Physical Chemistry blends chemistry with physics, studying matter’s behavior using concepts like thermodynamics, kinetics, quantum mechanics, and spectroscopy. It explains how and why chemical reactions occur at the molecular level.
Physical Chemistry
-
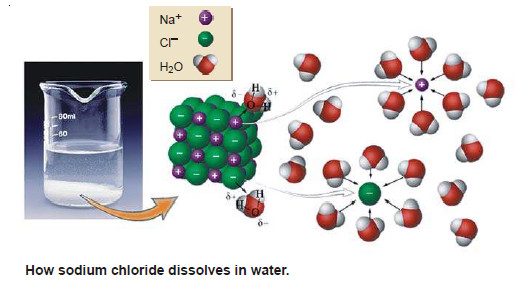
Solutions of solid substances in liquids
SOLUTIONS OF SOLIDS IN LIQUIDS – Solutions of a solid substance in a solvent are most commonly met with. –…
Read More » -
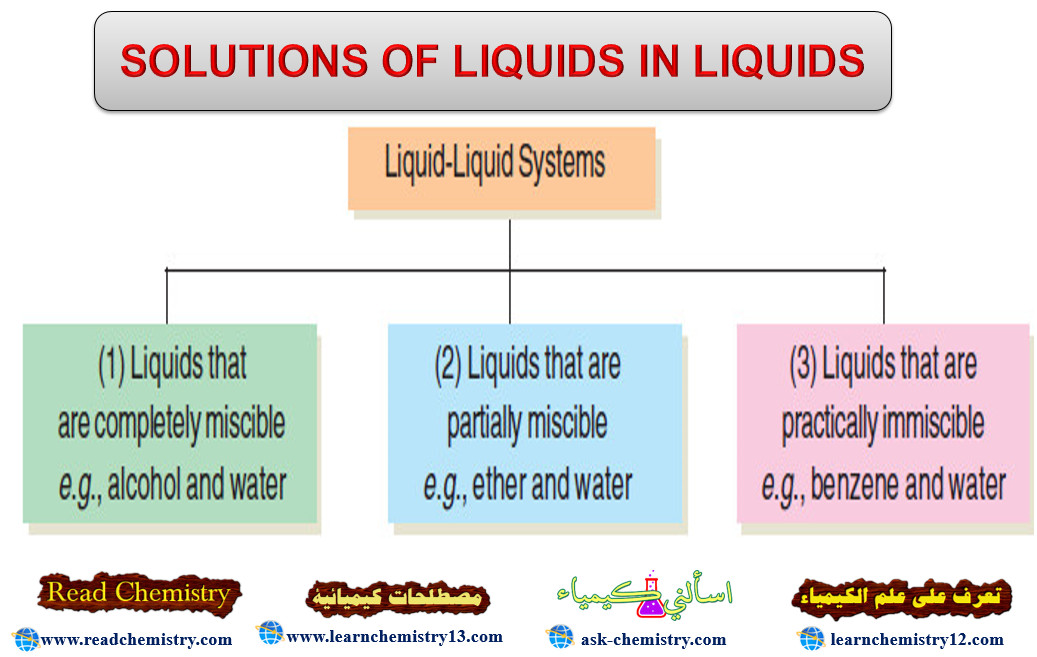
Solutions of liquids in liquids
SOLUTIONS OF LIQUIDS IN LIQUIDS – The solutions of liquids in liquids may be divided into three classes as follows:…
Read More » -
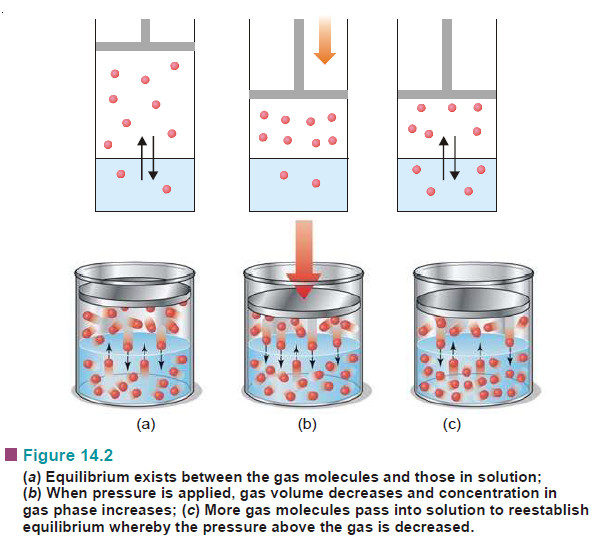
Henry’s Law – Solutions of gases in gases
The subject of Solutions of gases in gases – Henry’s Law will be discused Types of Solutions – The common…
Read More » -
Ways of Expressing Concentration
Concentration of A Solution – The concentration of a solution is defined as : the amount of solute present in…
Read More » -
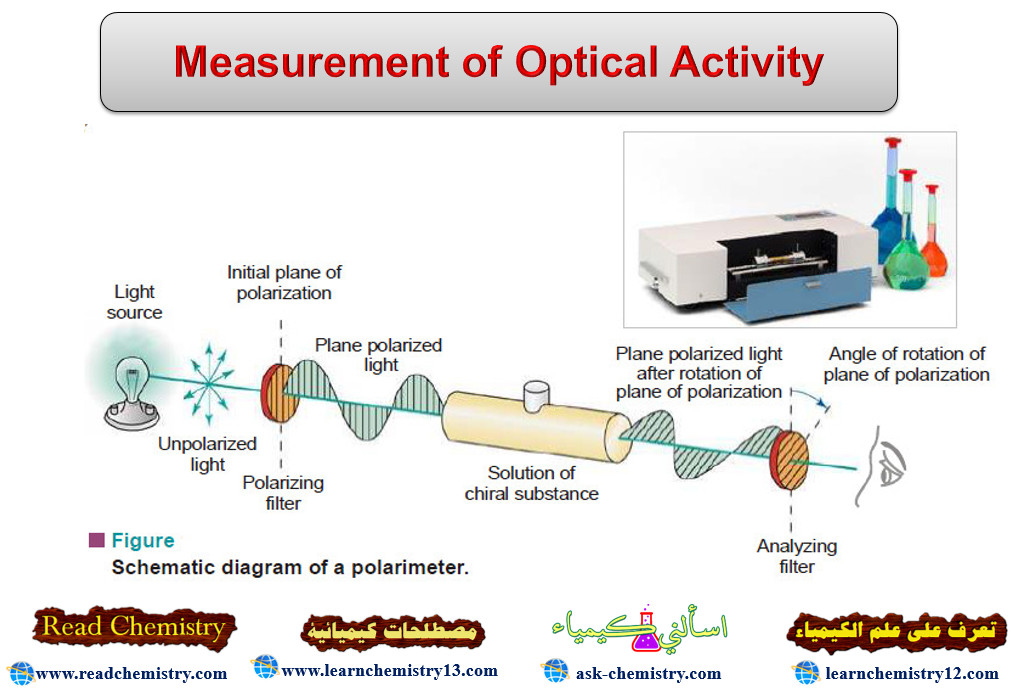
Measurement of Optical Activity
Optical Activity – Optical activity is one of imortant physcial properties of liqiuds – A beam of ordinary light consists…
Read More » -
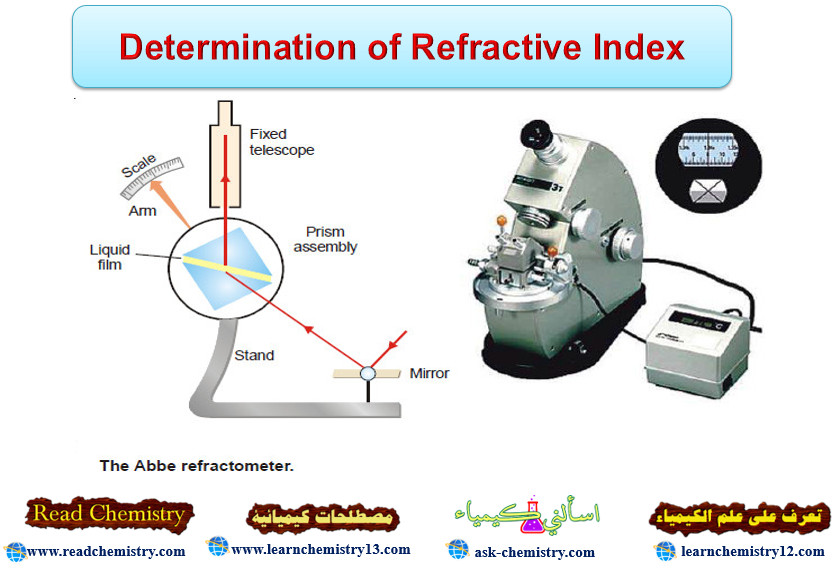
Determination of Refractive Index
Refractive Index – The refractive index (n) of a substance is defined as the ratio of the velocity of light…
Read More » -
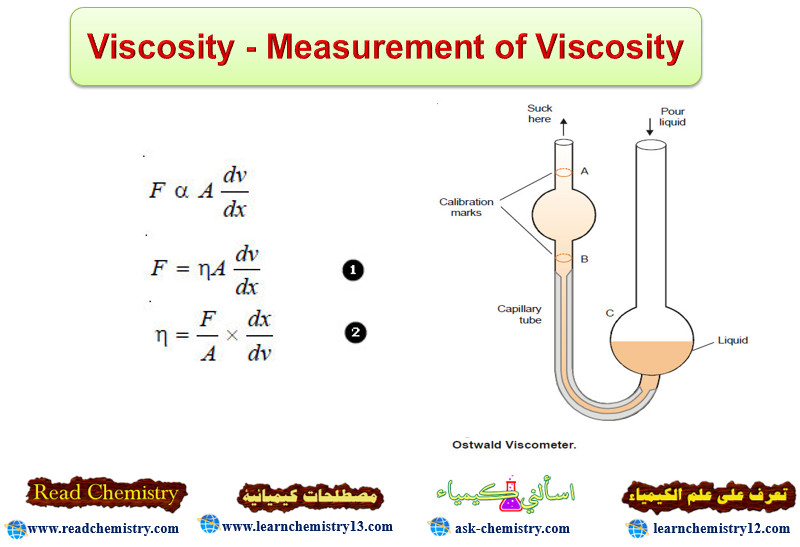
Viscosity – Measurement of Viscosity
