Physical Chemistry blends chemistry with physics, studying matter’s behavior using concepts like thermodynamics, kinetics, quantum mechanics, and spectroscopy. It explains how and why chemical reactions occur at the molecular level.
Physical Chemistry
-
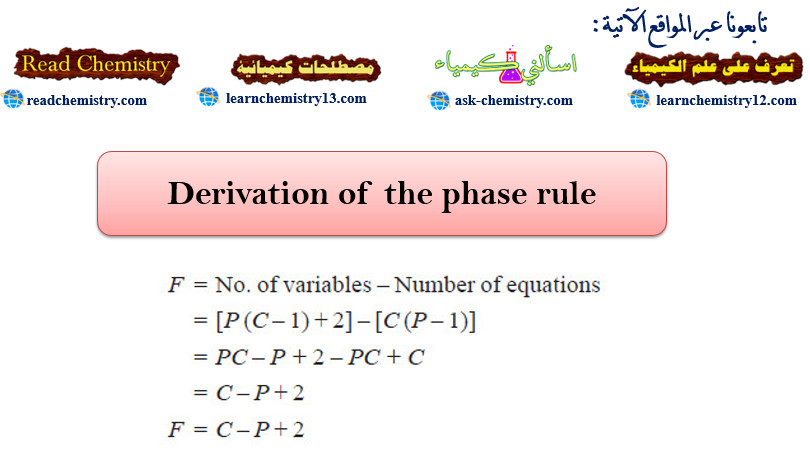
Derivation of the phase rule
Derivation of the phase rule – Here the derivation of the phase rule for one-component system and two-component system are…
Read More » -
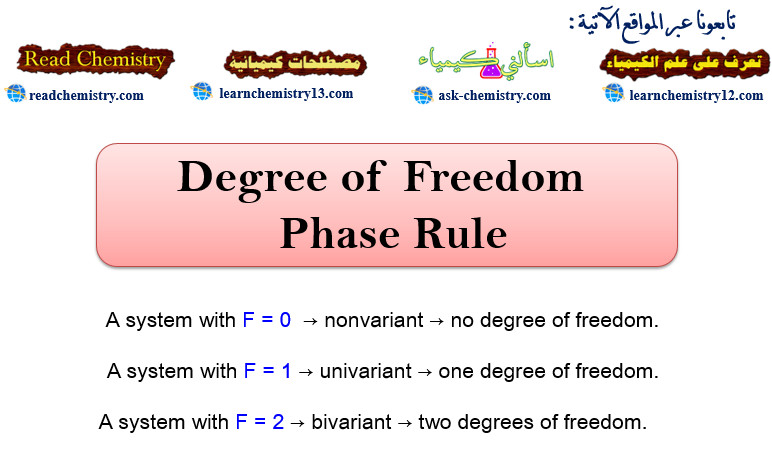
Degree of Freedom – phase Rule
Degree of Freedom – The term Degree of Freedom represented by F in the phase Rule equation (F = C…
Read More » -
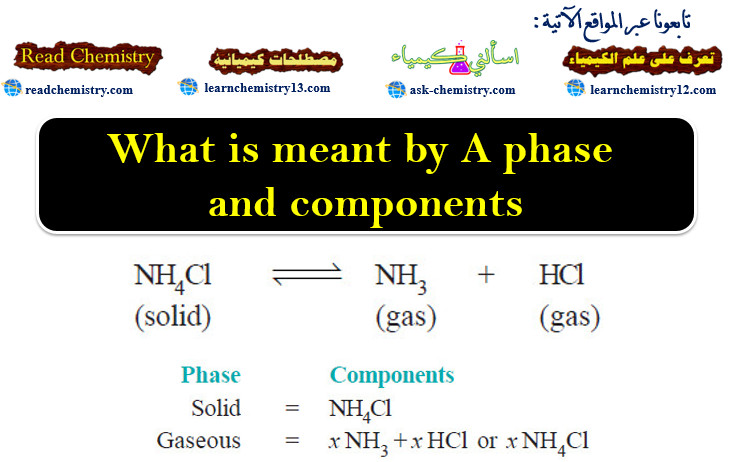
What is meant by A phase and components?
The Phase Rule statement – The phase Rule is an important generalization dealing with the behaviour of heterogeneous systems. –…
Read More » -
Applications of distribution law
Applications of distribution law – There are numerous applications of distribution law in the laboratory as well as in industry.…
Read More » -
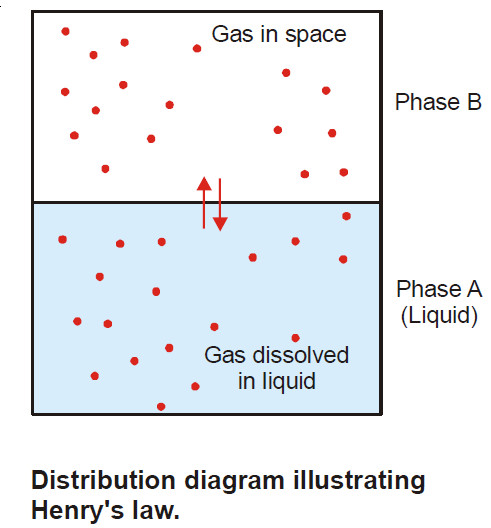
Henry’s law – a form of distribution law
Henry’s law statement – Henry’s law states: at a constant temperature the solubility of a gas in a liquid is…
Read More » -
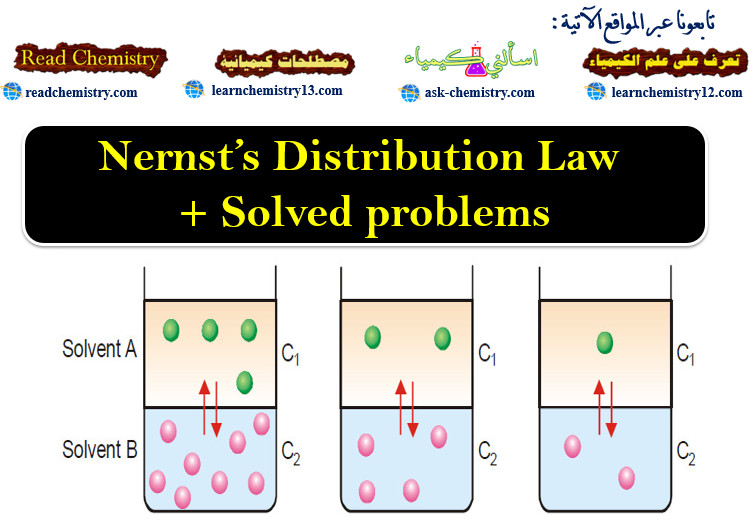
Nernst’s Distribution Law + Solved problems
Introduction to Nernst’s Distribution Law – In this topic Nernst’s Distribution Law wlll be discussed – If we take two…
Read More » -
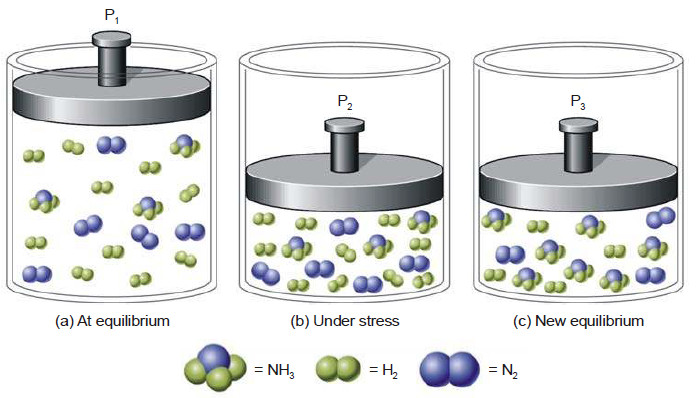
Le Chatelier’s principle
Le Chatelier’s principle – In 1884, the French Chemist Henry Le Chatelier proposed a general principle which applies to all…
Read More » -
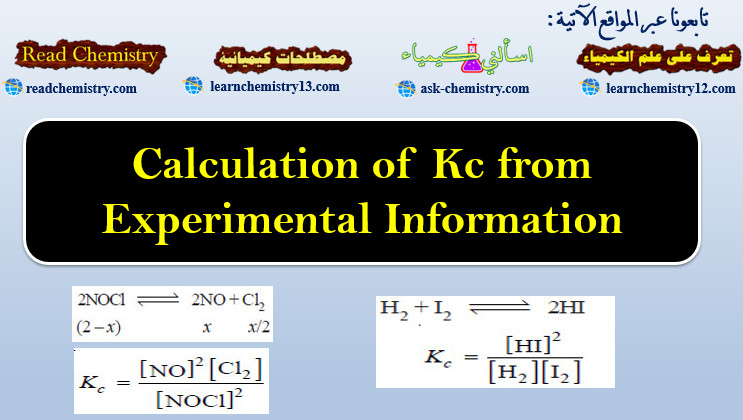
Calculation of Kc from Experimental Information
Calculation of Kc from Experimental Information – To determine the value of Kc of a reaction, write the balanced equation.…
Read More » -
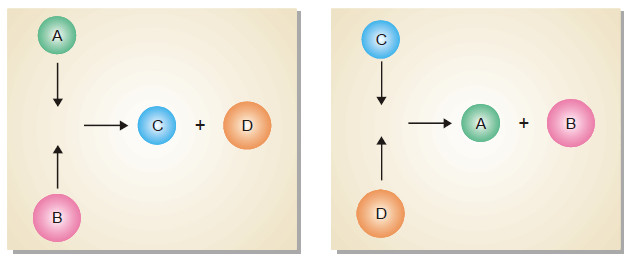
Equilibrium Constant Expression
Equilibrium constant: Equilibrium law – Now we will find the Expression of Equilibrium Constant. – Let us consider a general…
Read More » -
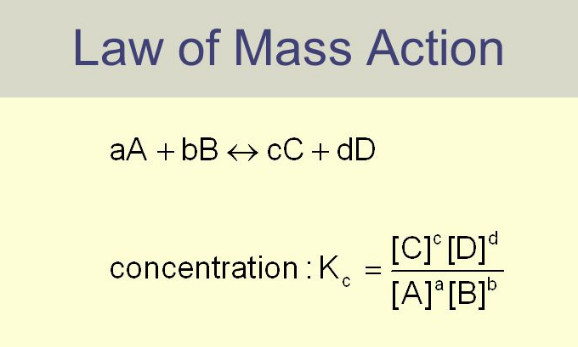
Law of Mass action
Law of Mass action – Two Norwegian chemists, Guldberg and Waage, studied experimentally a large number of equilibrium reactions. In…
Read More » -
Characteristics of Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical Equilibrium is the state of a reversible reaction when the two opposing reactions occur at the same rate and…
Read More » -
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test in the…
Read More » -
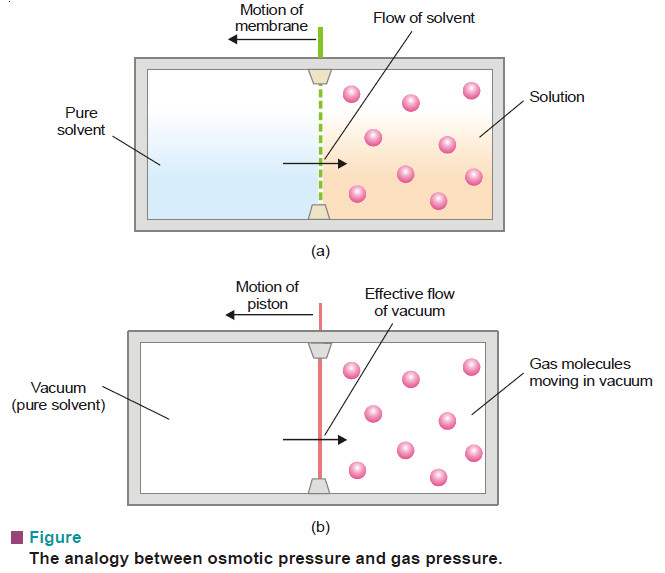
Laws of Osmotic Pressure
Laws of Osmotic Pressure – From a study of the experimental results obtained by Pfeffer, van’t Hoff showed that for…
Read More » -
Theories of Osmosis
Theories of Osmosis – Here we will discuss some theories of osmosis. – Several theories have been advanced to explain…
Read More » -
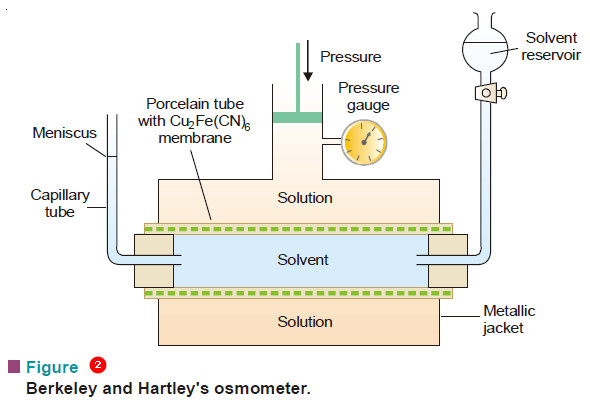
Determination of osmotic pressure
Determination of osmotic pressure – The osmotic pressure of a given solution can be determined experimentally by the methods detailed…
Read More » -
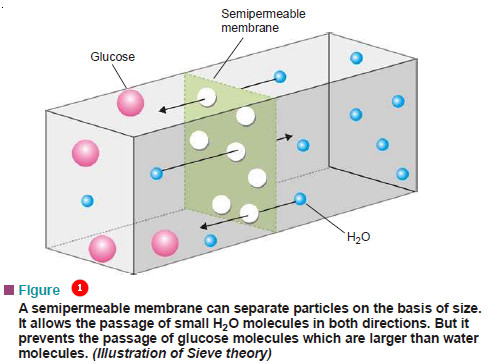
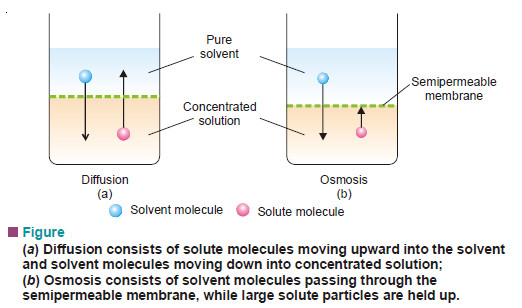
What is Osmosis and Osmotic Pressure?
Diffusion and Osmosis – Just as a gas can diffuse into vacant space or another gas, a solute can diffuse…
Read More » -
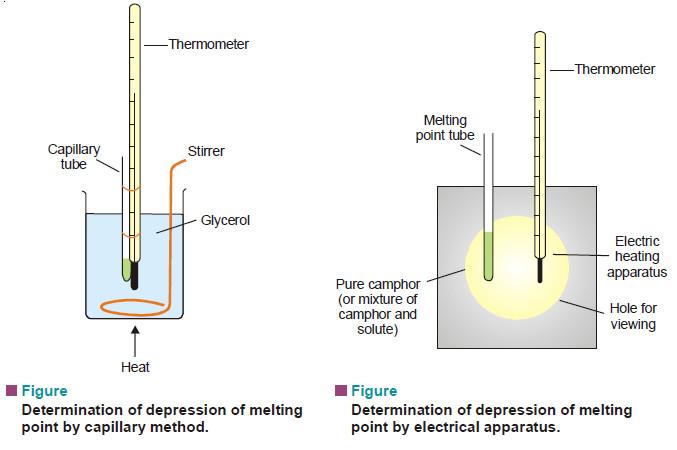
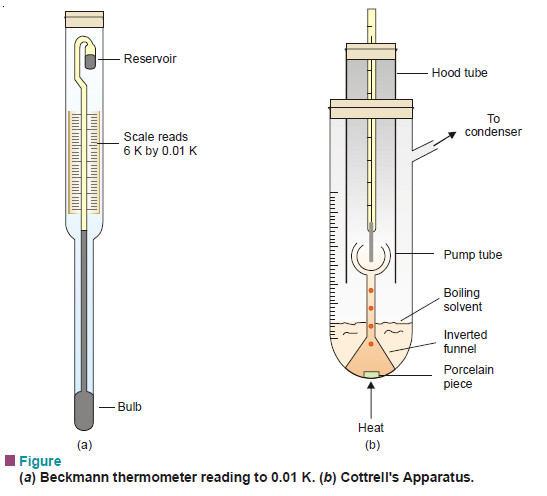
Measurement of freezing point Depression
The subject of Measurement of freezing point Depression will be discused FREEZING POINT DEPRESSION Relation between Depression of Freezing point…
Read More » -
Measurement of boiling point elevation
MEASUREMENT OF BOILING POINT ELEVATION – There are several methods available for the measurement of the elevation of boiling point.…
Read More » -
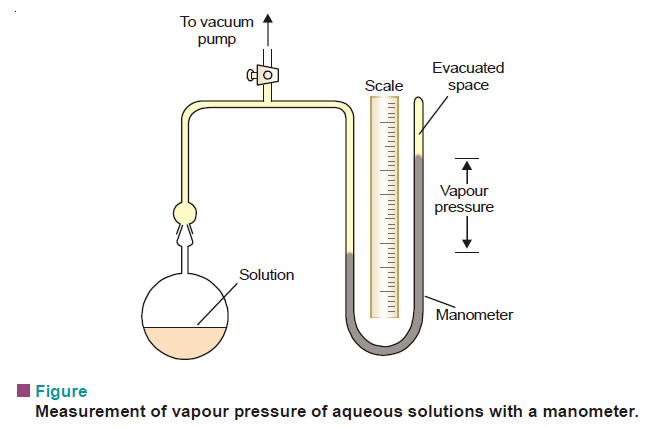
Measurement of lowering of vapour pressure
MEASUREMENT OF LOWERING OF VAPOUR PRESSURE (1) Barometric Method – Raoult measured the individual vapour pressure of a liquid and…
Read More » -
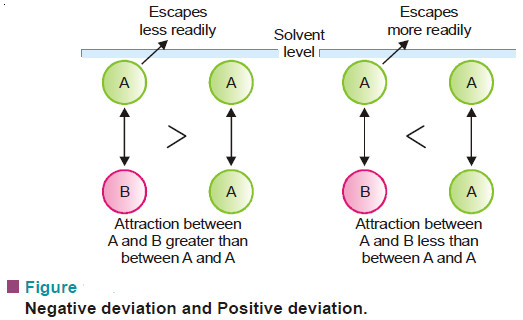
Lowering of vapour pressure- Raoult’s law
In this subject we will restrict our discussion to Raoult’s Law COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIES – Dilute solutions containing non-volatile solute exhibit…
Read More »