Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry focuses on the structure, properties, and reactions of carbon-containing compounds. It’s essential in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and biochemistry, exploring mechanisms, functional groups, and synthesis of complex molecules.
-
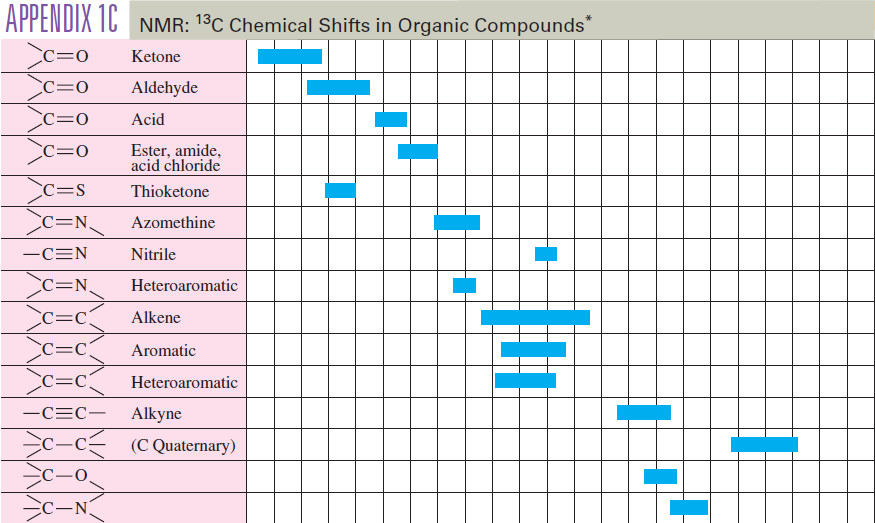
Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy
– In this topic, we will discuss The Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy. Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopy – Where does a carbonyl group…
Read More » -
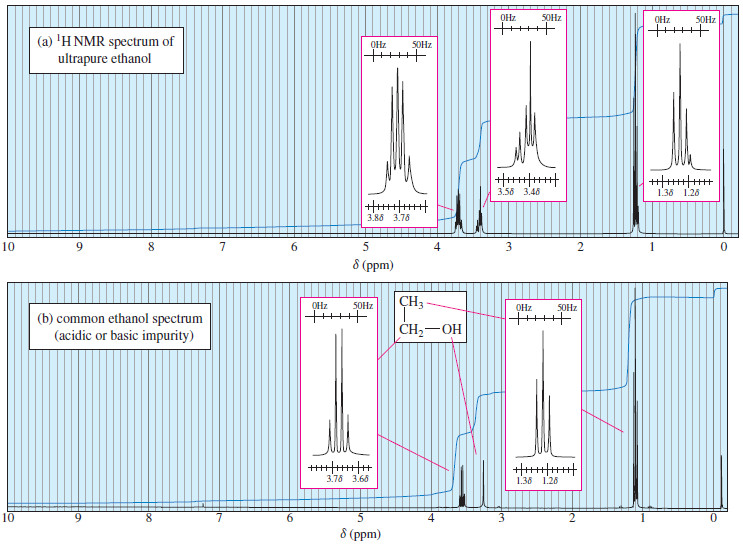
Time Dependence of NMR Spectroscopy
– In this topic, we will discuss The Time Dependence of NMR Spectroscopy. Time Dependence of NMR Spectroscopy – We…
Read More » -
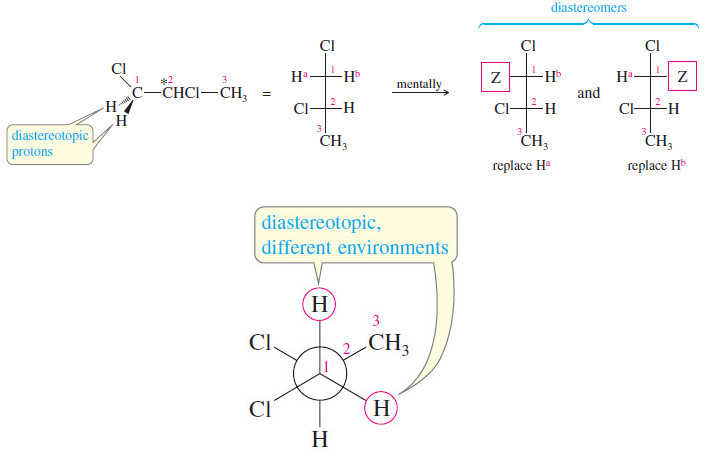
Stereochemical Nonequivalence of Protons in NMR Spectroscopy
– In the this topic we talk about Stereochemical Nonequivalence of Protons in NMR Spectroscopy. Stereochemical Nonequivalence of Protons –…
Read More » -
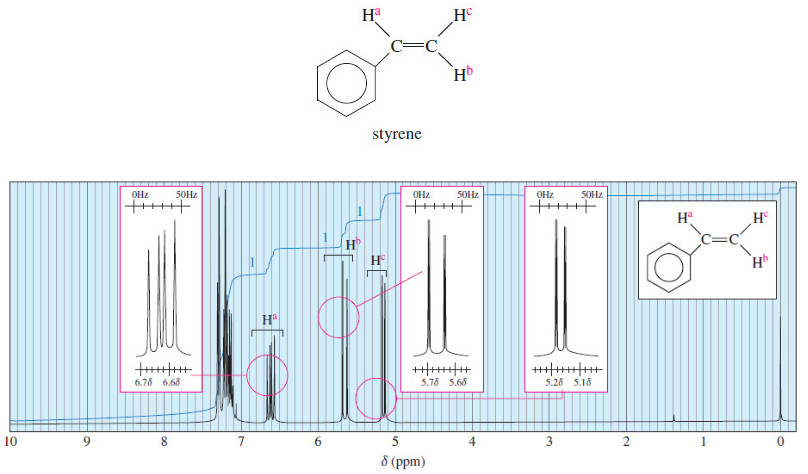
Complex Splitting in ¹H NMR Spectra
– In the last topic we talk about Spin-Spin Splitting in ¹H NMR Spectra, but In this topic, we will…
Read More » -
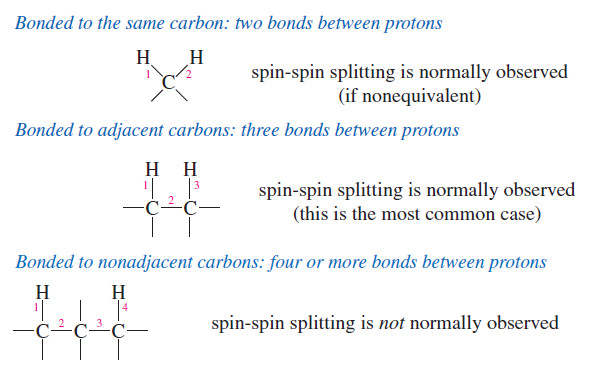
Spin-Spin Splitting in ¹H NMR Spectra
– In this topic, we will discuss The Spin-Spin Splitting in ¹H NMR Spectra. Theory of Spin-Spin Splitting – A…
Read More » -
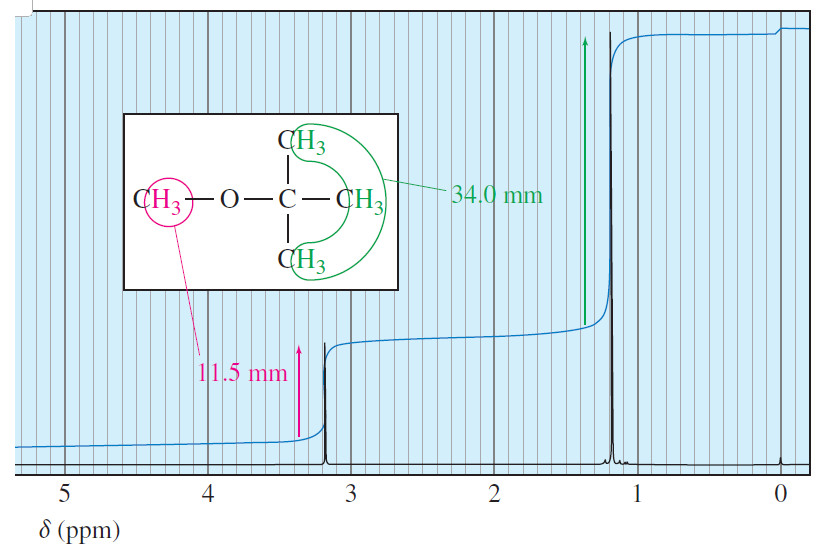
Areas of the Peaks in NMR Spectroscopy
– In this topic, we will discuss The Areas of the Peaks in NMR Spectroscopy Areas of the Peaks –…
Read More » -
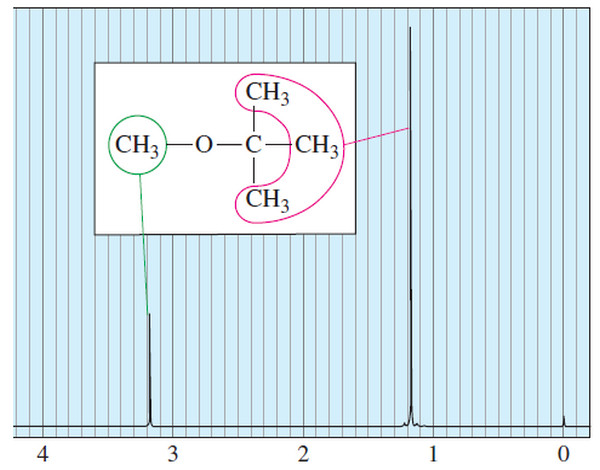
Number of Signals in NMR Spectroscopy
The Number of Signals – In general, the number of NMR signals corresponds to the number of different kinds of…
Read More » -
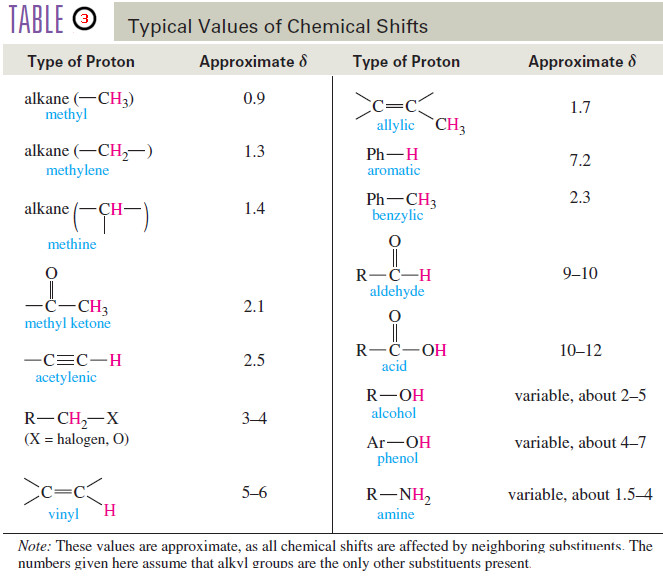
Chemical Shift in NMR Spectroscopy
– In this topic, we will discuss the Chemical Shift in 1H NMR Spectroscopy. What is Chemical Shift? – The…
Read More » -
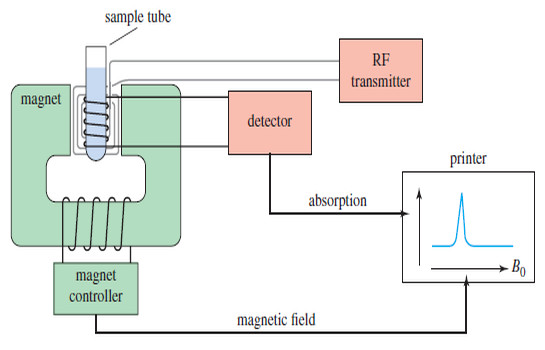