Viscosity – Viscosity is the resistance of a liquid to flow. – A liquid may be considered to be consisting…
Read More » -
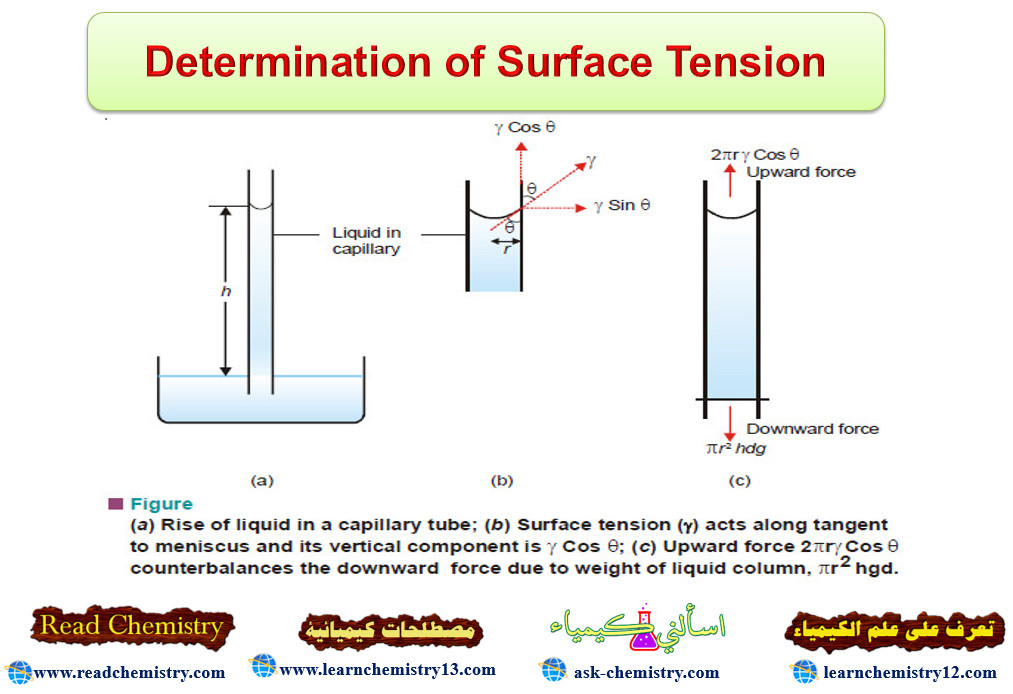
Determination of Surface Tension
Surface Tension – Surface Tension property of liquids arises from the intermolecular forces of attraction. – A molecule in the…
Read More » -
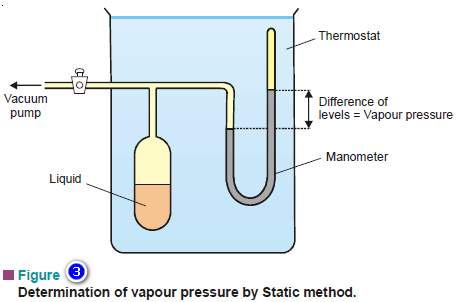
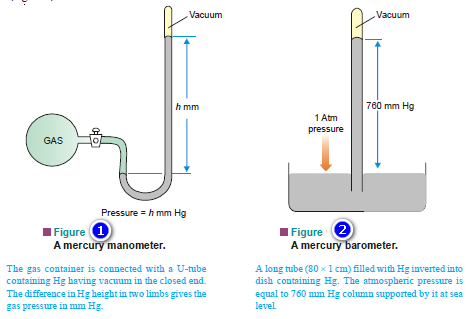
Vapour Pressure , Factors affecting on Vapour Pressure
– The vapour pressure of a liquid is defined as the pressure exerted by the vapour in equilibrium with the…
Read More » -
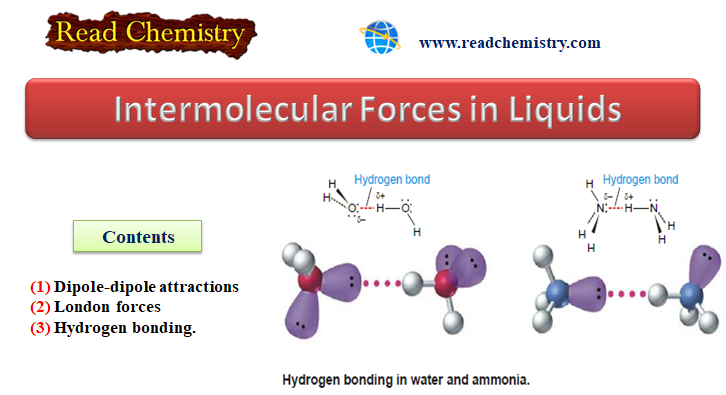
Intermolecular Forces in Liquids
