Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry focuses on the structure, properties, and reactions of carbon-containing compounds. It’s essential in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and biochemistry, exploring mechanisms, functional groups, and synthesis of complex molecules.
-
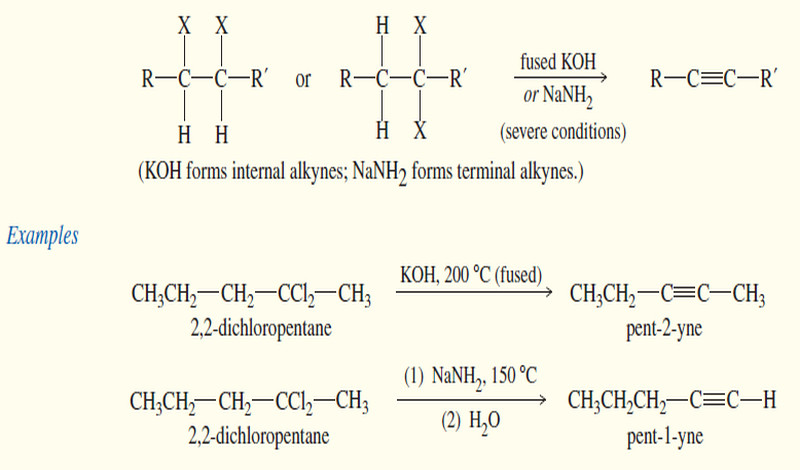
Synthesis of alkynes
Synthesis of alkynes – Two different approaches are commonly used for the synthesis of alkynes. – In the first, an…
Read More » -
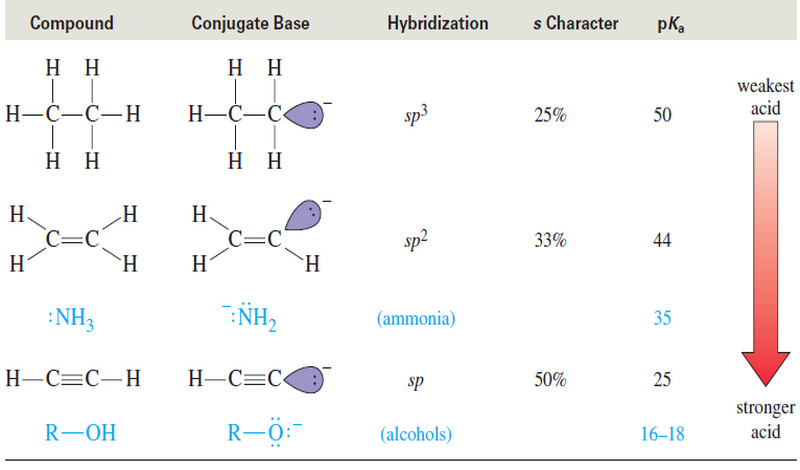
Acidity of Alkynes : Formation of Acetylide Ions
Acidity of Alkynes: Formation of Acetylide Ions – Acidity of Alkynes is the inportant factor of activity of Alkynes. –…
Read More » -
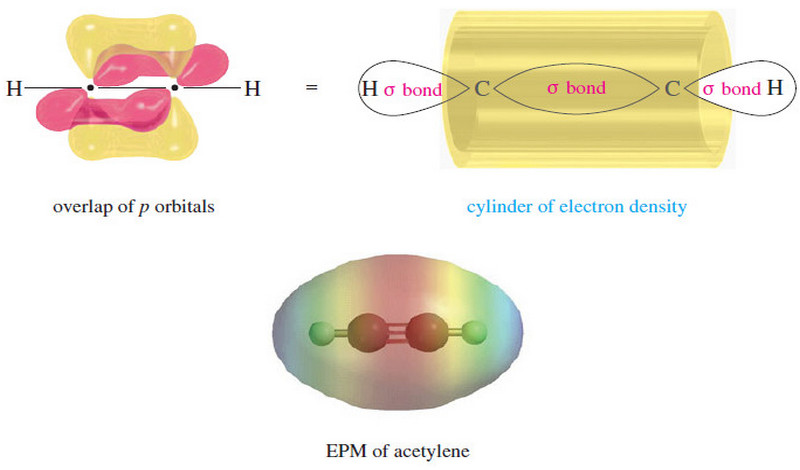
The electronic structure of Alkynes
– we studied theThe electronic structureof Alkynes (a triple bond) in This subject: The Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene): sp Hybridization…
