Physical Chemistry blends chemistry with physics, studying matter’s behavior using concepts like thermodynamics, kinetics, quantum mechanics, and spectroscopy. It explains how and why chemical reactions occur at the molecular level.
Physical Chemistry
-
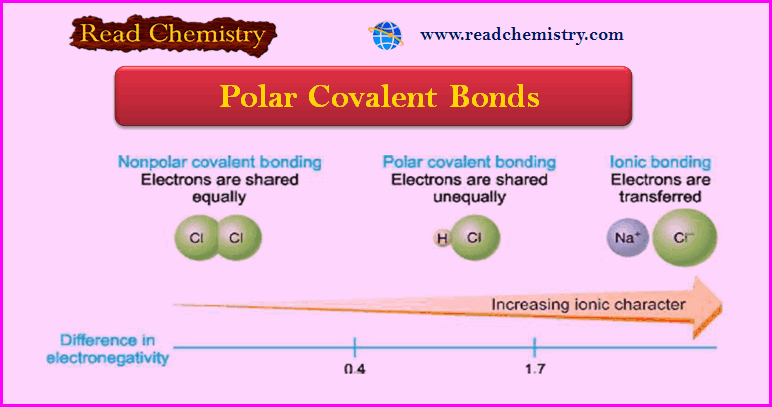
Polar Covalent Bond: Definition, Properties, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Polar Covalent Bond: Definition, Properties, Examples Polar Covalent Bonds – In the…
Read More » -
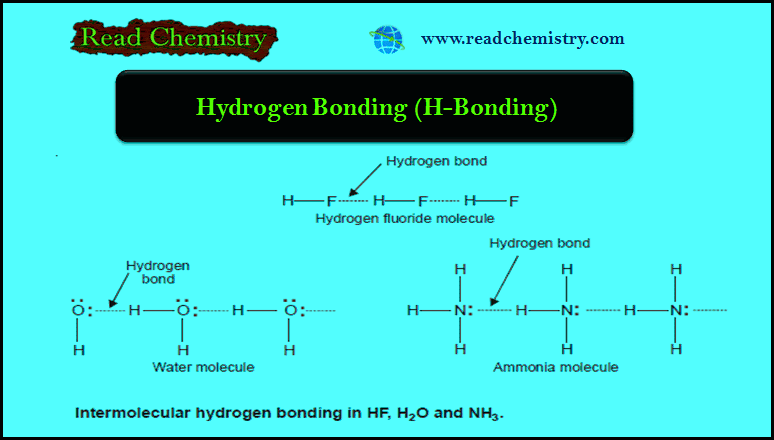
Hydrogen Bonding: Definition, types, Examples, Characteristics
– In this subject, we will discuss the hydrogen Bonding (Definition, types, Examples, Characteristics) Hydrogen Bonding (H-Bonding) – When hydrogen (H)…
Read More » -
Coordinate Bond: Definition, Formation, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Coordinate Bond: (Definition, Formation, Examples) Coordinate bond – In a normal covalent…
Read More » -
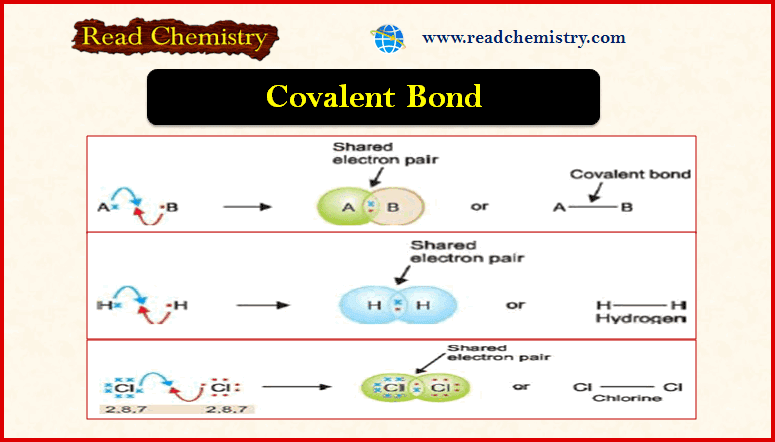
Covalent Bond: Definition, Examples, Types, Properties
– In this subject, we will discuss the Covalent Bond (Definition, Examples, Types, Properties) Covalent Bond – The electron transfer…
Read More » -
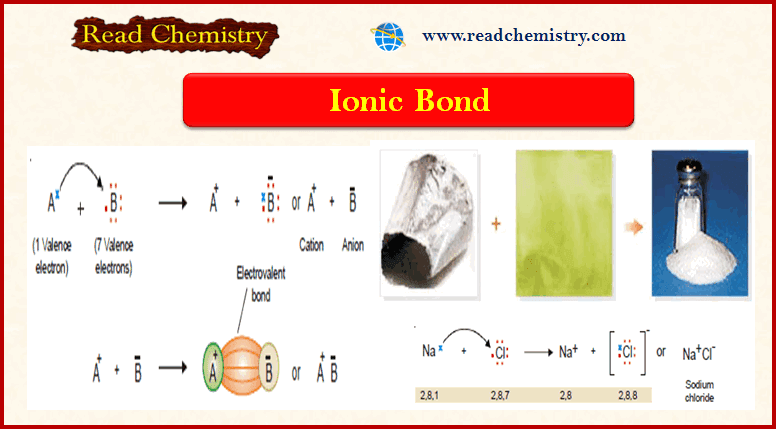
Ionic Bond: Definition, Examples, Types, Properties
– In this subject, we will discuss the Ionic Bond (Definition, Examples, Types, Properties) Ionic Bond – This type…
Read More » -
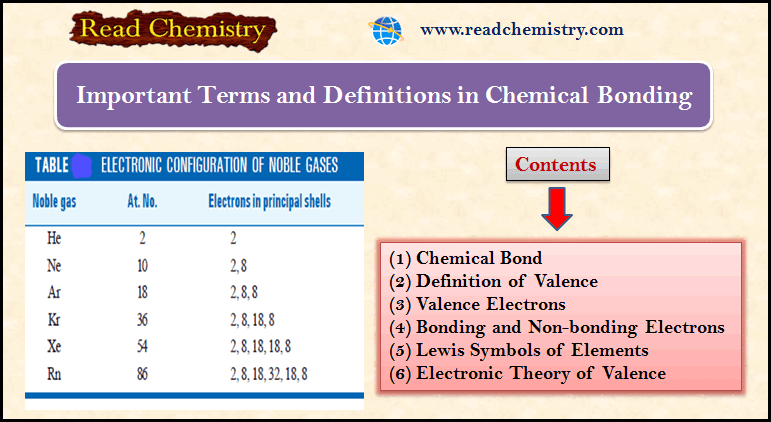
Chemical Bonding: Important terms and Definitions
– In this subject, we will discuss the important Terms and Definitions of Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bond – Molecules of…
Read More » -
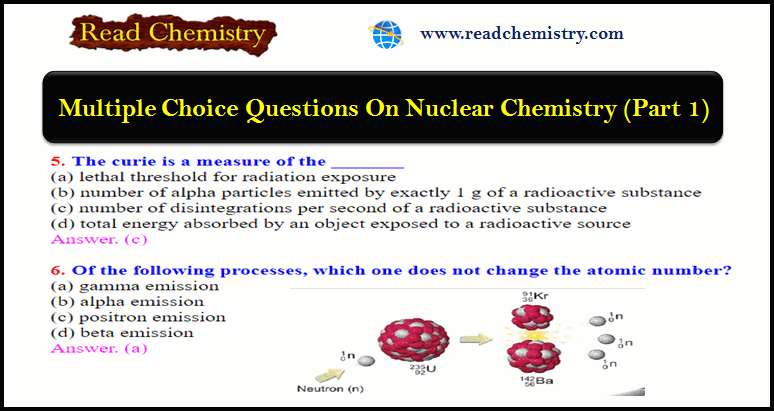
Nuclear Chemistry Quiz: Questions and Answers
Nuclear Chemistry Quiz – In this subject, you will find 40 questions and answers MCQ on Nuclear Chemistry 1. Which…
Read More » -
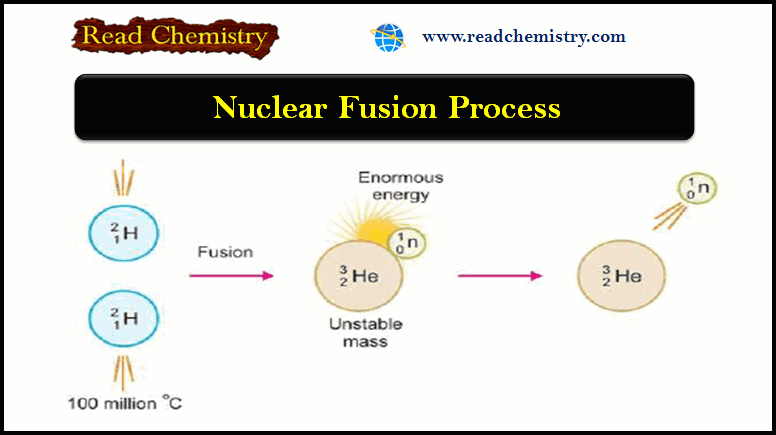
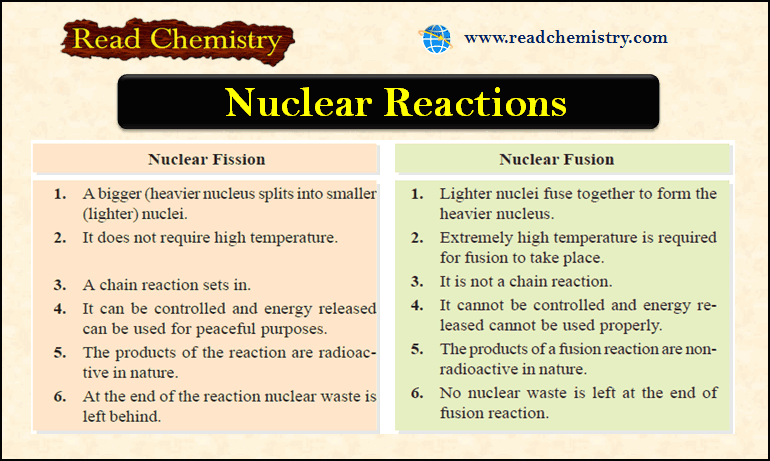
