-
Physical Chemistry
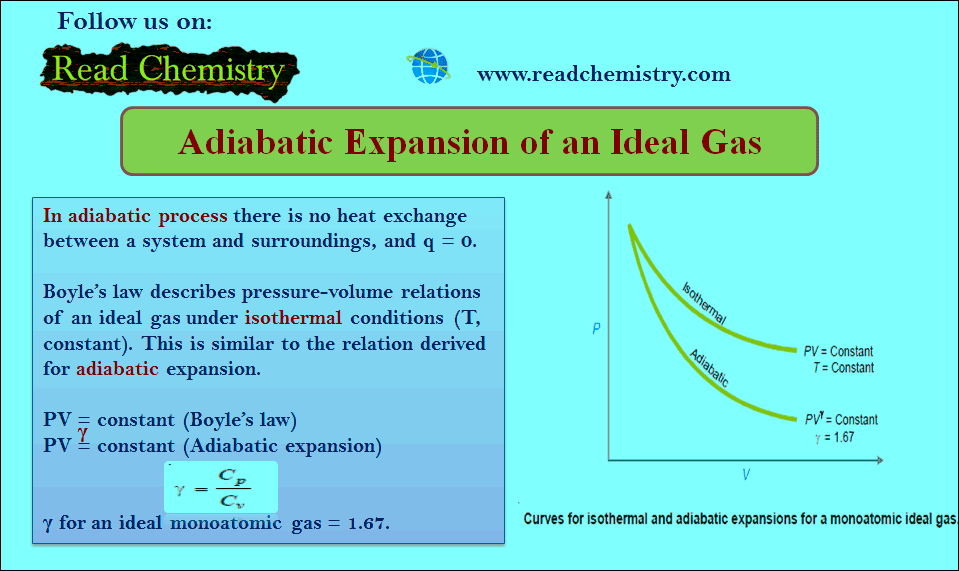
Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas
Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas – A process carried in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated so that…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
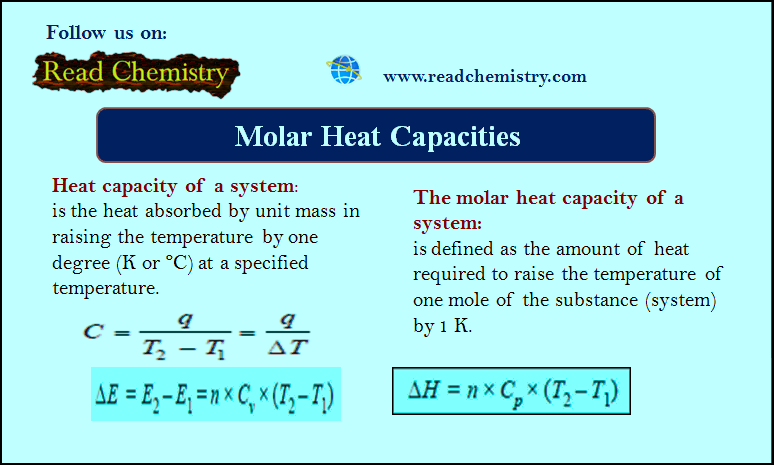
Heat Capacity – Molar Heat Capacity
Molar Heat Capacity – By heat capacity of a system, we mean the capacity to absorb heat and store energy.…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
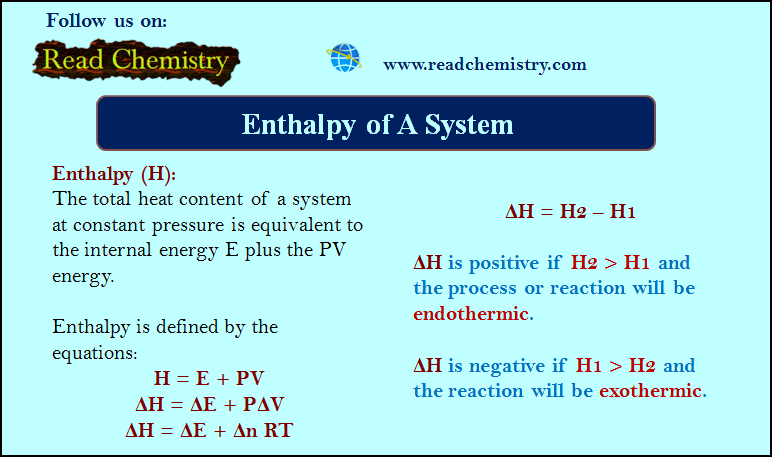
Enthalpy of A System
– Enthalpy (H) is the total heat content of a system at constant pressure and is equivalent to the internal…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
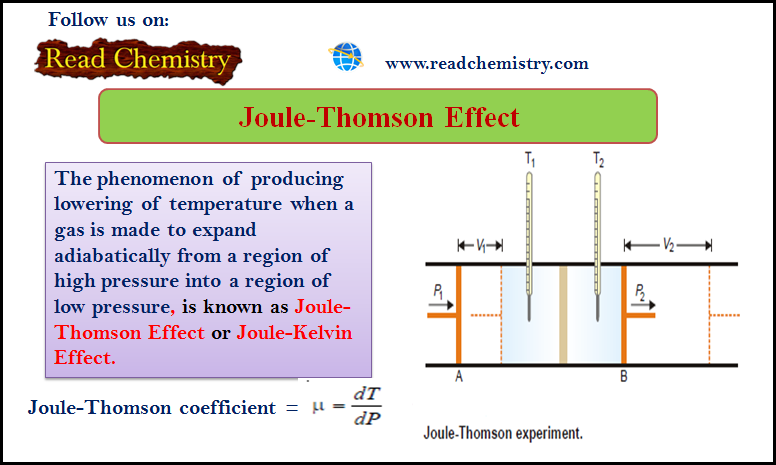
Joule-Thomson Effect
– The phenomenon of producing a lowering of temperature when a gas is made to expand adiabatically from a region…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
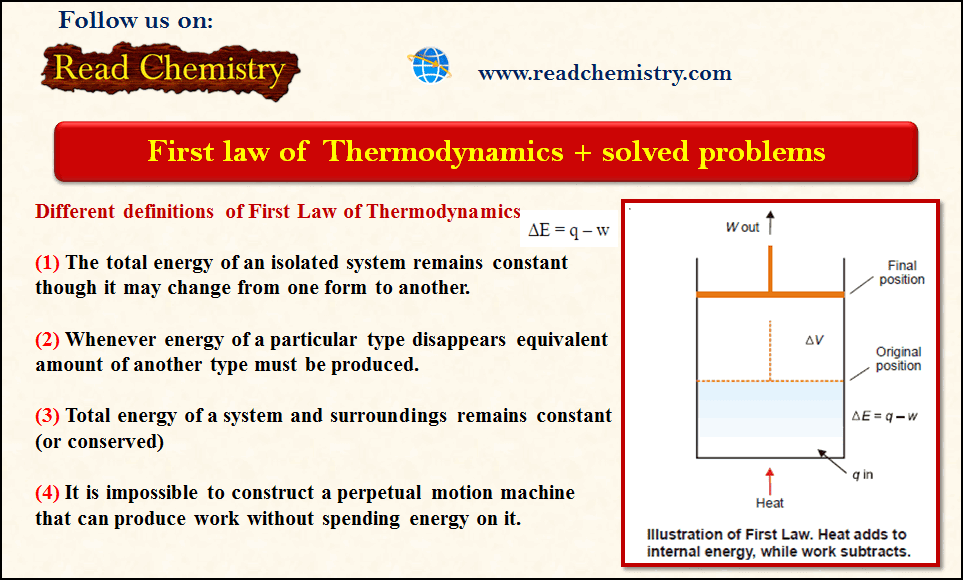
The First Law of Thermodynamics + Solved Problems
– The first law of Thermodynamics states that The total energy of an isolated system remains constant though it may…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
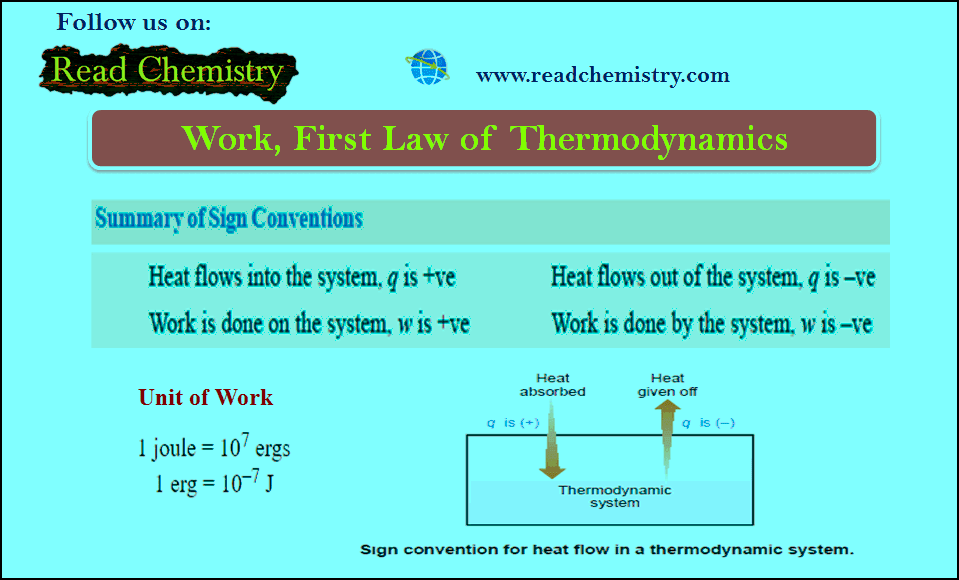
