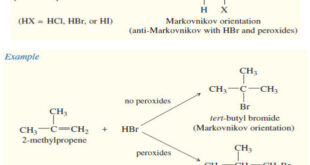
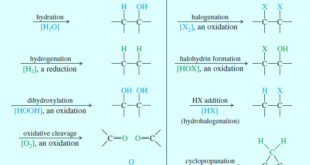
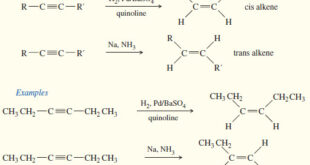
– In this subject we will discuss all famous reactions of alkenes. – The reactions of alkenes include five basic methods as follow: (1) Electrophilic Additions (a) Addition of hydrogen halides – A Russian chemist, Vladimir Markovnikov, first showed the orientation of addition of HBr to alkenes in 1869. – …
Read More »Olefin Metathesis
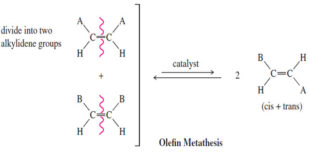
Olefin Metathesis – The double bond is the strongest bond in an alkene, yet it is also the most reactive bond. – Imagine how useful it would be if we could break molecules at their double bonds and reassemble them as we please. That is the goal of olefin metathesis. …
Read More »Polymerization of Alkenes
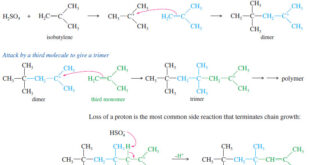
Polymerization of Alkenes – A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating units (the monomers) bonded together. – Alkenes serve as monomers for some of the most common polymers, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene, poly(vinyl chloride), and many others. – Alkenes polymerize to give addition polymers resulting …
Read More »Oxidative Cleavage of Alkenes
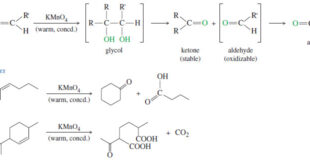
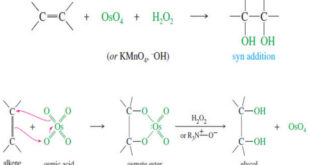
Oxidative Cleavage of Alkenes Cleavage by Permanganate – In a potassium permanganate dihydroxylation, if the solution is warm or acidic or too concentrated, oxidative cleavage of the glycol may occur. – In effect, the double bond is cleaved to two carbonyl groups. – The products are initially ketones and aldehydes, …
Read More »Syn Dihydroxylation of Alkenes
Syn Dihydroxylation of Alkenes – Converting an alkene to a glycol requires adding a hydroxyl group to each end of the double bond. This addition is called Dihydroxylation of Alkenes or dihydroxylation (or hydroxylation) of the double bond. – We have seen that epoxidation of an alkene, followed by acidic …
Read More »Chemical Bonding – Orbital Concept – MCQ test
Online MCQ test on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Concept – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test in the fundmental of Chemical Bonding – Orbital Concept. – It is a simple test to measure the strength of your knowledge in the basics of understanding the topics of Chemical …
Read More »Epoxidation of Alkenes
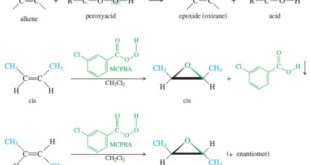
Epoxidation of Alkenes – Some of the most important reactions of alkenes involve oxidation. – When we speak of oxidation, we usually mean reactions that form carbon–oxygen bonds. (Halogens are oxidizing agents, and the addition of a halogen molecule across a double bond is formally an oxidation as well.) – …
Read More »Addition of Carbenes to Alkenes
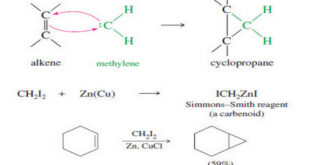
Addition of Carbenes to Alkenes – Methylene (:CH2) is the simplest of the carbenes: uncharged, reactive intermediates that have a carbon atom with two bonds and two nonbonding electrons. – Like borane (BH3), methylene is a potent electrophile because it has an unfilled octet. – It adds to the electronrich …
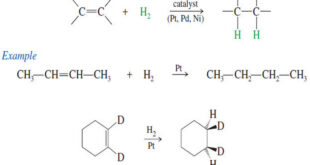
Read More »Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes
Catalytic Hydrogenation of Alkenes – Although we have mentioned catalytic hydrogenation before, we now consider the mechanism and stereochemistry in more detail. – Hydrogenation of an alkene is formally a reduction, with H2 adding across the double bond to give an alkane. – The process usually requires a catalyst containing …
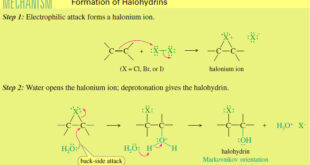
Read More »Formation of Halohydrin
Formation of Halohydrin – A halohydrin is an alcohol with a halogen on the adjacent carbon atom. – In the presence of water, halogens add to alkenes to form halohydrins. – The electrophilic halogen adds to the alkene to give a halonium ion, which is also electrophilic. – Water acts …
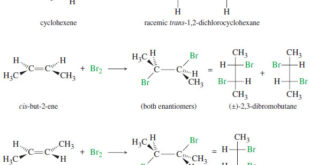