Read More » -
Importance of Alkynes : Acetylene
Commercial Importance of Alkynes : Acetylene and Methylacetylene Uses of Acetylene and Methylacetylene – Acetylene is by far the most…
Read More » -
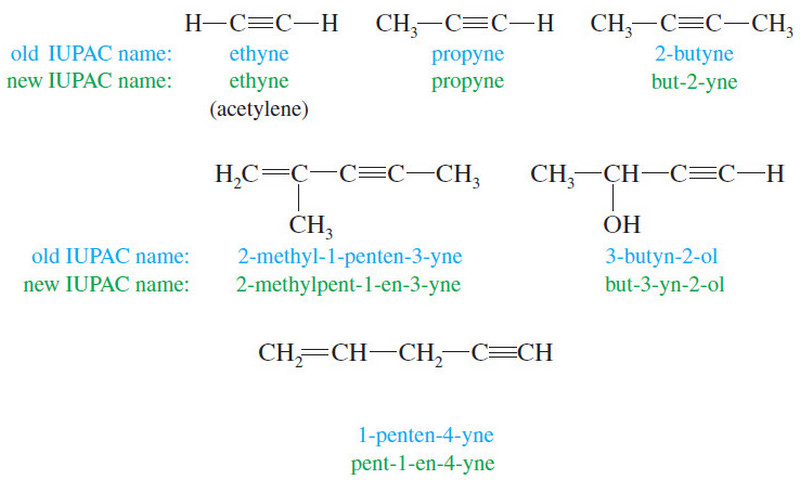
Nomenclature of Alkynes
What are Alkynes? – Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain carbon–carbon triple bonds. – Alkynes are also called acetylenes because they…
Read More » -
Reactions of Alkenes
– In this subject we will discuss all famous reactions of alkenes. – The reactions of alkenes include five basic…
Read More » -
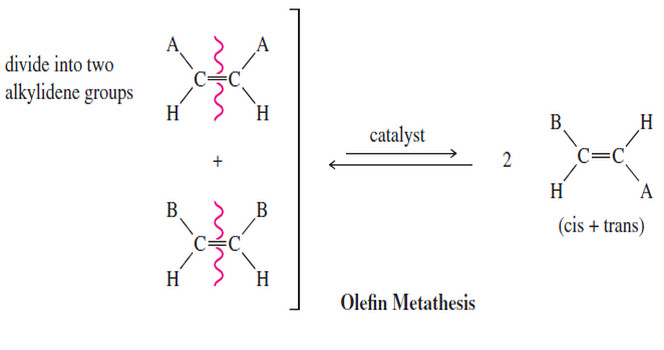
Olefin Metathesis
Olefin Metathesis – The double bond is the strongest bond in an alkene, yet it is also the most reactive…
Read More » -
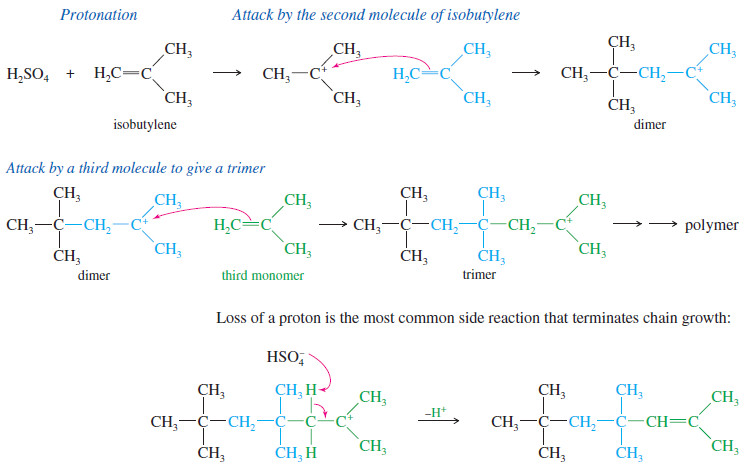
Polymerization of Alkenes
Polymerization of Alkenes – A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating units (the monomers) bonded together.…
Read More » -
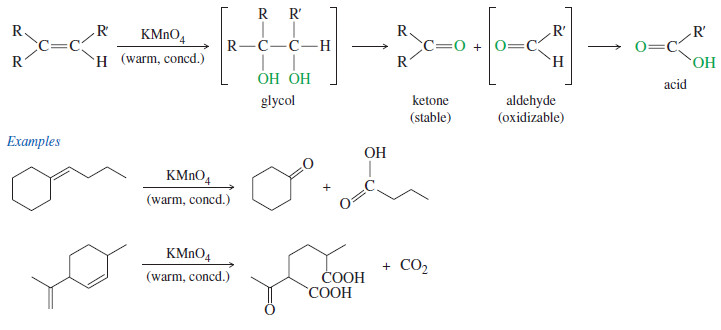
Oxidative Cleavage of Alkenes
Oxidative Cleavage of Alkenes Cleavage by Permanganate – In a potassium permanganate dihydroxylation, if the solution is warm or acidic…
Read More » -
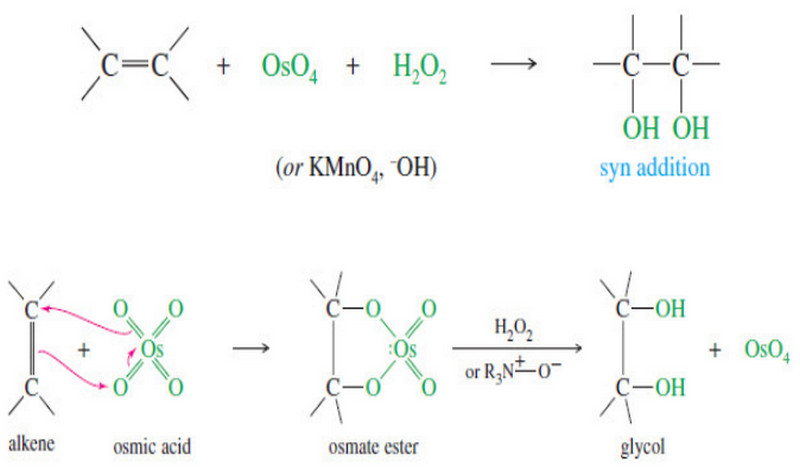
Syn Dihydroxylation of Alkenes
Syn Dihydroxylation of Alkenes – Converting an alkene to a glycol requires adding a hydroxyl group to each end of…
Read More » -
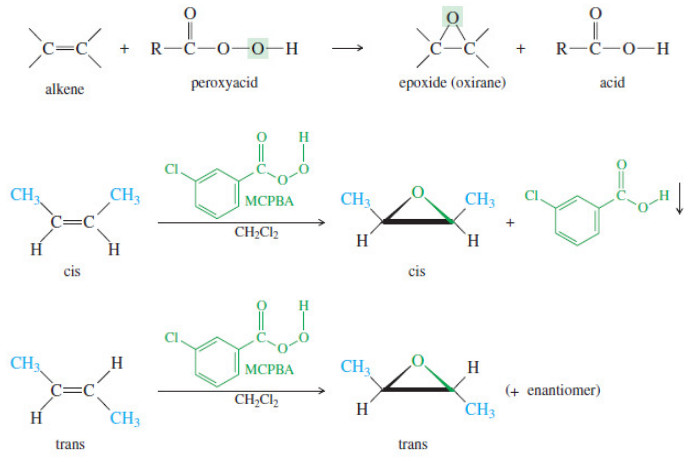
Epoxidation of Alkenes
Epoxidation of Alkenes – Some of the most important reactions of alkenes involve oxidation. – When we speak of oxidation,…
Read More » -
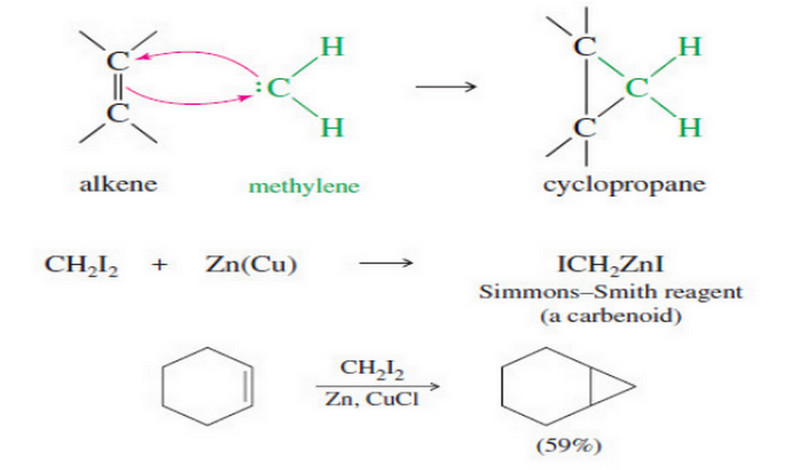
Addition of Carbenes to Alkenes
Addition of Carbenes to Alkenes – Methylene (:CH2) is the simplest of the carbenes: uncharged, reactive intermediates that have a…
Read More » -
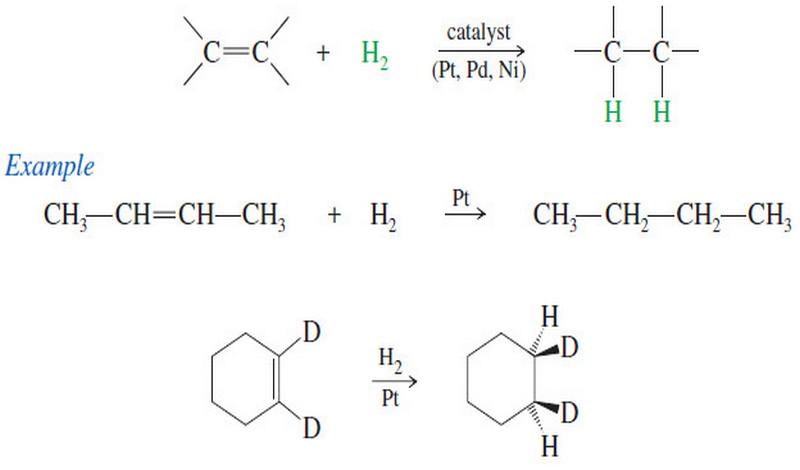
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes – Although we have mentioned catalytic hydrogenation before, we now consider the mechanism and stereochemistry in…
Read More » -
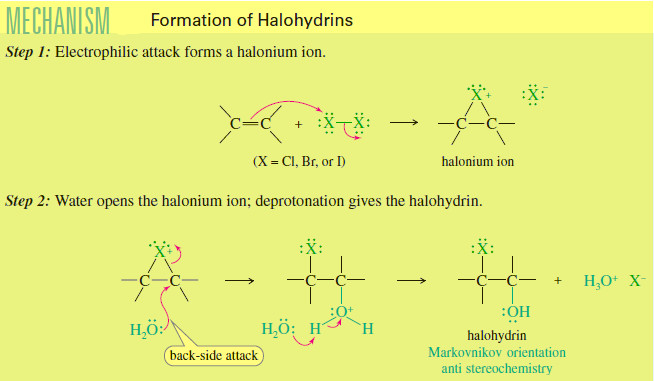
Formation of Halohydrin
Formation of Halohydrin – A halohydrin is an alcohol with a halogen on the adjacent carbon atom. – In the…
Read More » -
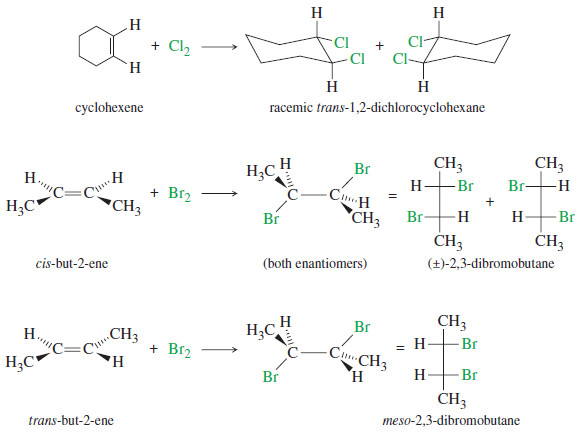
Addition of Halogens to Alkenes
Addition of Halogens to Alkenes – Addition of Halogens to Alkenes gives vicinal dihalides. (A) Mechanism of Halogen Addition –…
Read More » -
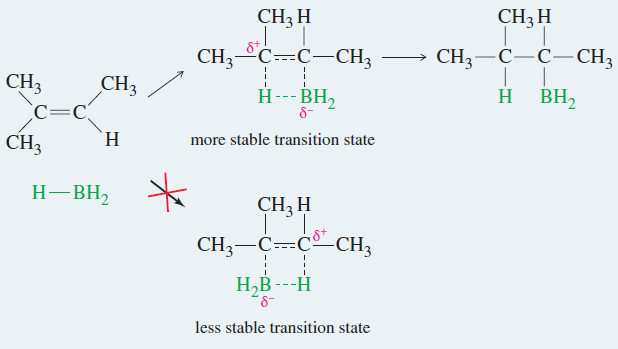
Hydroboration of Alkenes
Hydroboration of Alkenes – We have seen two methods for hydrating an alkene with Markovnikov orientation. – What if we…
Read More » -
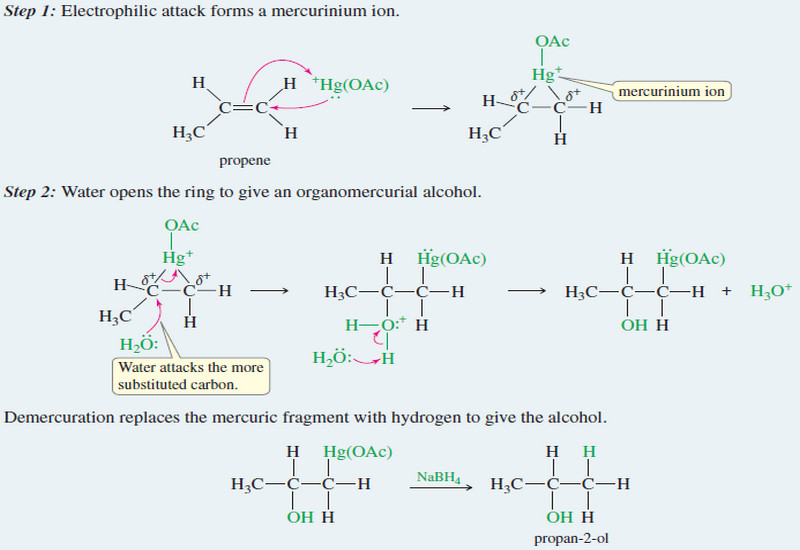
Oxymercuration–demercuration of alkenes