Work in Thermodynamics (Definition – Formula – Problems)
– In physics, mechanical work is defined as force multiplied by the distance through which the force acts. – In…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
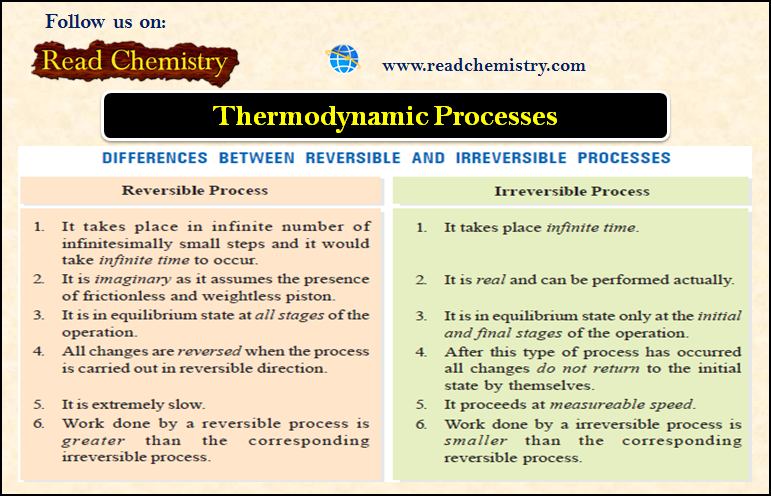
Thermodynamic Processes
– Thermodynamic Processes involve the change of conditions (temperature, pressure, and volume). Thermodynamic Processes – When a thermodynamic system changes…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
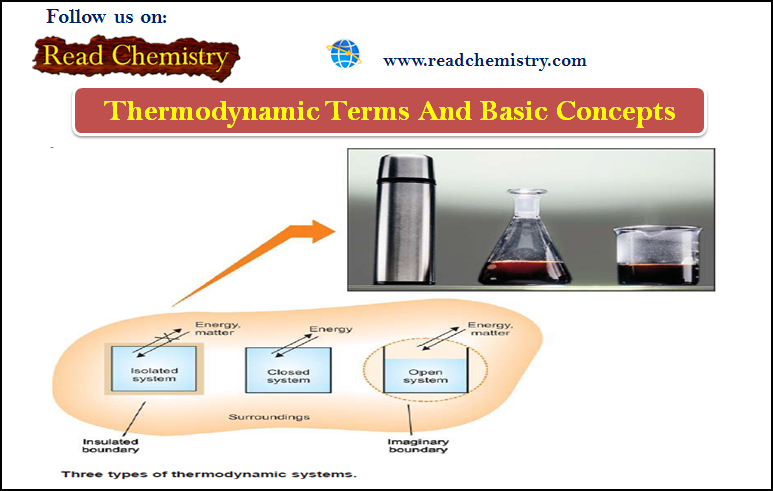
Thermodynamics – Basic terms and concepts in Thermodynamics