Nuclear Fusion: Definition, Occurrence, Examples, Applications
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Fusion Process ( Definition, Occurrence, Examples, Applications) Nuclear Fusion Process –…
Read More » -
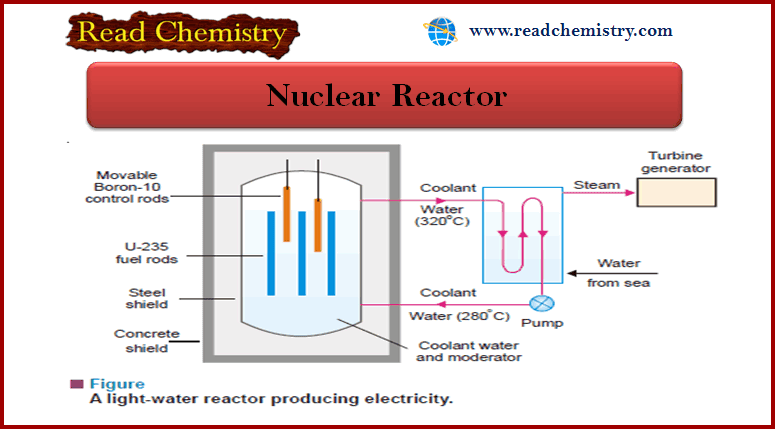
Nuclear Reactor: Definition, Components
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Reactor (Definition, Components) Nuclear Reactor – It has been possible to…
Read More » -
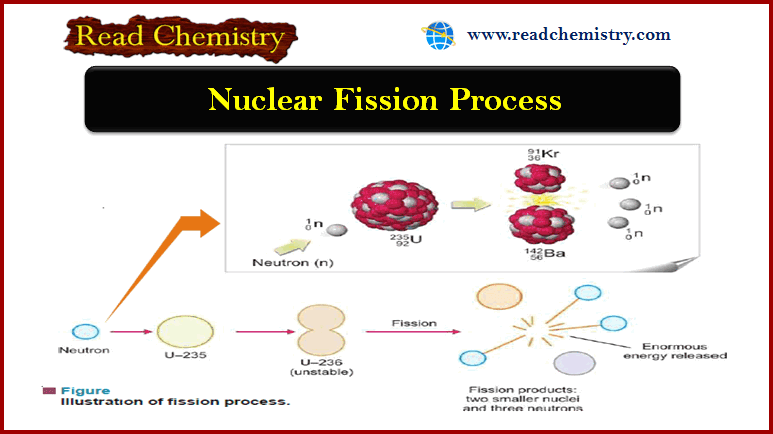
Nuclear Fission: Definition, Properties, Examples, Applications
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Fission (Definition, Properties, Examples, Applications) Nuclear Fission Process – In…
Read More » -
Concise Physical Chemistry book by Donald W.Rogers
– In this subject, we will discuss the free download of Concise Physical Chemistry book by Donald W.Rogers The Preface…
Read More » -
Free Download Electrochemistry book (Principles and Applications)
– In this subject, we will discuss Free Download Electrochemistry book (Principles, Methods, and Applications) The Preface of Electrochemistry book…
Read More » -
Fundamentals of Chemistry book by Romain Elsair – Free download
– In this subject, we will discuss the free download of Fundamentals of Chemistry book by Romain Elsair. Aim of…
Read More » -
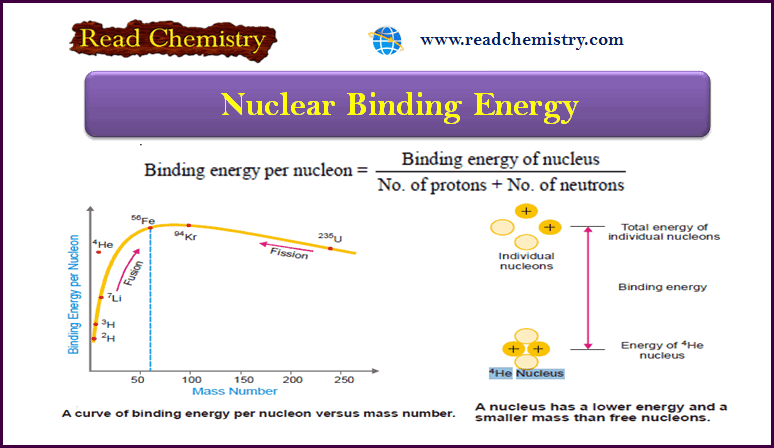
Nuclear Binding Energy: Definition, Formula, Explanation
– In this subject, we will discuss Nuclear Binding Energy: (Definition, Formula, Explanation) Nuclear Binding Energy – The atomic nucleus…
Read More » -
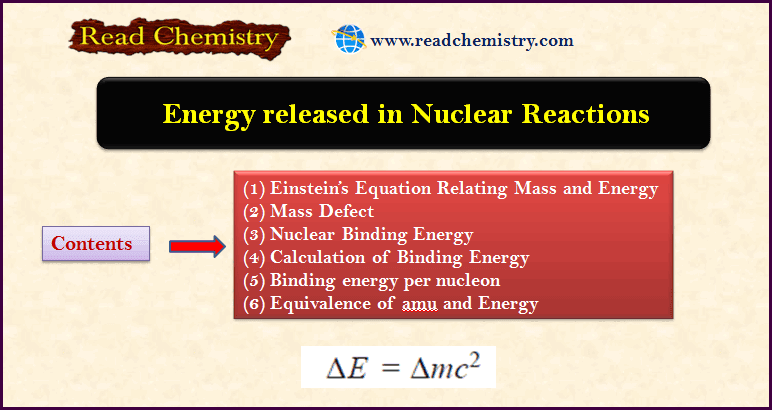
Energy released in Nuclear Reactions: Nuclear Binding Energy
– In this subject, we will discuss the energy released in Nuclear Reactions: Nuclear Binding Energy Einstein’s Equation Relating Mass and…
Read More » -
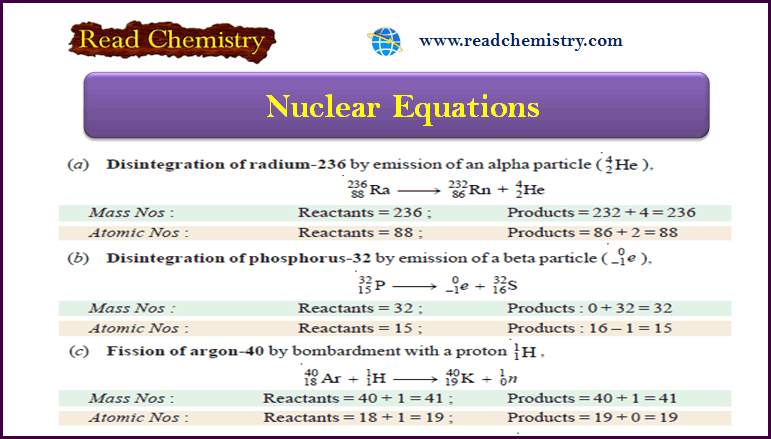
Nuclear Equations: Balancing, Rules, Practice
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Equations: Balancing, Rules, Practice Nuclear Equations – Similar to a chemical…