Intermolecular Forces in Liquids – Intermolecular forces in liquids are collectively called van der Waals forces. – These forces are…
Read More » -
Gases – General Characteristics of gases
States of the matter – All matter exists in three states: gases, liquids and solids. – A molecular-level representation of…
Read More » -
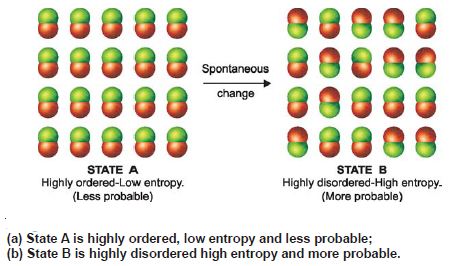
Spontaneous Processes – Second Law of Thermodynamics
Spontaneous Processes – A process that proceeds of its own accord, without any outside assistance, is termed a spontaneous or…
Read More » -
MCQ on Chapter Thermochemistry ΔH, ΔE
1. For exothermic reactions, ΔH is _______ while for endothermic reactions it is _______. (a) positive, negative (b) positive, positive…
Read More » -
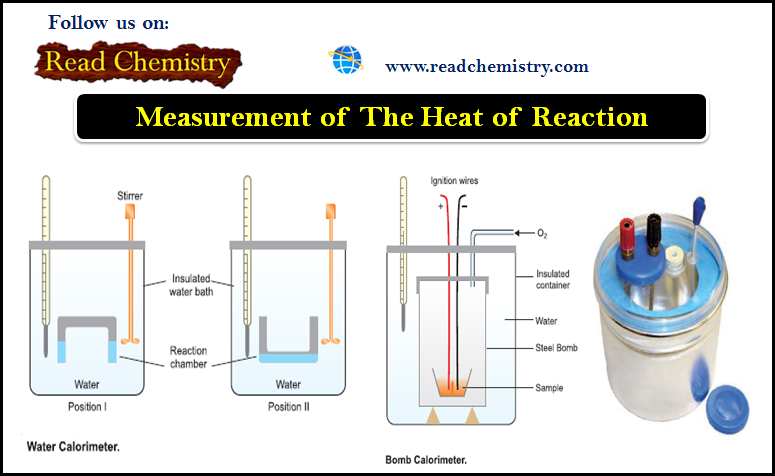
Measurement of The Heat of Reaction
Measurement of The Heat of Reaction – The experimental measurement of the heat of reaction or enthalpy change is known…
Read More » -
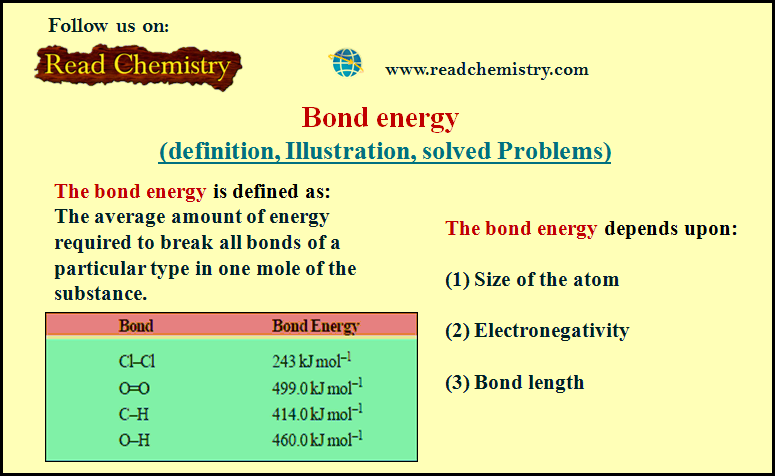
Bond energy (definition, Illustration, solved Problems)
Bond energy – When a bond between two atoms is formed, there is a release of energy. – The same…
Read More » -
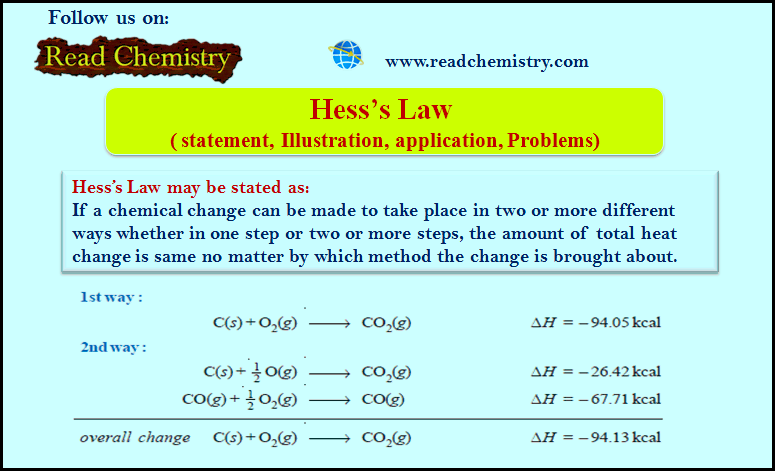
Hess’s Law ( statement, Illustration, application, Problems)
– Hess’s Law may be stated as: (If a chemical change can be made to take place in two or…
Read More » -
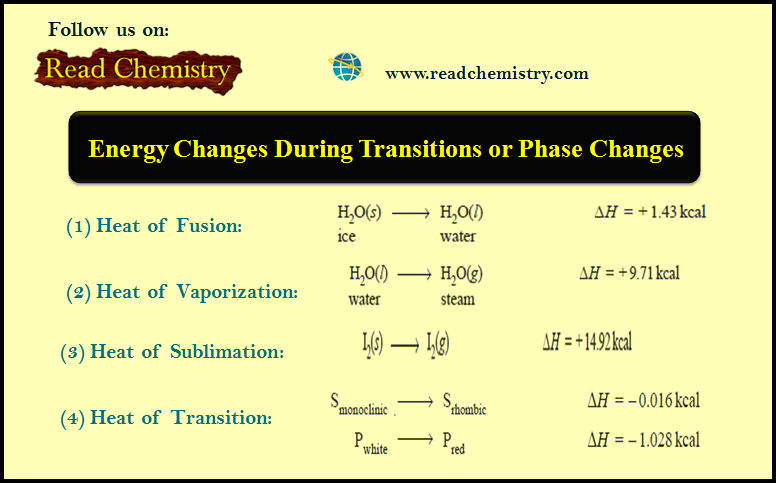
Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes
– In this subject, we will discuss Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes. Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase…