NMR spectrometer
What happens in an NMR spectrometer? – Before discussing the design of spectrometers, let’s review what happens in an NMR…
Read More » -
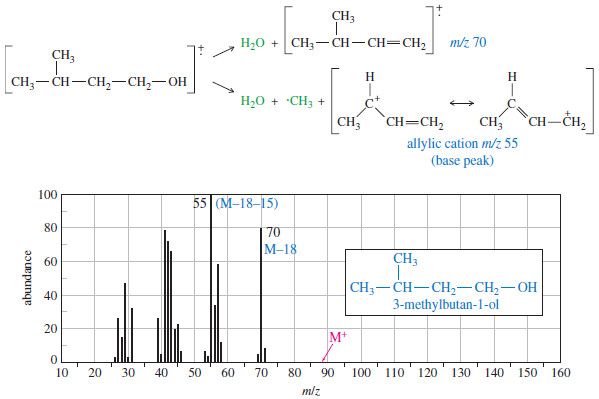
Fragmentation Patterns in Mass Spectrometry
– In this topic, we will discuss the Fragmentation Patterns in Mass Spectrometry. Fragmentation Patterns in Mass Spectrometry – In…
Read More » -
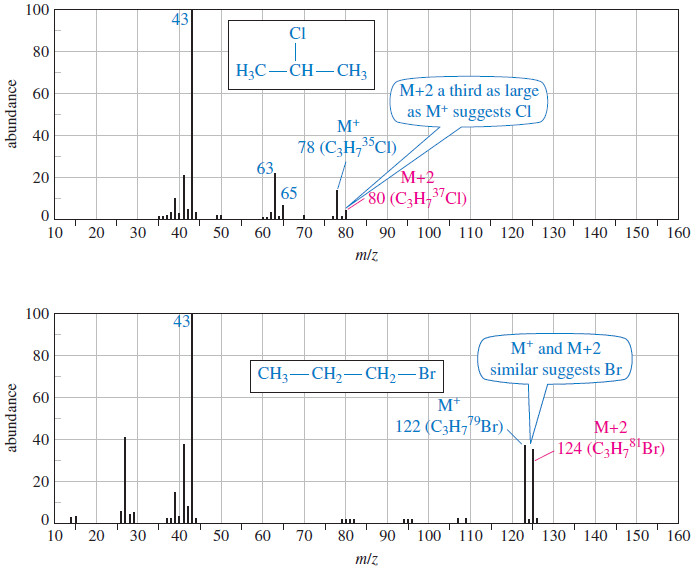
Determination of the Molecular Formula by Mass Spectrometry
Determination of the Molecular Formula by Mass Spectrometry – we can Determine the Molecular Formula by Mass Spectrometry and we…
Read More » -
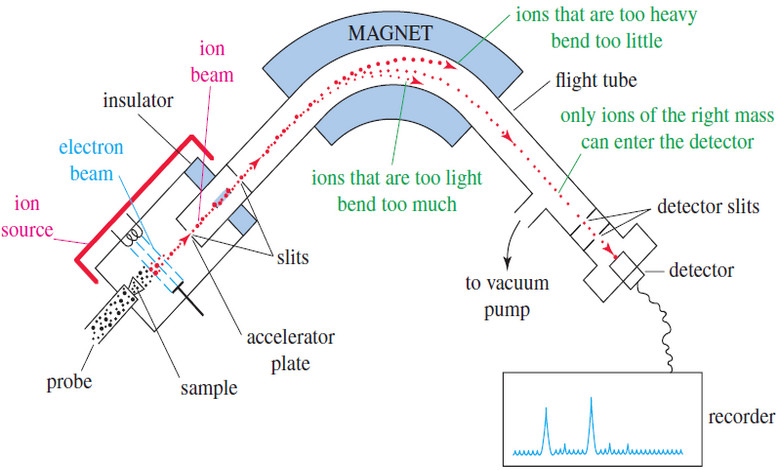
Mass Spectrometry : Introduction
Mass spectrometry (MS) provides the molecular weight and valuable information about the molecular formula, using a very small sample. Introduction…
Read More » -
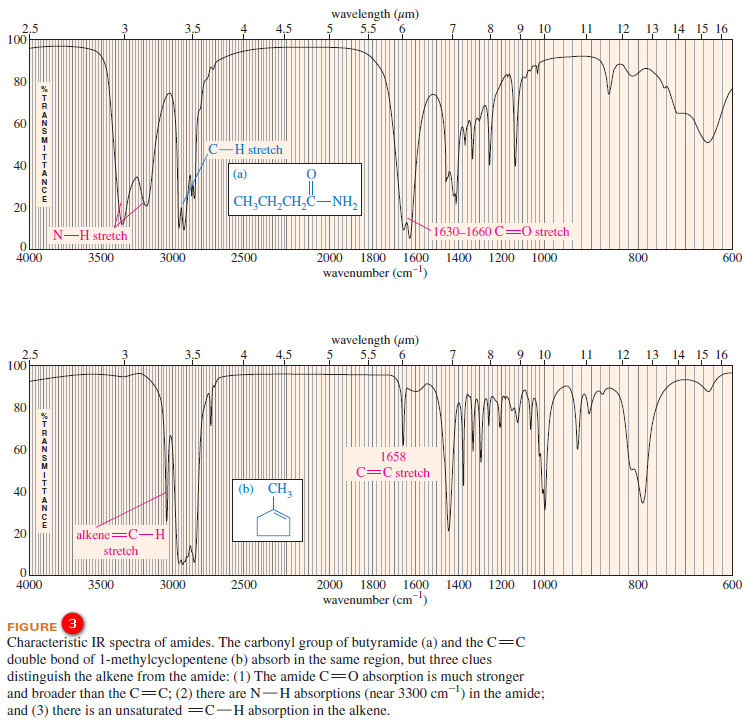
Characteristic Absorptions of Carbonyl Compounds
– In this subject, we will talk about Characteristic Absorptions of Carbonyl Compounds such as Ketones, Aldehydes, Amines, and Acids.…
Read More » -
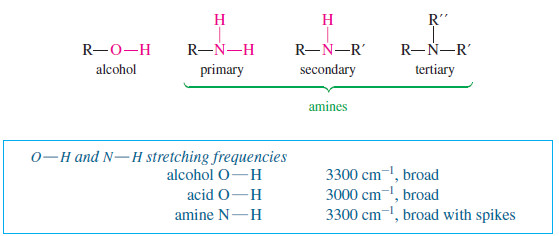
Characteristic Absorptions of Alcohols and Amines
– In this topic, we will discuss the Characteristic Absorptions of Alcohols and Amines by examples. Characteristic Absorptions of Alcohols…
Read More » -
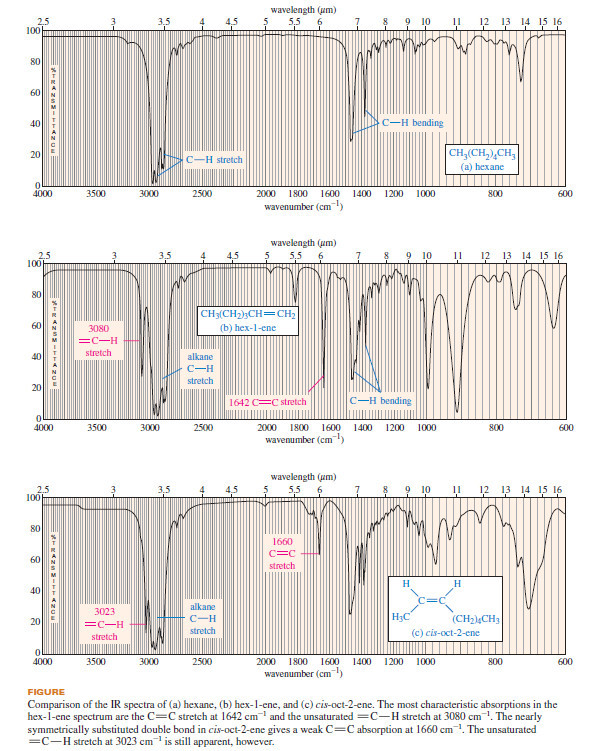