Read More »Addition of Halogens to Alkenes
Addition of Halogens to Alkenes – Addition of Halogens to Alkenes gives vicinal dihalides. (A) Mechanism of Halogen Addition – A halogen molecule (Br2, Cl2, or I2) is electrophilic; a nucleophile can react with a halogen, displacing a halide ion: – In this example, the nucleophile attacks the electrophilic nucleus …
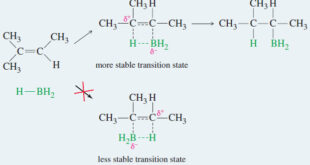
Read More »Hydroboration of Alkenes
Hydroboration of Alkenes – We have seen two methods for hydrating an alkene with Markovnikov orientation. – What if we need to convert an alkene to the anti-Markovnikov alcohol? – For example, the following transformation cannot be accomplished using the hydration procedures covered thus far. – Such an anti-Markovnikov hydration …
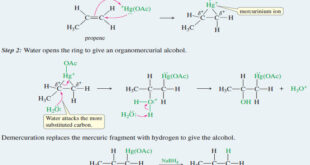
Read More »Oxymercuration–demercuration of alkenes
– Oxymercuration–demercuration of alkenes is another method for converting alkenes to alcohols with Markovnikov orientation. Hydration of alkenes by Oxymercuration–Demercuration – Many alkenes do not easily undergo hydration in aqueous acid. – Some alkenes are nearly insoluble in aqueous acid, and others undergo side reactions such as rearrangement, polymerization, or …
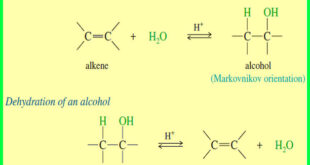
Read More »Hydration of Alkenes: Addition of Water
Hydration of Alkenes will be discussed by Addition of Water Addition of Water: Hydration of Alkenes – An alkene may react with water in the presence of a strongly acidic catalyst to form an alcohol. – Formally, this reaction is a hydration (the addition of water), with a hydrogen atom …
Read More »Common Uses of Alkyl Halides
Alkyl halides as Solvents – Alkyl halides are used primarily as industrial and household solvents. – Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) was once used for dry cleaning, spot removing, and other domestic cleaning. – Carbon tetrachloride is toxic and carcinogenic (causes cancer), however, so dry cleaners now use 1,1,1-trichloroethane and other solvents …
Read More »Chemical Bonding – Lewis Theory – Online MCQ test
Online MCQ test on Chemical Bonding – Lewis Theory – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test in the fundmental of Chemical Bonding – Lewis Theory . – It is a simple test to measure the strength of your knowledge in the basics of understanding the topics of …
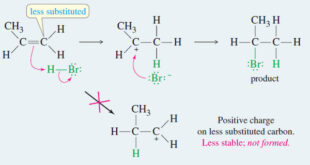
Read More »Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes: Markovnikov’s Rule
Addition of Hydrogen Halides to Alkenes : Markovnikov’s Rule Orientation of Addition: Markovnikov’s Rule – The simple mechanism shown for addition of HBr to but-2-ene applies to a large number of electrophilic additions. – We can use this mechanism to predict the outcome of some fairly complicated reactions. – For …
Read More »Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes
Electrophilic Addition to Alkenes Reactivity of the Carbon–Carbon Double Bond – All alkenes have a common feature: a carbon–carbon double bond. – The reactions of alkenes arise from the reactivity of the carbon–carbon double bond. – Once again, the concept of the functional group helps to organize and simplify the …
Read More »Structure of atom – Classical mechanics – Online MCQ test
Online MCQ test on Structure of atom – Classical mechanics – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test in the fundmental of Structure of atom – Classical mechanics . – It is a simple test to measure the strength of your knowledge in the basics of understanding the …
Read More »Synthesis of Alkenes – Six methods
Methods for Synthesis of Alkenes – Six methods for Synthesis of Alkenes will be discussed as follow: (1) Dehydrohalogenation of alkyl halides – Dehydrohalogenation is the elimination of a hydrogen and a halogen from an alkyl halide to form an alkene. – dehydrohalogenation can take place by the E1 and …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry