Online MCQ test on gaseous state – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test in the fundmental of gaseous state . – It is a simple test to measure the strength of your knowledge in the basics of understanding the topics of gaseous state. – The test consists …
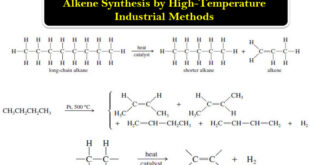
Read More »Alkene Synthesis by High-Temperature Industrial Methods
Alkene Synthesis by High-Temperature Industrial Methods (1) Catalytic Cracking of Alkanes – The least expensive way to make alkenes on a large scale is by the catalytic cracking of petroleum: heating a mixture of alkanes in the presence of a catalyst (usually aluminosilicates). – Alkenes are formed by bond cleavage …
Read More »Alkene Synthesis by Dehydration of Alcohols
Alkene Synthesis by Dehydration of Alcohols – Dehydration of alcohols is a common method for making alkenes. The word dehydration literally means “removal of water.” – Dehydration is reversible, and in most cases the equilibrium constant is not large. – In fact, the reverse reaction (hydration) is a method for …
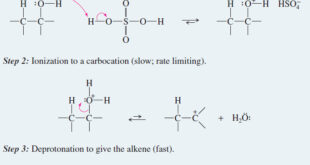
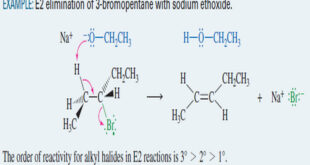
Read More »Alkene Synthesis by Elimination of Alkyl Halides
Alkene Synthesis by Elimination of Alkyl Halides – Dehydrohalogenation is the elimination of a hydrogen and a halogen from an alkyl halide to form an alkene. – dehydrohalogenation can take place by the E1 and E2 mechanisms. – The second-order elimination (E2) is usually better for synthetic purposes because the …
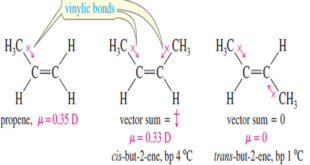
Read More »Physical Properties of Alkenes
Physical Properties of Alkenes (1) Boiling Points and Densities – Most physical properties of alkenes are similar to those of the corresponding alkanes. – For example, the boiling points of but-1-ene, cis-but-2-ene, trans-but-2-ene, and n-butane are all close to 0 °C. – Also like the alkanes, alkenes have densities around …
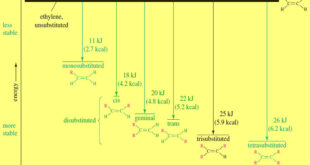
Read More »Stability of Alkenes
Stability of Alkenes – In making alkenes, we often find that the major product is the most stable alkene. – Many reactions also provide opportunities for double bonds to rearrange to more stable isomers. – Therefore, we need to know how the stability of an alkene depends on its structure. …
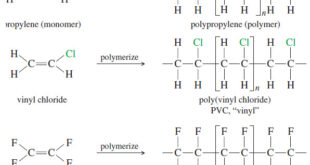
Read More »Commercial Importance of Alkenes
Commercial Importance of Alkenes – Because the carbon–carbon double bond is readily converted to other functional groups, alkenes are important intermediates in the synthesis of polymers, drugs, pesticides, and other valuable chemicals. – Ethylene is the organic compound produced in the largest volume, at around 160 billion pounds per year …
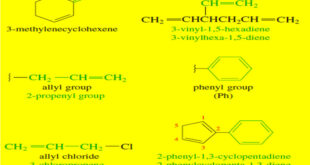
Read More »Nomenclature of Alkenes
Nomenclature of Alkenes – Simple alkenes are named much like alkanes, using the root name of the longest chain containing the double bond. The ending is changed from -ane to -ene. – For example, (ethane) becomes “ethene,” (propane) becomes “propene,” and “cyclohexane” becomes “cyclohexene”. – When the chain contains more …
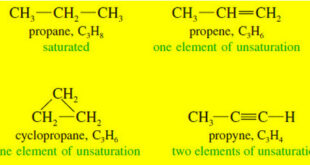
Read More »Elements of Unsaturation
Elements of Unsaturation (1) Elements of Unsaturation in Hydrocarbons – Alkenes are said to be unsaturated because they are capable of adding hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. – The product, an alkane, is called saturated because it cannot react with any more hydrogen. – The presence of a …
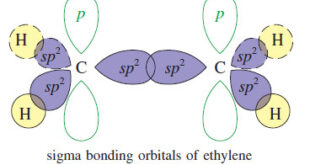
Read More »The Orbital Description of the Alkene Double Bond
The Orbital Description of the Alkene Double Bond – In a Lewis structure, the double bond of an alkene is represented by two pairs of electrons between the carbon atoms. – The Pauli exclusion principle tells us that two pairs of electrons can go into the region of space between …
Read More »Acids and Bases – Online MCQ test
Online MCQ test on Acids and Bases – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test in the fundmental of Acids and Bases . – It is a simple test to measure the strength of your knowledge in the basics of understanding the topics of Acids and Bases – …
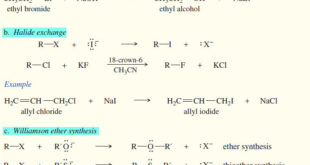
Read More »Reactions of Alkyl Halides
In this subject we will discuss the Reactions of Alkyl Halides with chemical equations and examples Introduction to Alkyl Halides – Our study of organic chemistry is organized into families of compounds classified by their functional groups. – We use alkyl halides to introduce substitution and elimination, two of the …
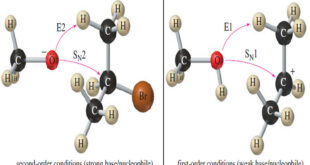
Read More »Predicting SN1 SN2 E1 E2 reactions
Predicting the mechanisms: SN1, SN2, E1, E2 reactions – In this subject we will learn how to predict the the mechanisms of SN1, SN2, E1, E2 reactions – Given a set of reagents and solvents, how can we predict what products will result and which mechanisms will be involved? – …
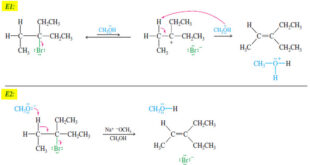
Read More »Comparison of E1 and E2 reactions
Comparison of E1 and E2 Elimination Mechanisms – Let’s summarize the major points to remember about the E1 and E2 reactions, focusing on the factors that help us predict which of these mechanisms will operate under a given set of experimental conditions. Then we will organize these factors into a …
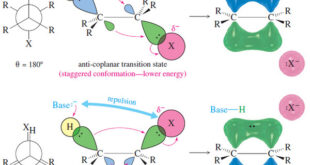
Read More »Stereochemistry of the E2 Reaction
Stereochemistry of the E2 Reaction – In this subject Stereochemistry of the E2 Reaction will be discussed – Like the SN2 reaction, the E2 reaction follows a concerted mechanism: Bond breaking and bond formation take place at the same time, and the partial formation of new bonds lowers the energy …
Read More »Thermochemistry – online MCQ test
Online MCQ test on Thermochemistry – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test in the fundmental of Thermochemistry. – It is a simple test to measure the strength of your knowledge in the basics of understanding the topics of Thermochemistry – The test consists of only (15) questions …
Read More »Nuclear Chemistry – online MCQ test
Online MCQ test in Nuclear Chemistry – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test in the fundmental of Nuclear Chemistry. – It is a simple test to measure the strength of your knowledge in the basics of understanding the topics of Nuclear Chemistry – The test consists of …
Read More »E2 Reaction : Second-Order Elimination
Second-Order Elimination: The E2 Reaction – Eliminations can also take place under second-order conditions with a strong base present. – As an example, consider the reaction of tert-butyl bromide with methoxide ion in methanol. – This is a second-order reaction because methoxide ion is a strong base as well as …
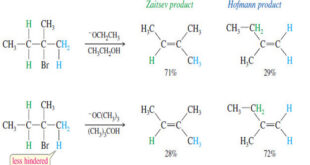
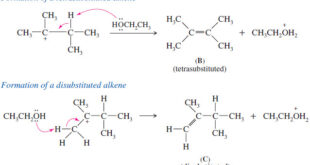
Read More »Zaitsev’s Rule : Positional Orientation of Elimination
Positional Orientation of Elimination: Zaitsev’s Rule – In this subject , Positional Orientation of Elimination: Zaitsev’s Rule will be discussed – Many compounds can eliminate in more than one way, to give mixtures of alkenes. – In many cases, we can predict which elimination product will predominate. – In the …
Read More »E1 Reaction : First-Order Elimination
First-Order Elimination : The E1 Reaction – An elimination involves the loss of two atoms or groups from the substrate, usually with formation of a pi bond. – Elimination reactions frequently accompany and compete with substitutions. – By varying the reagents and conditions, we can often modify a reaction to …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry