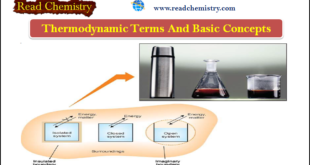
– Thermodynamic Processes involve the change of conditions (temperature, pressure, and volume). Thermodynamic Processes – When a thermodynamic system changes from one state to another, the operation is called a Process. – Thermodynamic Processes involve the change of conditions (temperature, pressure, and volume). – The various types of thermodynamic processes …
Read More »Thermodynamics – Basic terms and concepts in Thermodynamics
What is Thermodynamics? – Thermodynamics is The study of the flow of heat or any other form of energy into or out of a system as it undergoes a physical or chemical transformation. – In studying and evaluating the flow of energy into or out of a system, it will …
Read More »Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules
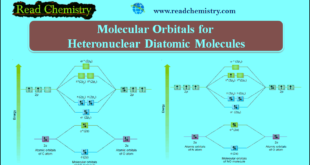
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties of some of The homonuclear diatomic molecules. but in this subject, we will talk about Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules (MO Theory) – When two different atoms are bonded …
Read More »Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules
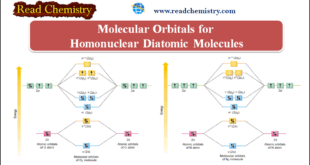
Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties of some of The Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules. but in this subject, we will talk about Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules (MO Theory) – After having discussed the basic principles …
Read More »MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory – In this subject, you will find 46 questions and answers MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory 1. When a chemical bond between two atoms is formed, the potential energy of the system_______ (a) decreases (b) increases (c) remains the same (d) …
Read More »Molecular Orbital Theory
Molecular Orbital Theory – The molecular orbital theory proposed by Hund and Mulliken in 1932 explains the formation of a covalent bond in a better way. – According to molecular orbital theory all atomic orbitals of the atoms participating in molecule formation get disturbed when the concerned nuclei approach nearer. …
Read More »MCQ on Chapter: structure of atom – wave mechanical approach
MCQ on the structure of the atom – In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on Chapter structure of atom – wave mechanical approach 1. The number of unpaired electrons in oxygen atom is_______ (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 Answer. (b) 2. The …
Read More »Electronegativity and Electron Affinity
– In this subject, we will discuss the difference Between Electronegativity and Electron Affinity Electron Affinity – A neutral atom can accept an electron to form a negative ion. In this process, in general, energy is released. – The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the amount of energy released …
Read More »Ionization Energy (Definition – Trends – Measurement)
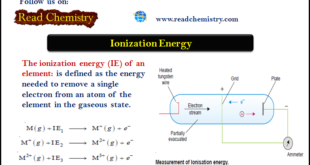
– The ionization energy (IE) of an element is defined as the energy needed to remove a single electron from an atom of the element in the gaseous state. Ionization Energy – The process of removing an electron from an isolated atom to form a positive ion is called ionization. …
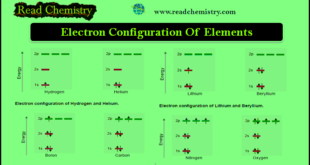
Read More »Electron Configuration Of Elements
– In this subject, we will discuss the rules of Electron Configuration Of Elements Electron Configuration Of Elements – We have seen before that to define completely the state of an atom it is obligatory to refer to all the four quantum numbers (n, l, m, and s) of every …
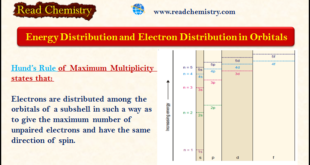
Read More »Distribution of Electrons in Orbitals
– In this subject, we will discuss the Distribution of Electrons in Orbitals according to Hund’s Rule. Energy Distribution and Orbitals – In our earlier discussion, we have seen that the energy of an electron is determined by the first two quantum numbers (n) and (l), while the other two …
Read More »Pauli Exclusion Principle
– The Pauli exclusion principle is of immense value in telling the maximum number of electrons accommodated in any shell. Quantum Numbers and the Energy of an Orbital – The nature of an electron, its position, and energy, is fully implied only by mentioning the values of four quantum numbers ascribed …
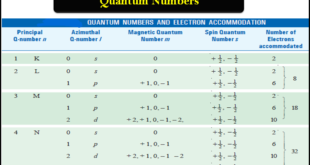
Read More »Quantum Numbers (Principal, Azimuthal, Magnetic and Spin)
Quantum Numbers – Bohr’s electronic energy shells or levels, designated as Principal Quantum Numbers (n), could hardly explain the hydrogen spectrum adequately. – Spectra of other elements that are quite complex, also remained unexplained by this concept. – Many single lines of the spectra are found to consist of a …
Read More »Schrödinger Wave Equation
Schrödinger Wave Equation – In order to provide sense and meaning to the probability approach, Schrödinger derived an equation known after his name as the Schrödinger Wave Equation. – Calculation of the probability of finding the electron at various points in an atom was the main problem before Schrödinger. – …
Read More »Heisenberg’s uncertainty Principle
– Heisenberg’s uncertainty Principle: As it is impossible to know the position and the velocity of any one electron on account of its small size, the best we can do is to speak of the probability or relative chance of finding an electron with a probable velocity. Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle …
Read More »MCQ: Structure of atom – Classical Mechanics
1. In the spectrum of hydrogen atom, the series which falls in ultraviolet region is_______ (a) Lyman series (b) Balmer series (c) Paschen series (d) Brackett series Answer. (a) 2. The e/m value for the particles constituting cathode rays is the same regardless of_______ (a) the gas present in cathode …
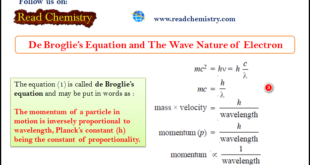
Read More »De Broglie Equation – The Wave Nature of Electron
De Broglie Equation – de Broglie had arrived at his hypothesis (de Broglie equation) with the help of Planck’s Quantum Theory and Einstein’s Theory of Relativity. – He derived a relationship between the magnitude of the wavelength associated with the mass (m) of a moving body and its velocity. – …
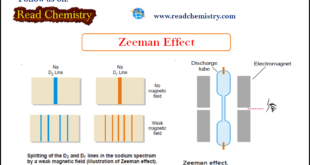
Read More »Zeeman Effect
Zeeman Effect – In 1896 Zeeman discovered that spectral lines are split up into components when the source emitting lines is placed in a strong magnetic field. It is called the Zeeman effect after the name of the discoverer. – The apparatus used to observe the Zeeman effect is shown …
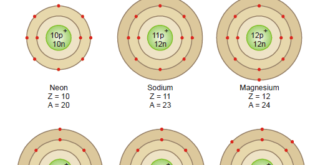
Read More »Bohr-Bury Scheme – Electron arrangement in the orbits
– The Bohr-Bury scheme considers that the maximum number of electrons that each orbit can contain is 2 × n2, where n is the number of orbits. – Having known that planetary electrons numerically equal to the atomic number are revolving about the atomic nucleus in closed orbits, the question …
Read More »Bohr Model of atom – Bohr Theory
– Bohr theory was based on Planck’s quantum theory and was built on some postulates. – Rutherford’s nuclear model simply stated that atom had a nucleus and the negative electrons were present outside the nucleus. – It did not say anything as to how and where those electrons were arranged. …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry