-
Physical Chemistry
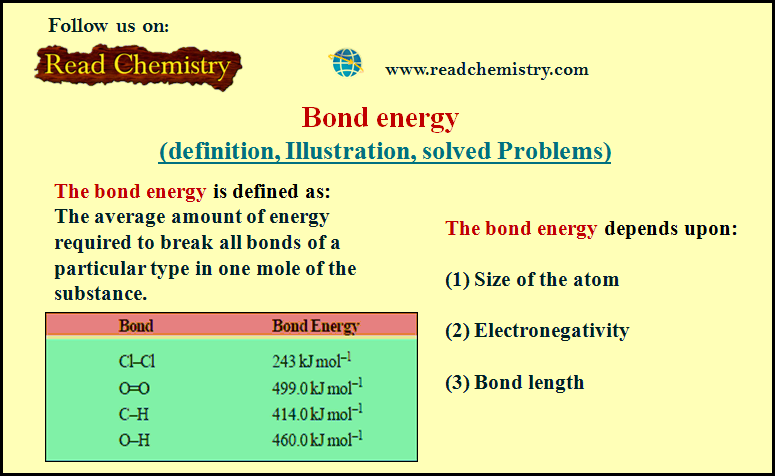
Bond energy (definition, Illustration, solved Problems)
Bond energy – When a bond between two atoms is formed, there is a release of energy. – The same…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
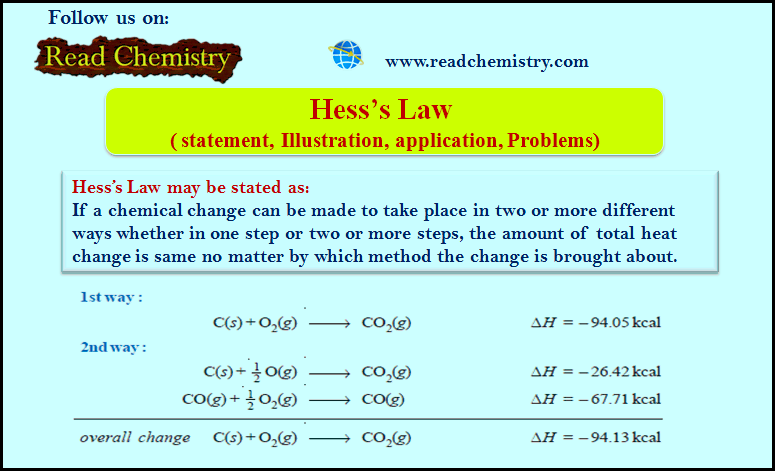
Hess’s Law ( statement, Illustration, application, Problems)
– Hess’s Law may be stated as: (If a chemical change can be made to take place in two or…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
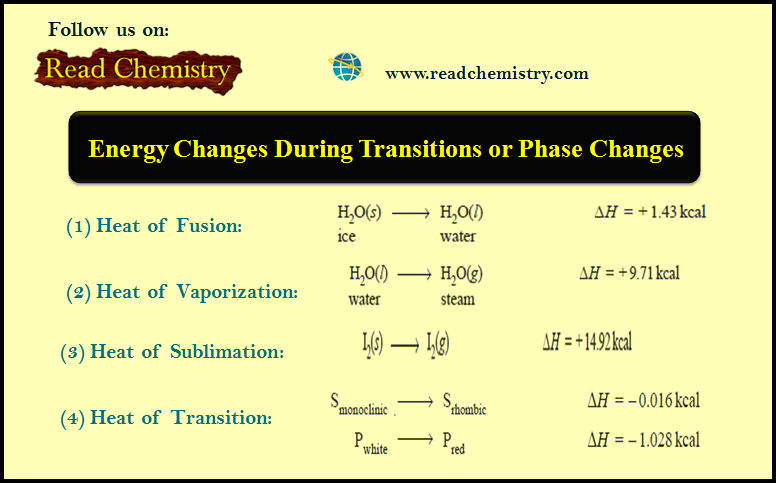
Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes
– In this subject, we will discuss Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes. Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
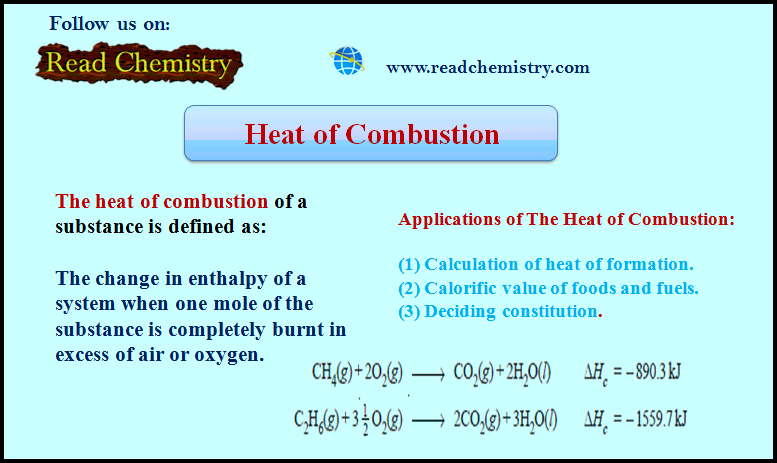
Heat of Combustion (Definition, Applications, Solved Problems)
Heat of Combustion – The heat of combustion of a substance is defined as The change in enthalpy of…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
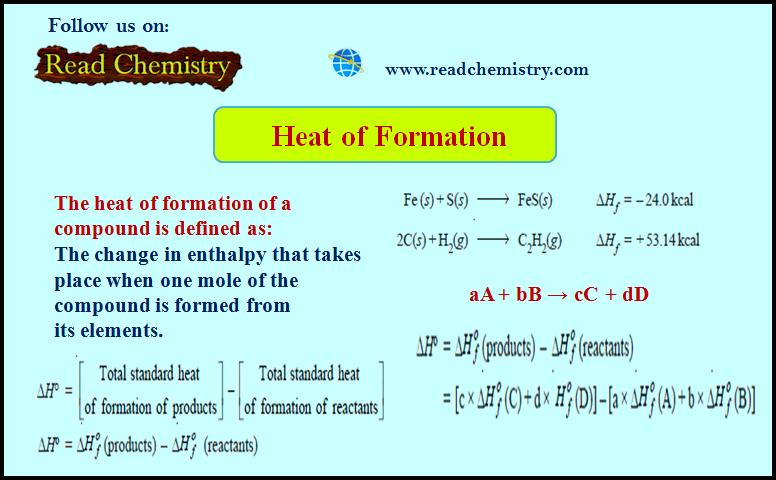
Heat of Formation (Definition, Applications, Solved Problems)
Heat of Formation – The heat of formation of a compound is defined as The change in enthalpy that takes…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
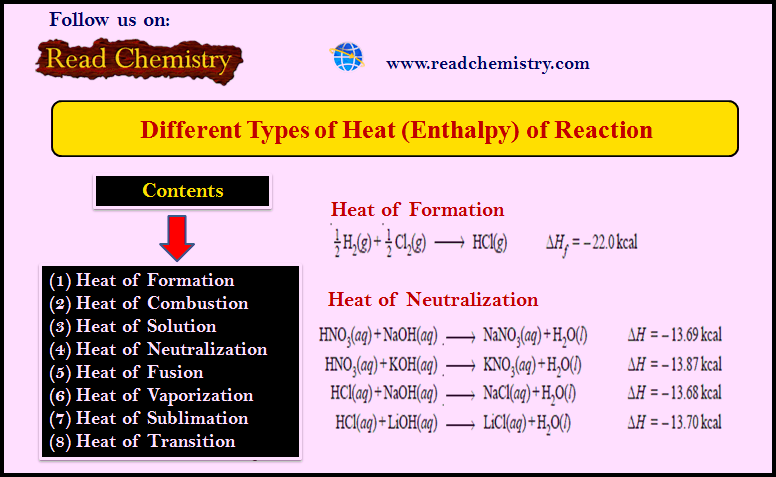
Different Types of Heat of Reaction (Enthalpy)
– The heat of reaction or enthalpy changes accompanying chemical reactions are expressed in different ways, depending on the nature…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
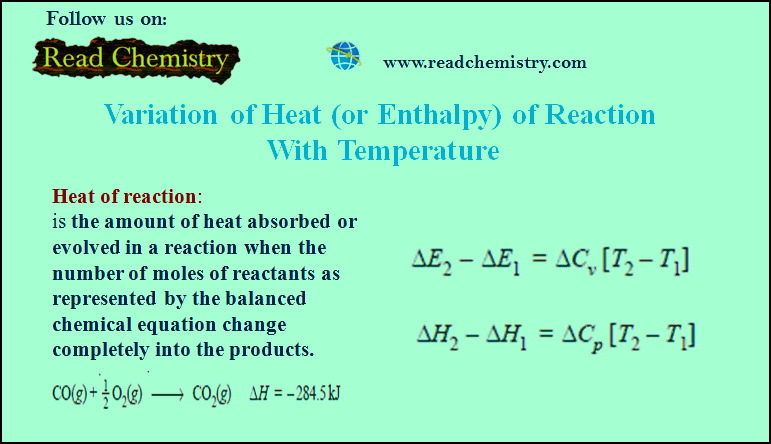
Variation of heat of reaction with temperature
– In this subject, the Variation of heat of reaction with temperature will be discussed. Heat of Reaction or Enthalpy…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
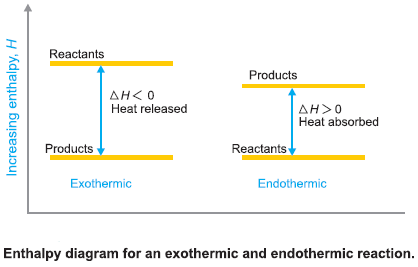
Enthalpy of Reaction
– For reactions involving solids and liquids only the change in volume (ΔV) is very small and the term P…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
MCQ on the First law of Thermodynamics
MCQ on the First Law of Thermodynamics – In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
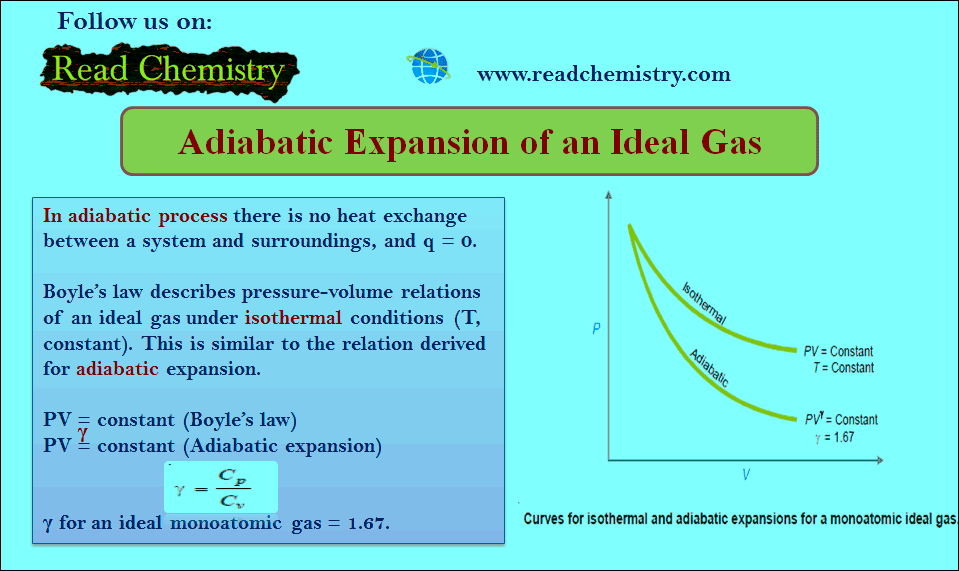
Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas
Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas – A process carried in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated so that…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
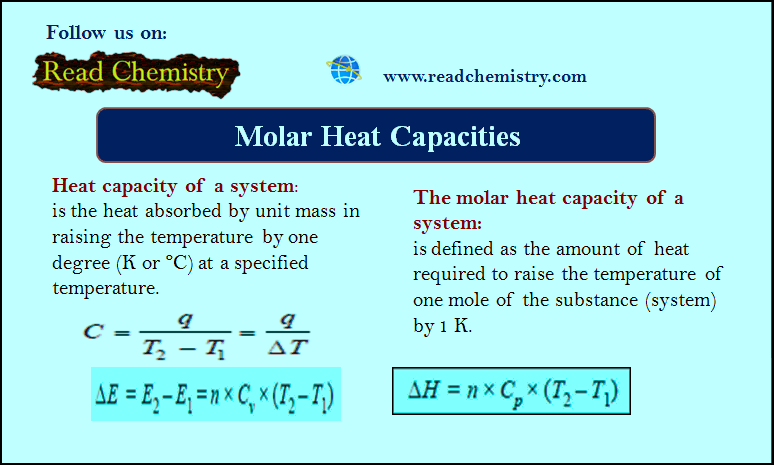
Heat Capacity – Molar Heat Capacity
Molar Heat Capacity – By heat capacity of a system, we mean the capacity to absorb heat and store energy.…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
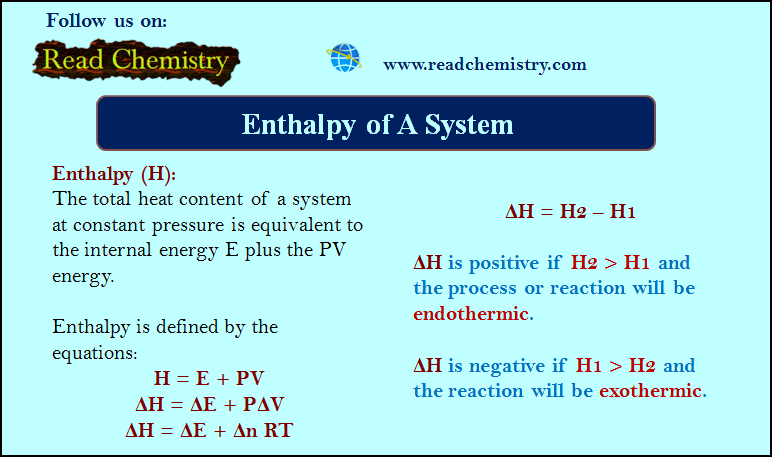
Enthalpy of A System
– Enthalpy (H) is the total heat content of a system at constant pressure and is equivalent to the internal…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
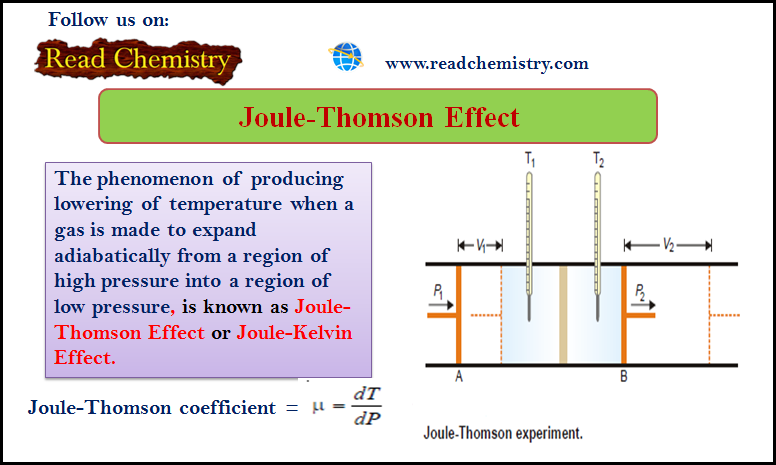
Joule-Thomson Effect
– The phenomenon of producing a lowering of temperature when a gas is made to expand adiabatically from a region…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
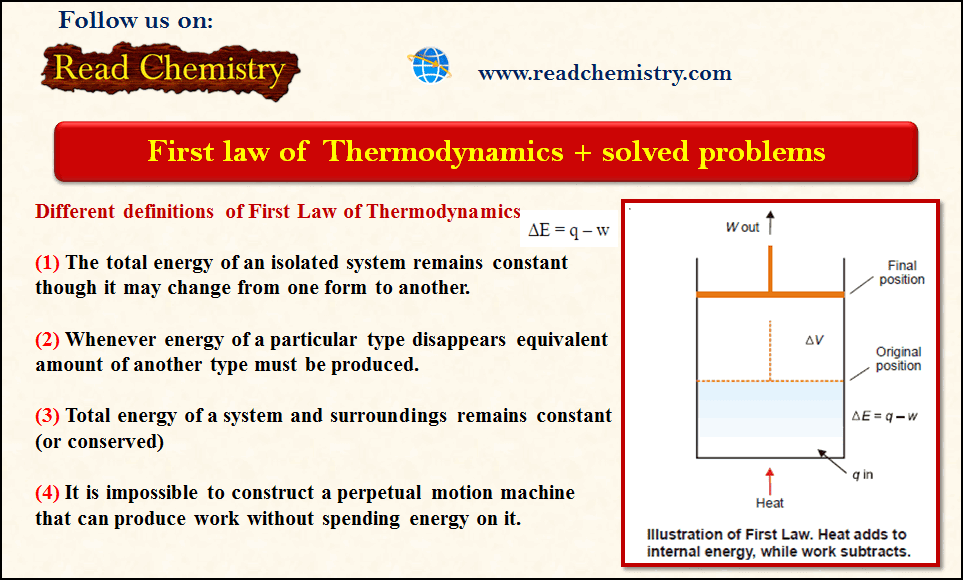
The First Law of Thermodynamics + Solved Problems
– The first law of Thermodynamics states that The total energy of an isolated system remains constant though it may…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
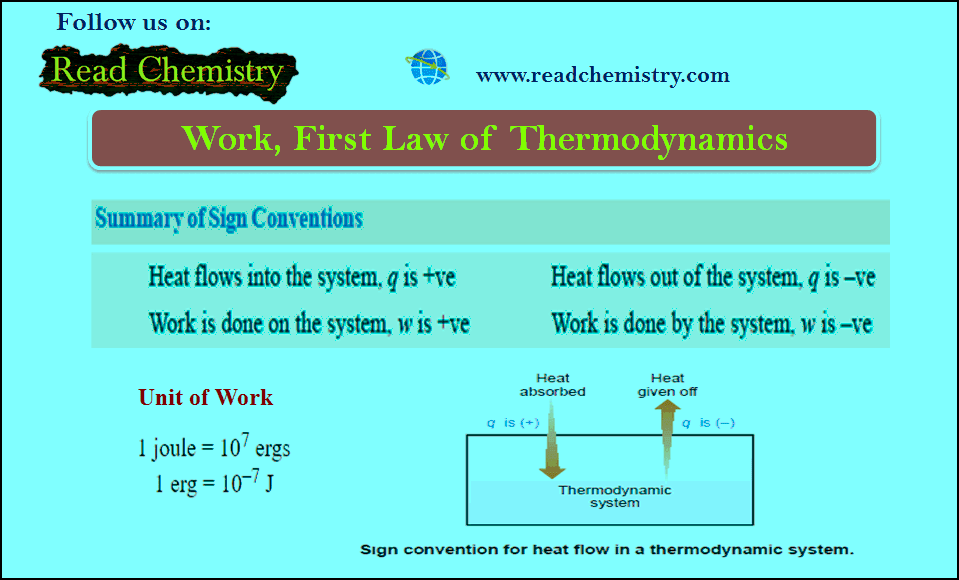
Work in Thermodynamics (Definition – Formula – Problems)
– In physics, mechanical work is defined as force multiplied by the distance through which the force acts. – In…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