Read More » -
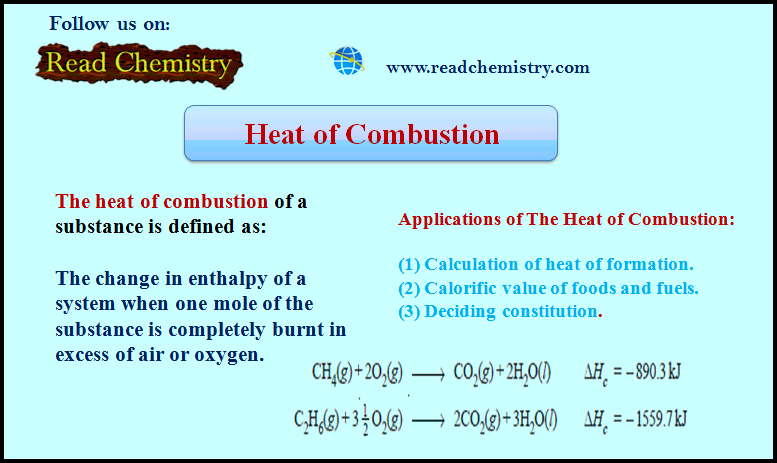
Heat of Combustion (Definition, Applications, Solved Problems)
Heat of Combustion – The heat of combustion of a substance is defined as The change in enthalpy of…
Read More » -
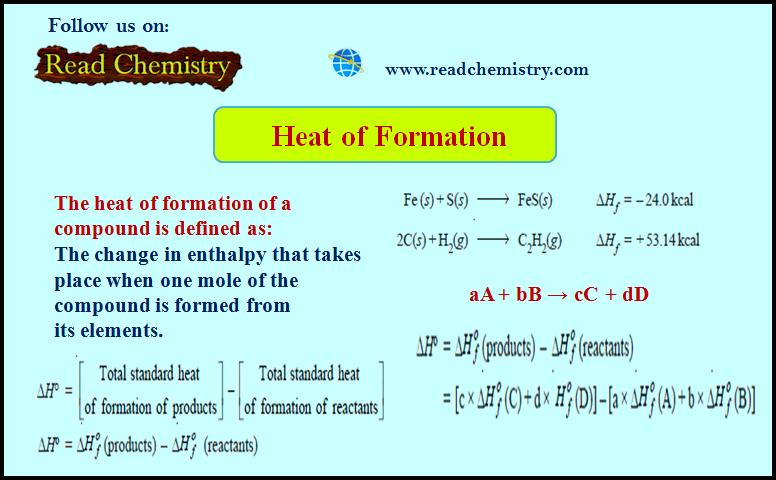
Heat of Formation (Definition, Applications, Solved Problems)
Heat of Formation – The heat of formation of a compound is defined as The change in enthalpy that takes…
Read More » -
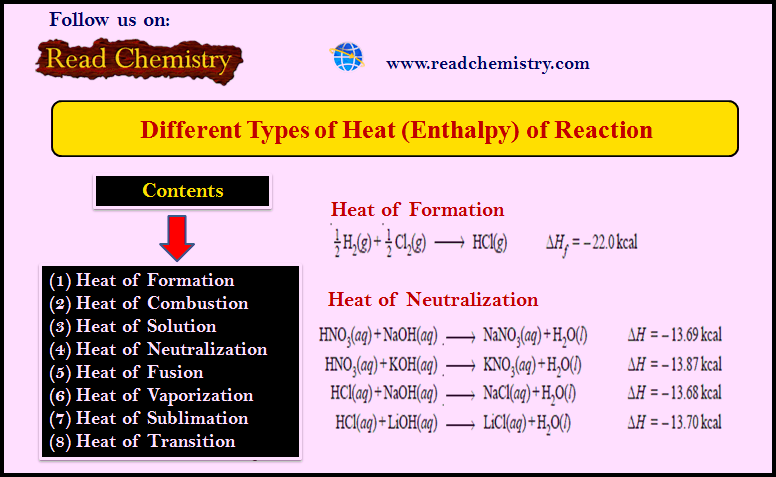
Different Types of Heat of Reaction (Enthalpy)
– The heat of reaction or enthalpy changes accompanying chemical reactions are expressed in different ways, depending on the nature…
Read More »