Read More » -
Nuclear Reaction: Definition, Types, Examples, Equations
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Reaction: Definition, Types, Examples, and Equations. Nuclear Reaction – In a…
Read More » -
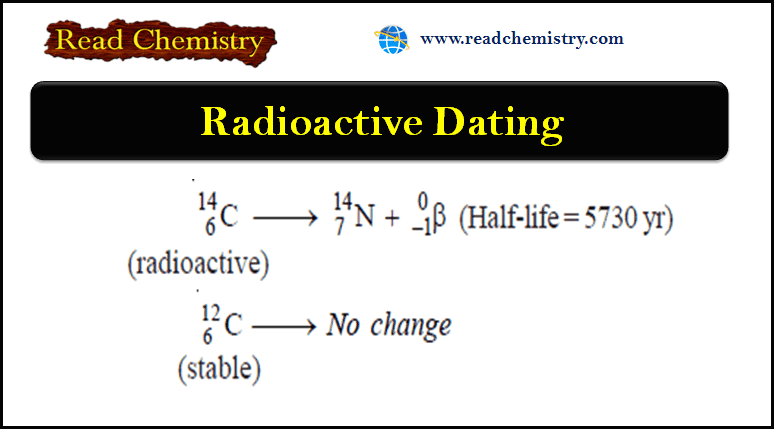
Radioactive Dating: Definition, Formula, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Radioactive Dating: Definition, Formula, Examples Radioactivity – Several elements such as uranium…
Read More » -
Half-life time and radioactive decay: Equations, Calculations
– In this subject, we will discuss the Half-life time and radioactive decay: Equations, Calculations Rate of radioactive decay –…
Read More » -
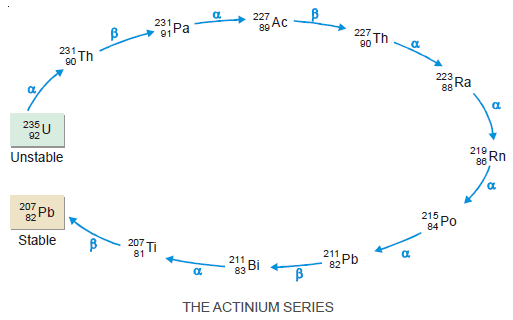
Radioactive Disintegration Series: Definition, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Radioactive Disintegration Series: Definition, Examples Radioactivity – Several elements such as uranium…
Read More »