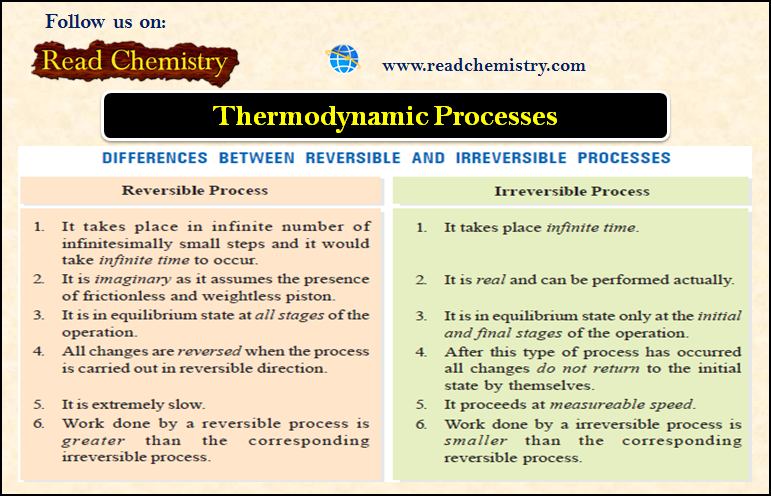
Thermodynamic Processes
– Thermodynamic Processes involve the change of conditions (temperature, pressure, and volume). Thermodynamic Processes – When a thermodynamic system changes…
Read More » -
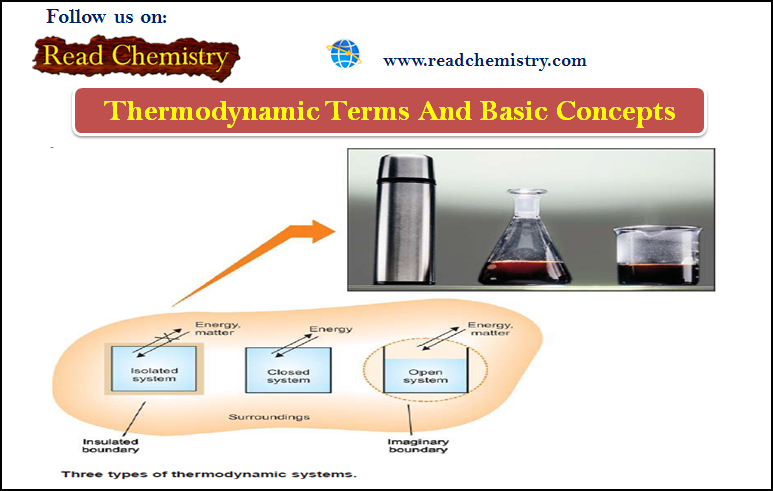
Physical Chemistry
Thermodynamics – Basic terms and concepts in Thermodynamics
What is Thermodynamics? – Thermodynamics is The study of the flow of heat or any other form of energy into…
Read More » -
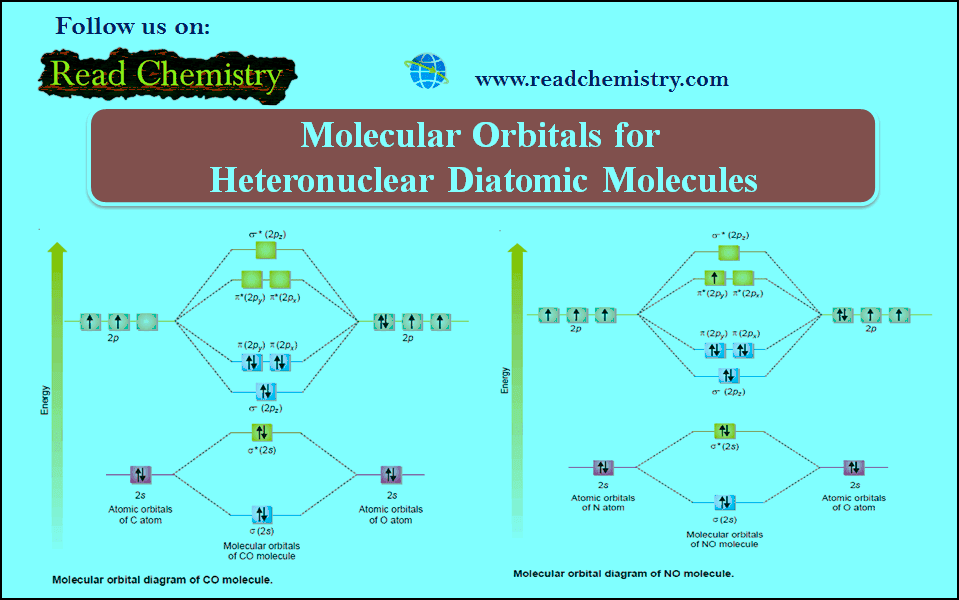
General Chemistry
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules
Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory – In this subject, you will find 46 questions and answers MCQ on…
Read More »