Alkanes: Definition, Formula, Structure, List, Examples
What is Alkanes?
– Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons; that is, they contain only carbon-carbon single bonds.
– In this context, saturated means that each carbon has the maximum number of hydrogens bonded to it.
– We often refer to alkanes as aliphatic hydrocarbons because the physical properties of the higher members of this class resemble those of the long carbon-chain molecules we find in animal fats and plant oils (Greek: aleiphar, fat, or oil).
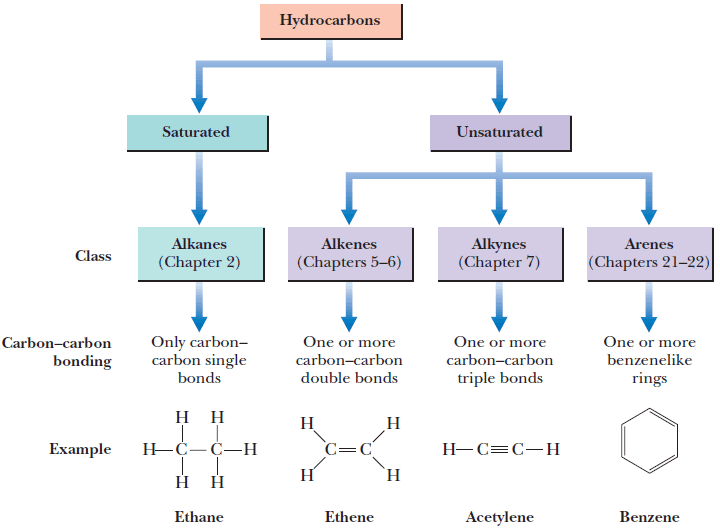
Classification of Hydrocarbon
– A hydrocarbon that contains one or more carbon-carbon double bond, triple bond, or benzene ring is classified as an unsaturated hydrocarbon.
– The figure shows the Classification of Hydrocarbon
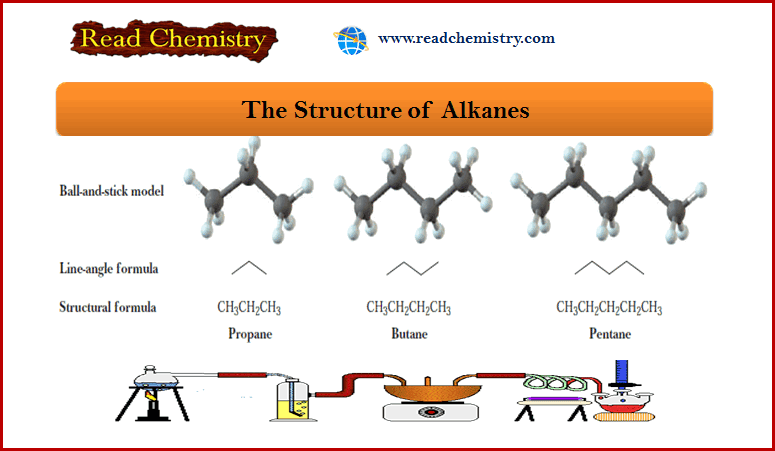
The Structure of Alkanes
– Methane (CH4) and ethane (C2H6) are the first two members of the alkane family.
– The figure shows Lewis structures and molecular models for Methane and Ethane.
– The shape of methane is tetrahedral and all H-C-H bond angles are 109.5°.
– Each carbon atom in ethane is also tetrahedral, and all bond angles are approximately 109.5°.
– Although the three-dimensional shapes of larger alkanes are more complex than those of methane and ethane, the four bonds about each carbon are still arranged in a tetrahedral manner, and all bond angles are approximately 109.5°.
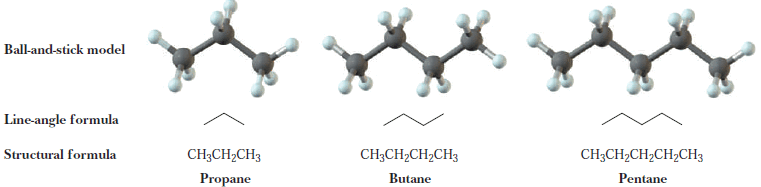
– The next three alkanes are propane, butane, and pentane.
– In the following representations, these hydrocarbons are drawn first as condensed structural formulas that show all carbons and hydrogens. They are also drawn in an even more abbreviated form called a line-angle formula.
– In a line-angle formula, each vertex and line ending represents a carbon atom.
– Although we do not show hydrogen atoms in line-angle formulas, we assume that they are there in sufficient numbers to give each carbon four bonds.
Structural formulas for Alkanes
– We can write structural formulas for alkanes in still another abbreviated form.
– The structural formula of pentane, for example, contains three CH2 (methylene) groups in the middle of the chain.
– We can collect them and write the structural formula of pentane as CH3(CH2)3CH3.
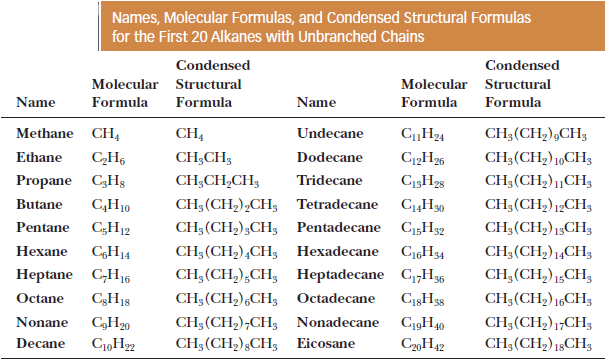
– The table gives the names and molecular formulas of the first 20 alkanes.
– Note that the names of all these alkanes end in -ane.
– We will have more to say about naming alkanes in the following lessons.
General molecular formula of Alkanes
– Alkanes have the general molecular formula CnH2n+2.
– Thus, given the number of carbon atoms in an alkane, we can determine the number of hydrogens in the molecule and its molecular formula.
– For example, decane, with 10 carbon atoms, must have ( 2 × 10) + 2 = 22 hydrogen atoms and a molecular formula of C10H22.
Constitutional isomers of alkanes
– Constitutional isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas.
– By “different structural formulas,” we mean that constitutional isomers differ in the kinds of bonds they have (single, double, or triple) and/or in the connectivity of their atoms.
– For the molecular formulas CH4, C2H6, and C3H8, only one connectivity is possible.
– For the molecular formula C4H10, two connectivities are possible.
– In one of these, named butane, the four carbons are bonded in a chain; in the other, named 2-methylpropane, three carbons are bonded in a chain with the fourth carbon as a branch on the chain.
– Butane and 2-methylpropane are constitutional isomers; they are different compounds and have different physical and chemical properties.
– Their boiling points, for example, differ by approximately 11°C.
– To determine whether two or more structural formulas represent constitutional isomers (that is, different compounds with the same molecular formula), write the molecular formula of each and then compare them.
– All compounds that have the same molecular formula, but different structural formulas (different connectivities of their atoms), are constitutional isomers.
Solved Problems
Problem (1): Do the condensed formulas in each pair represent the same compound or constitutional isomers?
Solution
(a) The molecules are drawn here as both condensed structural formulas and line angle formulas.
– Each formula has an unbranched chain of six carbons; the two are identical and represent the same compound.
(b) Each formula has a chain of five carbons with two -CH3 branches.
– Although the branches are identical, they are at different locations on the chains; these formulas represent constitutional isomers
Problem (2): Write line-angle formulas for the five constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C6H14
Solution
– In solving problems of this type, you should devise a strategy and then follow it. Here is one such strategy:
– First, draw a line-angle formula for the constitutional isomer with all six carbons in an unbranched chain.
– Then, draw line-angle formulas for all constitutional isomers with five carbons in a chain and one carbon as a branch on the chain.
– Finally, draw line-angle formulas for all constitutional isomers with four carbons in a chain and two carbons as branches.
– No constitutional isomers with only three carbons in the longest chain are possible for C6H14.
Number of constitutional isomers in Alkanes
– The ability of carbon atoms to form strong bonds with other carbon atoms results in a staggering number of constitutional isomers.
– As the table shows, there are 3 constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C5H12, 75 constitutional isomers with the molecular formula C10H22, and almost 37 million with the molecular formula C25H52.
– For even a small number of carbon and hydrogen atoms, a very large number of constitutional isomers is possible.
– Because constitutional isomers have different chemical properties, a rich diversity of chemistry is possible within these sets.
Reference: Organic chemistry / William H. Brown, Christopher S. Foote, Brent L. Iverson, Eric V. Anslyn, Bruce M. Novak. ( sixth edition) . United States