– Oxymercuration–demercuration of alkenes is another method for converting alkenes to alcohols with Markovnikov orientation. Hydration of alkenes by Oxymercuration–Demercuration…
Read More » -
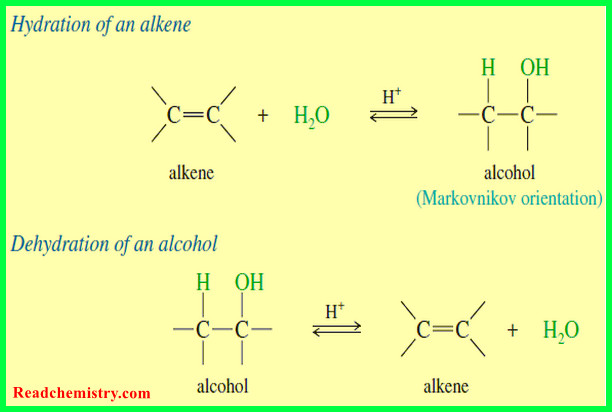
Hydration of Alkenes: Addition of Water
Hydration of Alkenes will be discussed by Addition of Water Addition of Water: Hydration of Alkenes – An alkene may…
Read More » -
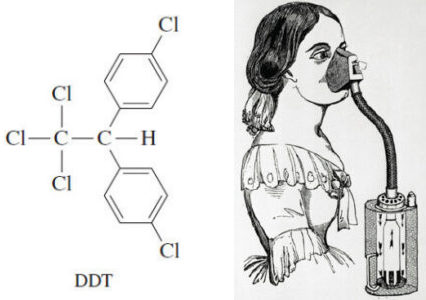
Common Uses of Alkyl Halides
Alkyl halides as Solvents – Alkyl halides are used primarily as industrial and household solvents. – Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) was…
Read More » -
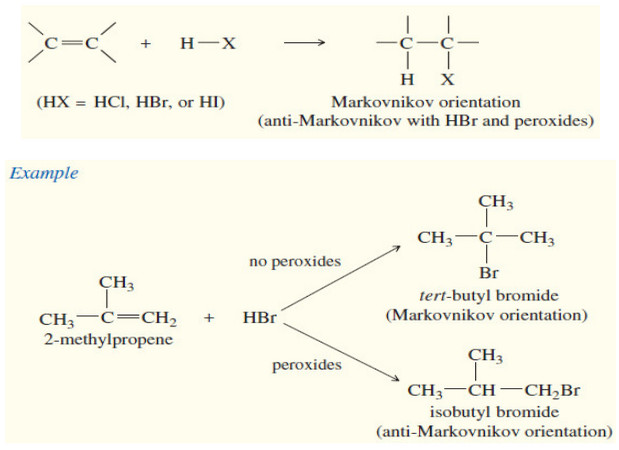
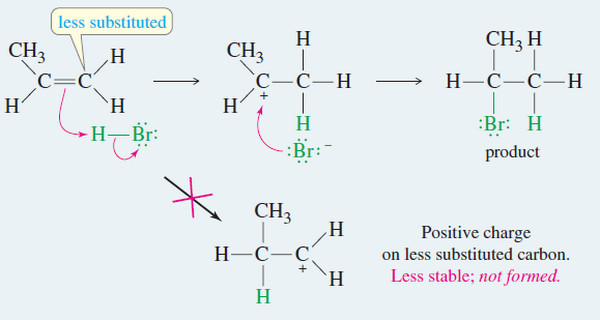
Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes: Markovnikov’s Rule
Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes : Markovnikov’s Rule Orientation of Addition: Markovnikov’s Rule – The simple mechanism shown for…
Read More »