Hydrocarbons: Infrared Spectroscopy of Hydrocarbons
Infrared Spectroscopy of Hydrocarbons – Hydrocarbons contain only carbon–carbon bonds and carbon–hydrogen bonds. – An infrared spectrum does not provide…
Read More » -
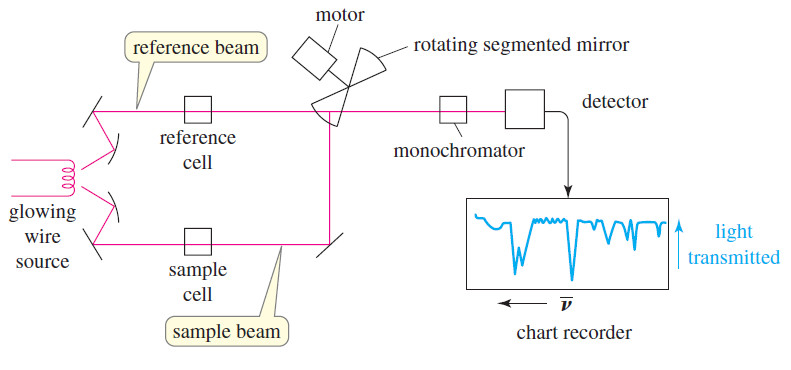
IR Spectrum – Measurement of the IR Spectrum
– In this subject, we talk about how to Measure the IR Spectrum. Measurement of the IR Spectrum – Infrared…
Read More » -
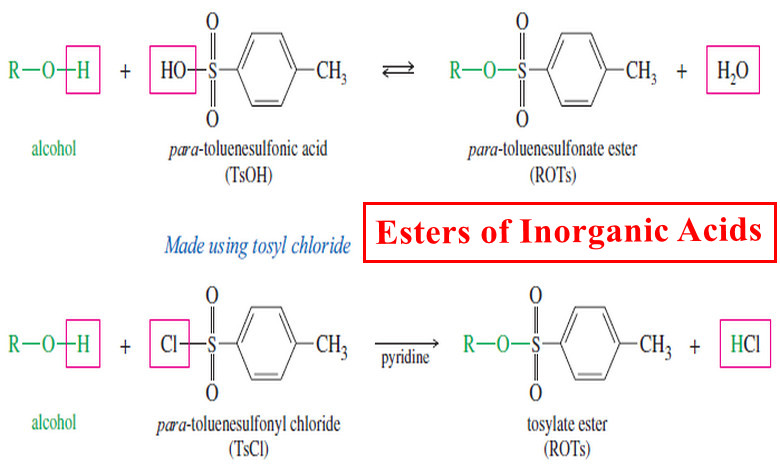
Inorganic Esters – Esters of Inorganic Acids
Esters of Inorganic Acids – In addition to forming esters with carboxylic acids, alcohols form inorganic esters with inorganic acids…
Read More » -
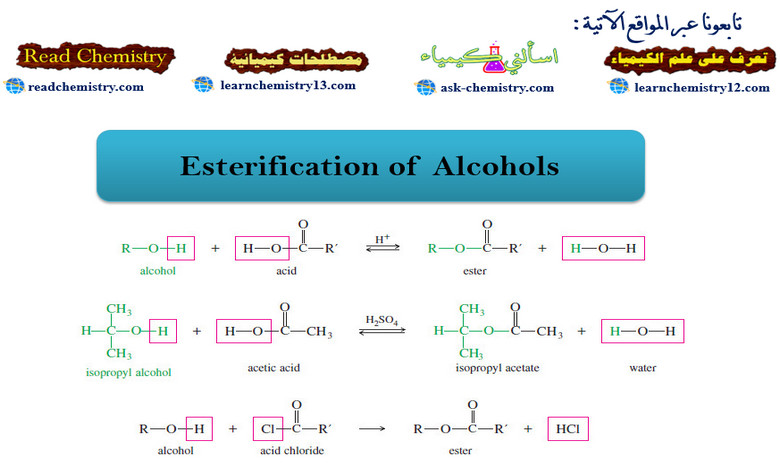