What is Thermodynamics? – Thermodynamics is The study of the flow of heat or any other form of energy into…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
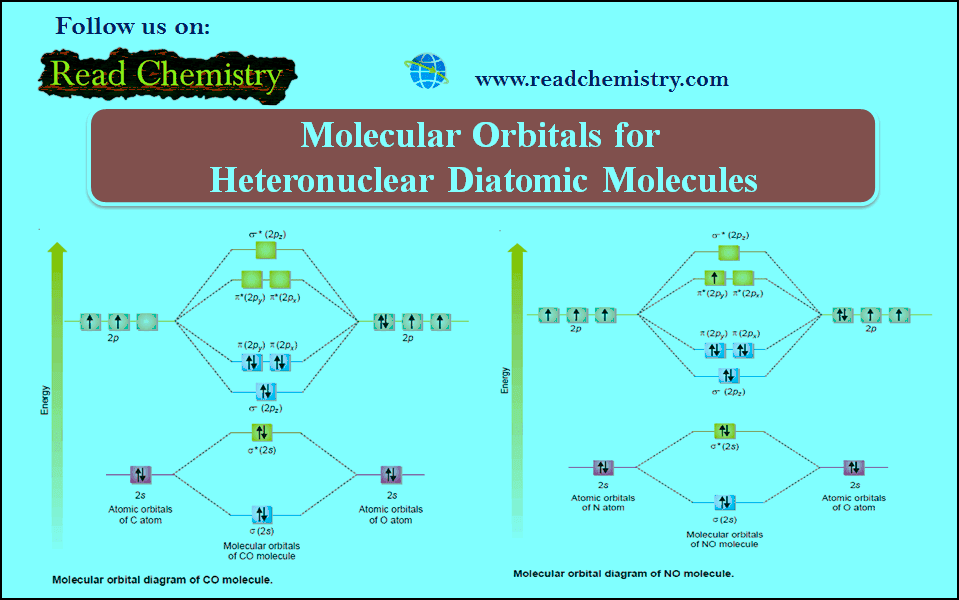
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules
Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory – In this subject, you will find 46 questions and answers MCQ on…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
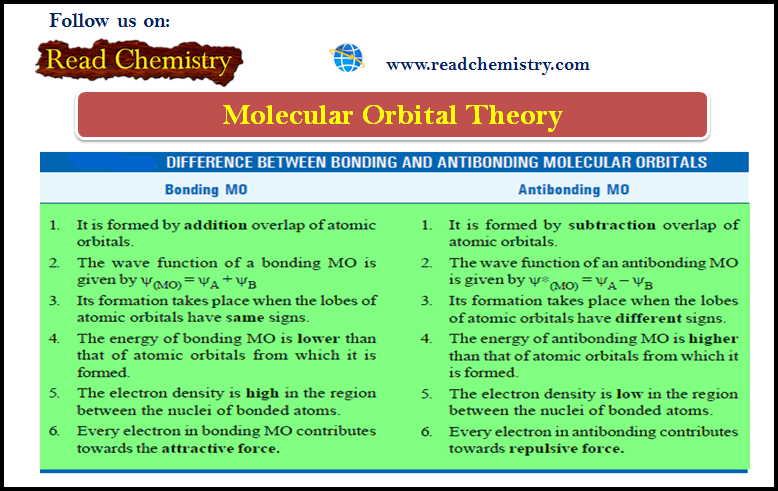
Molecular Orbital Theory
Molecular Orbital Theory – The molecular orbital theory proposed by Hund and Mulliken in 1932 explains the formation of a…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
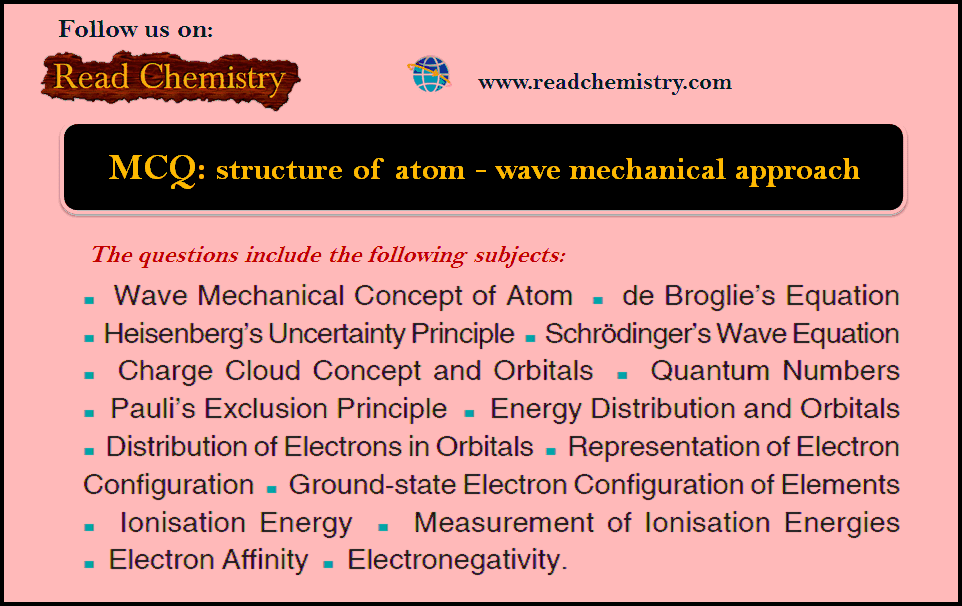
MCQ on Chapter: structure of atom – wave mechanical approach
MCQ on the structure of the atom – In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
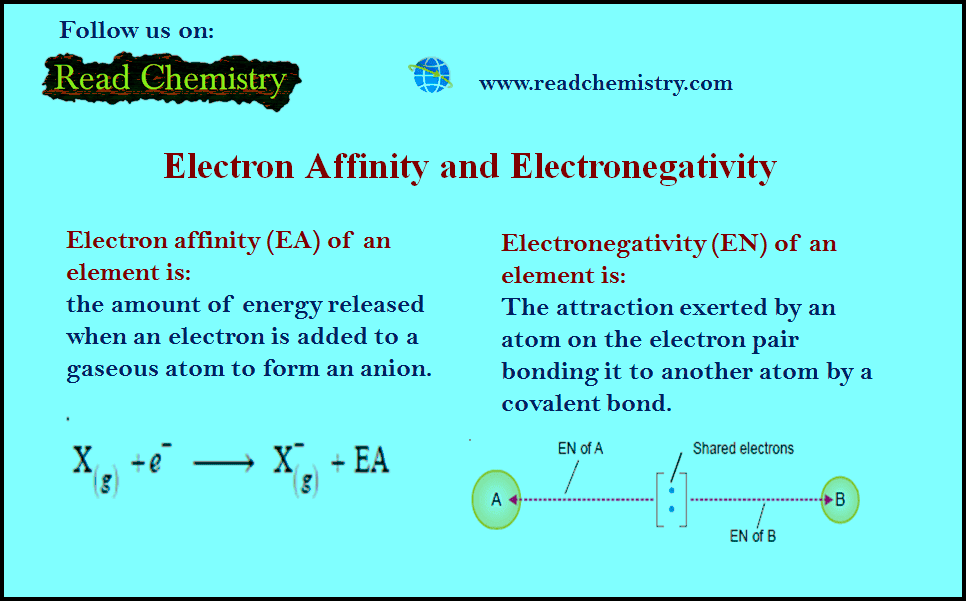
Electronegativity and Electron Affinity
– In this subject, we will discuss the difference Between Electronegativity and Electron Affinity Electron Affinity – A neutral atom…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
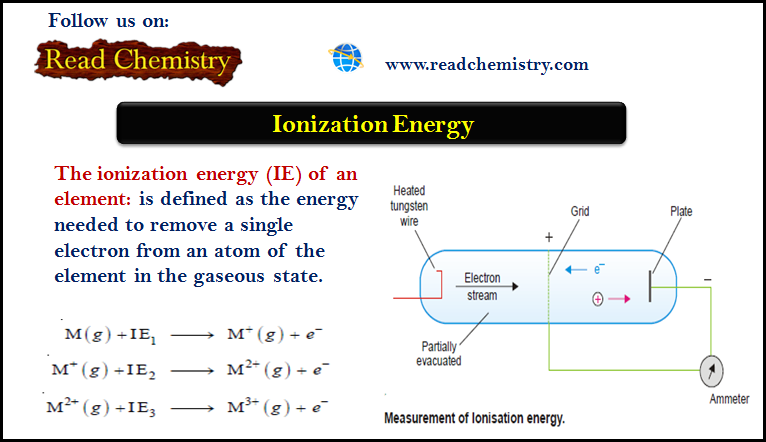
Ionization Energy (Definition – Trends – Measurement)
– The ionization energy (IE) of an element is defined as the energy needed to remove a single electron from…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
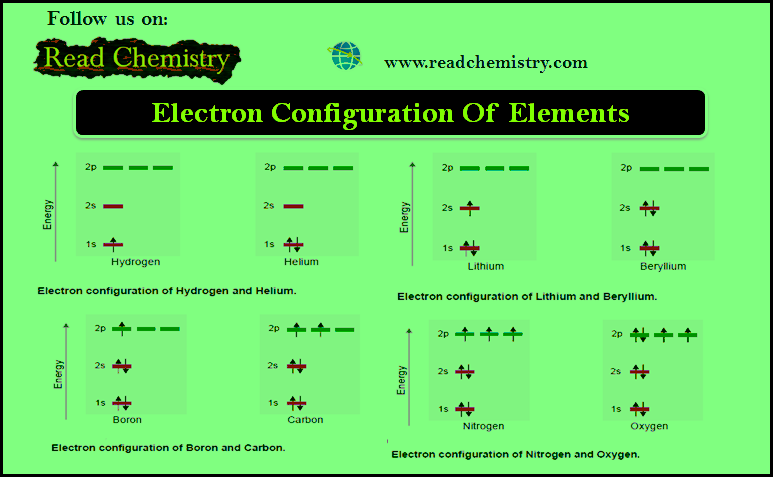
Electron Configuration Of Elements
– In this subject, we will discuss the rules of Electron Configuration Of Elements Electron Configuration Of Elements – We…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
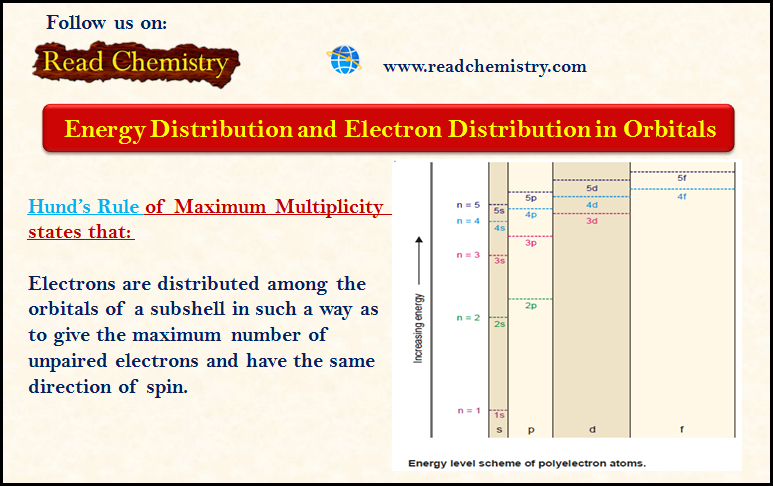
Distribution of Electrons in Orbitals
– In this subject, we will discuss the Distribution of Electrons in Orbitals according to Hund’s Rule. Energy Distribution and…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
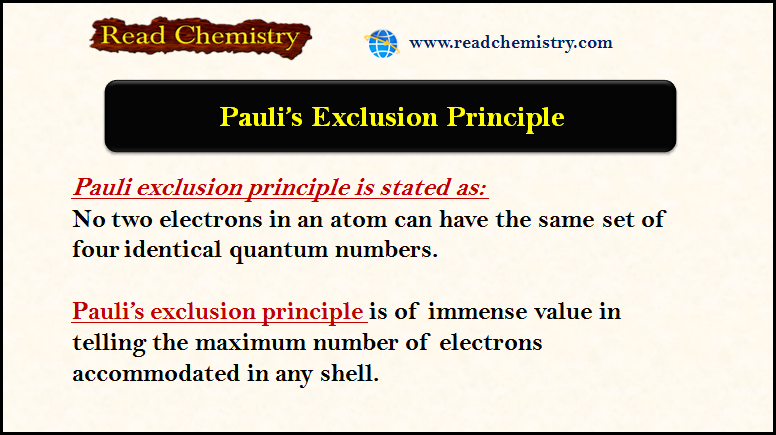
Pauli Exclusion Principle
– The Pauli exclusion principle is of immense value in telling the maximum number of electrons accommodated in any shell.…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
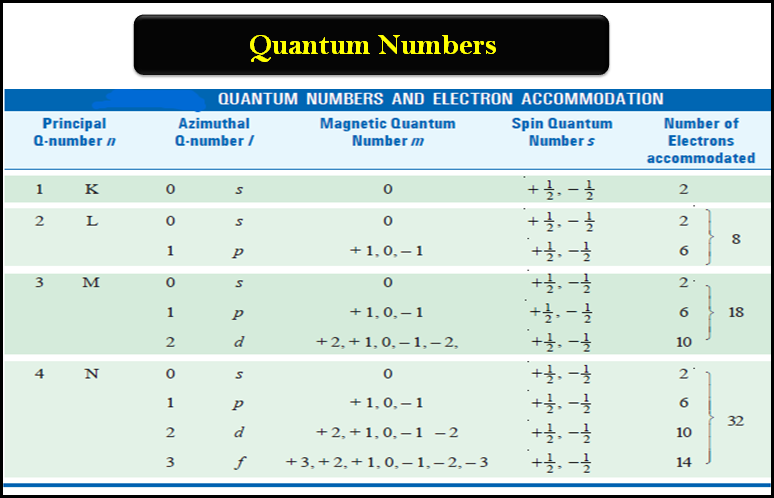
Quantum Numbers (Principal, Azimuthal, Magnetic and Spin)
Quantum Numbers – Bohr’s electronic energy shells or levels, designated as Principal Quantum Numbers (n), could hardly explain the hydrogen…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
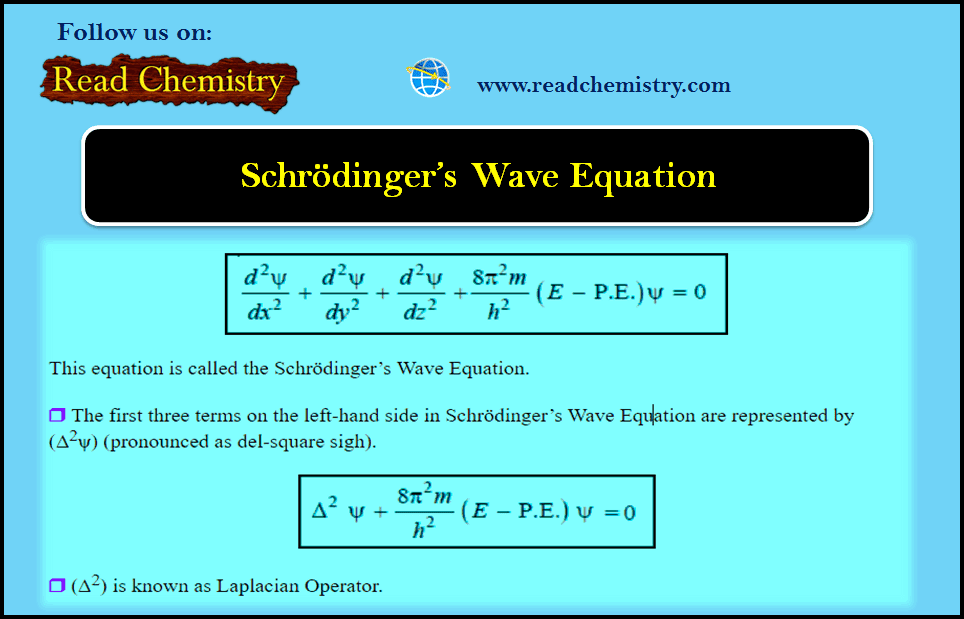
Schrödinger Wave Equation
Schrödinger Wave Equation – In order to provide sense and meaning to the probability approach, Schrödinger derived an equation known…
Read More »