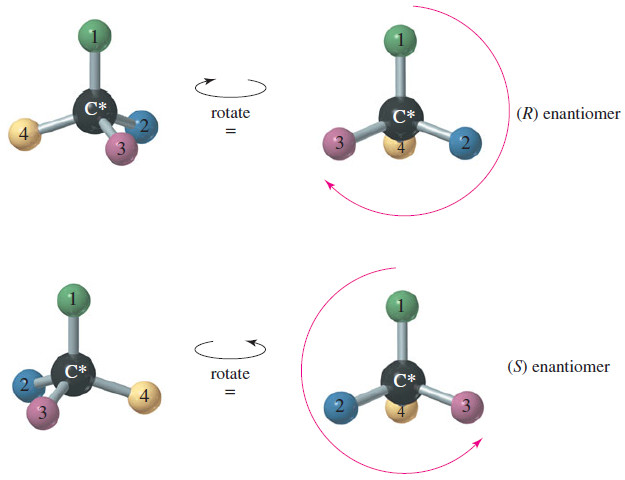
(R) and (S) of Asymmetric Carbon Atoms
(R) and (S) Nomenclature of Asymmetric Carbon Atoms – Alanine is one of the amino acids found in common proteins.…
Read More » -
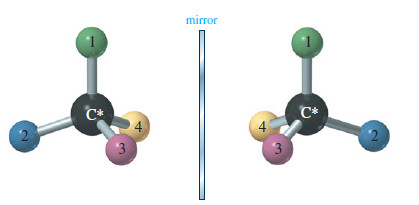
Chirality in Organic Chemistry
What is Chirality? – What is the difference between your left hand and your right hand? They look similar, yet…
Read More » -
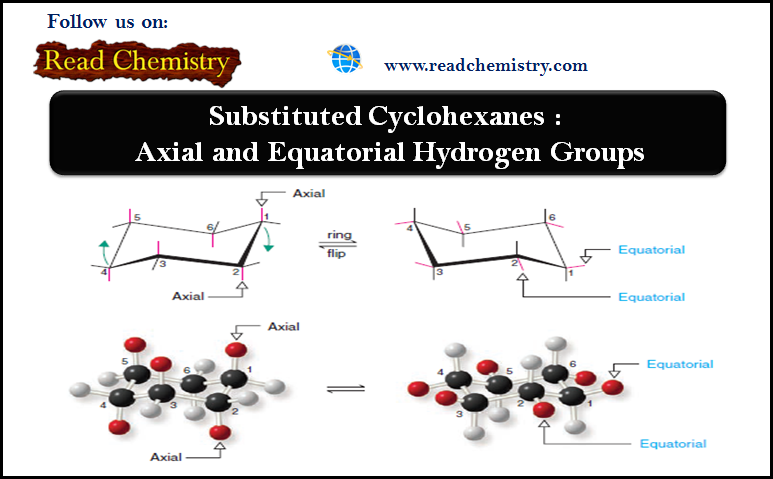
Cyclohexane: Axial and Equatorial Bonds in Cyclohexane
– In this subject, we will discuss the Substituted Cyclohexane: Axial and Equatorial Hydrogen Groups Substituted Cyclohexane: Axial and Equatorial…
Read More » -
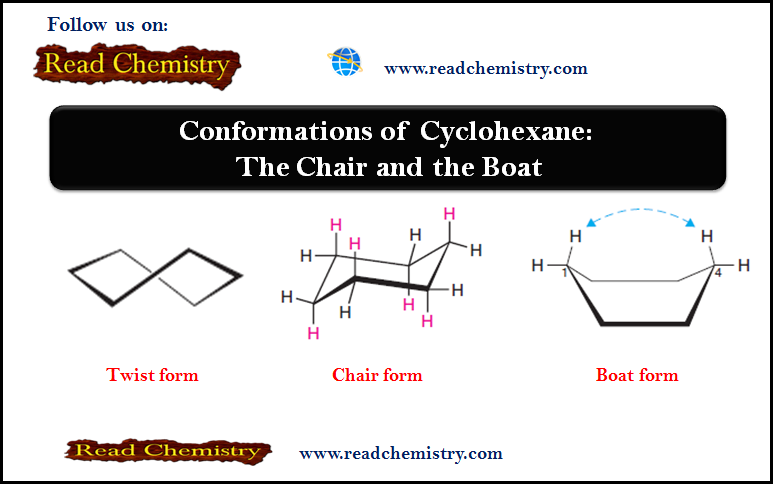
Conformations of Cyclohexane: The Chair and the Boat
– In this subject, we will discuss Conformations of Cyclohexane: The Chair and the Boat Conformations of Cyclohexane: The Chair…
Read More » -
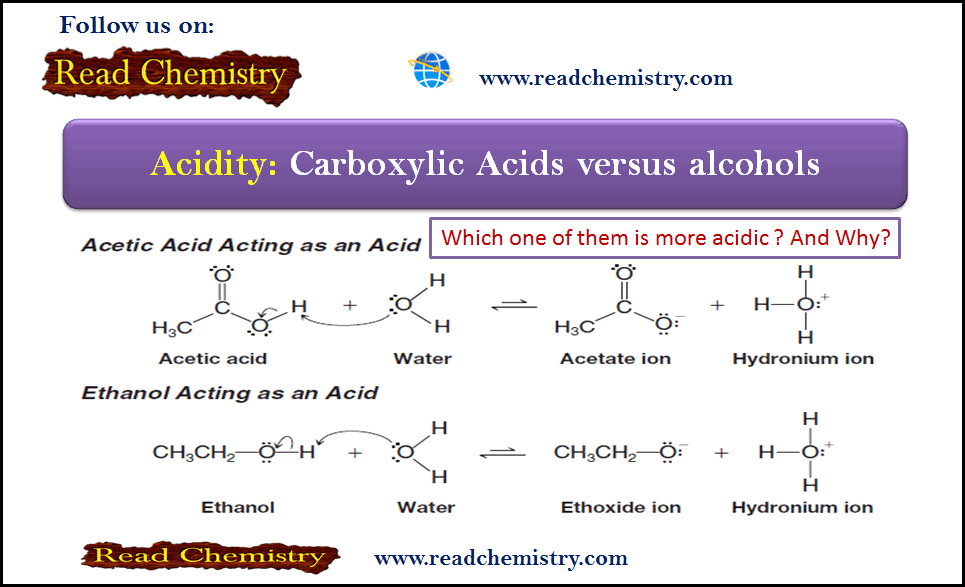
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols
– In this subject, we will discuss the Acidity Differences between Alcohols and Carboxylic Acids Acidity of Carboxylic Acids and…
Read More » -
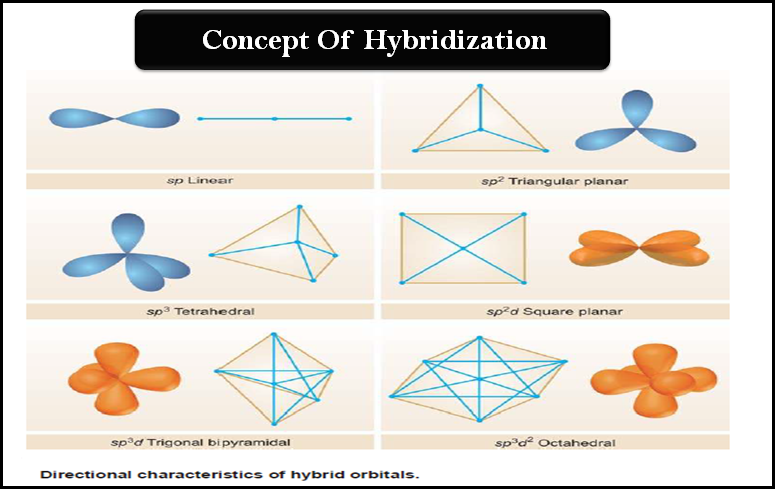
Hybridization: Definition, Types, Rules, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Hybridization: Definition, Types, Rules, and Examples – While the formation of simple…
Read More » -
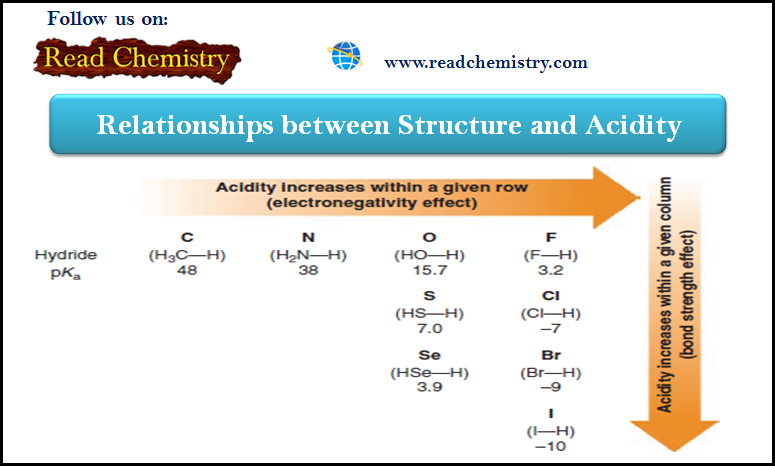
Acidity: The relationship between Structure and Acidity
– In this subject, we will discuss the Relationships between Structure and Acidity. – The strength of a Brønsted–Lowry acid…
Read More »