Esterification of Alcohols
– In this subject we will talk about the Esterification of Alcohols. What are Alcohols? – Alcohols are organic compounds…
Read More » -
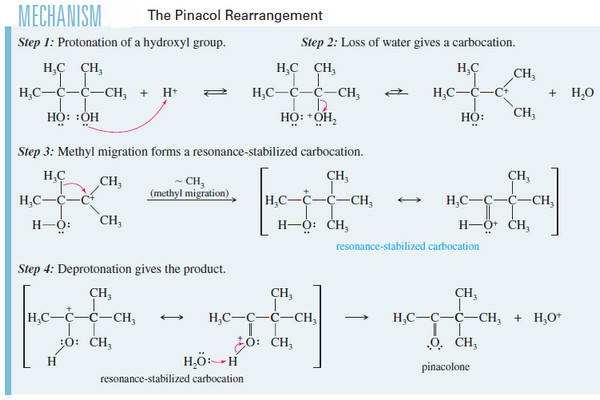
Reactions of Diols
Unique Reactions of Diols – Unique Reactions of Diols are: (1) The Pinacol Rearrangement (2) Periodic Acid Cleavage of Glycols…
Read More » -
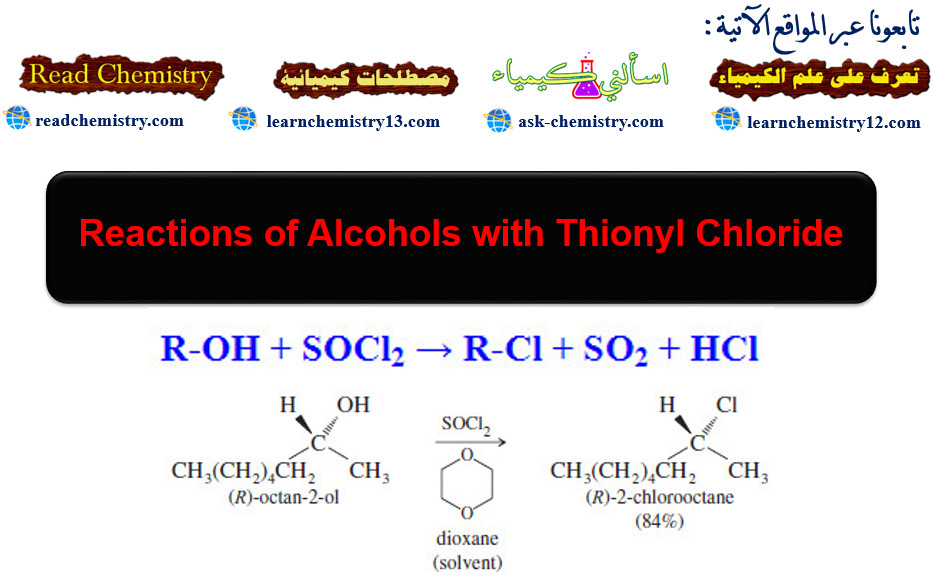
Reactions of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride
Reactions of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride – Reactions of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride give alkyl chloride. – Thionyl chloride (SOCl2)…
Read More »