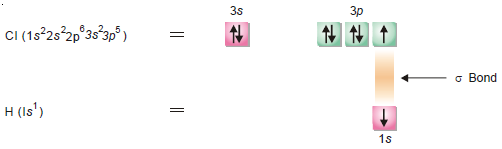Orbital Representation of Molecules
– In this subject, we will discuss the Orbital Representation of some Molecules
(1) Orbital Representation of H2 molecule
– Each hydrogen atom has one electron in 1s-orbital.
– Two such atoms join to form a molecule of hydrogen.
– In this case s–s overlapping between two 1s-orbitals of hydrogen atoms taken place resulting in the formation of hydrogen molecule.
– There exists a sigma bond between two H-atoms.
– The situation is represented below:
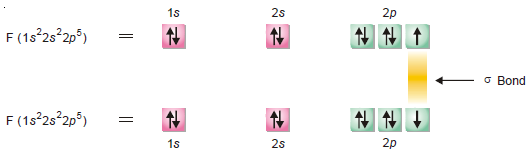
(2) Orbital Representation of F2 molecule
– Fluorine (at. no. 9) atom has electron configuration 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py2 2pz1.
– The unpaired electron in 2pz orbital of one atom overlaps with similar orbital of other Fluorine atom along internuclear axis leading to the formation of σ bond.
– It is represented as follows:
(3) Formation of HCl molecule
– During the formation of HCl molecule, 1s orbital of Hydrogen atom having an unpaired electron overlaps with 3pz orbital of chlorine atom having electronic configuration 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3px2 3py2 3pz1.
– This overlapping takes place along the internuclear axis leading to the formation of σ bond as shown below:
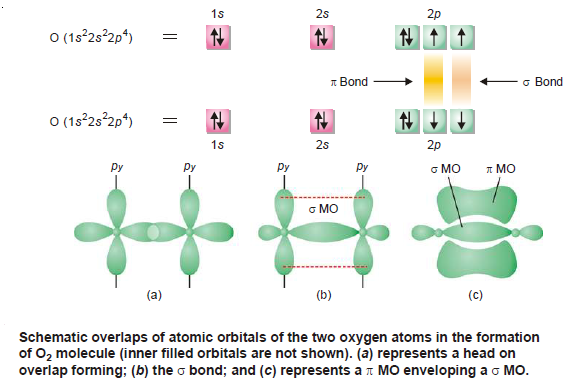
(4) Formation of O2 molecule
– Oxygen (at. no. 8) atom has electronic configuration 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py1 2pz1.
– In the formation of O2 molecule 2pz orbital of one oxygen atom overlaps with the similar orbital of the other atom along internuclear axis leading to the formation of a sigma (σ) bond.
– The other 2pyorbital of one oxygen atom overlaps with the similar orbital of the another oxygen atom in sidewise manner forming a pi (π) bond.
– Thus an oxygen molecule contains a double bond consisting of a sigma (σ) bond and a pi (π) bond.
– The orbital overlap is represented below:
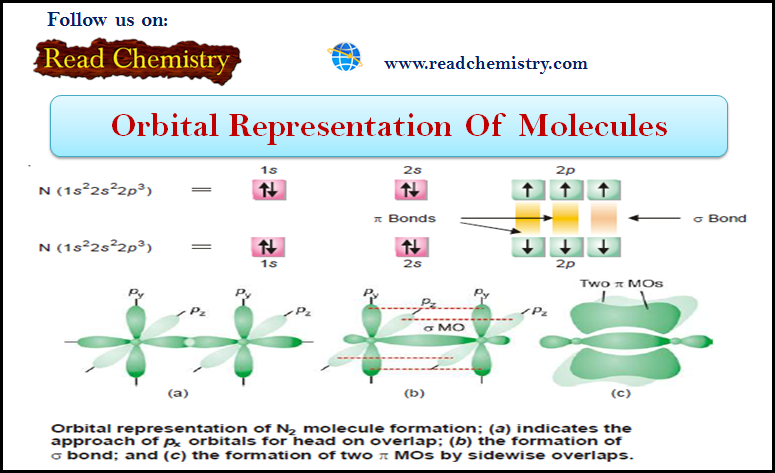
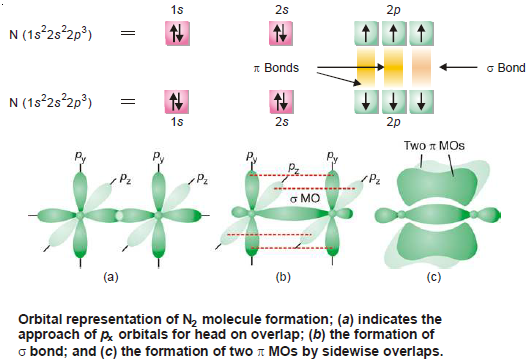
(5) Formation of N2 Nitrogen molecule
– Nitrogen atom has three bonding electrons 2px1 2py1 2pz1 is its valence shell.
– These electrons are present in three p-orbitals which are directed along three axes at right angles.
– When two N atoms approach each other, 2pz orbitals overlap in head-on manner to form a sigma (σ) bond, leaving two sets of parallel 2py and 2px orbitals.
– Now the electron clouds in these orbitals interact to produce two pi (π) bonds by the sidewise overlaps.
– Thus in N2 molecule two N atoms are bonded by a triple bond consisting of one sigma (σ) and two pi (π) bonds.
– The orbital overlap in N2 molecule is shown below:
– Thus there is one sigma and two pi bonds in a molecule of nitrogen.
– It is equivalent to a triple bond in the classical theory.
(6) Orbital Representation of H2O molecule
– Oxygen atom has two half-filled orbitals in its second energy shell as its electronic configuration is 1s2 2s2 2px2 2py1 2pz1.
– Here 2pz orbital having an unpaired electron overlaps with 1s orbital of hydrogen forming a sigma (σ) bond.
– In a similar way, 2py orbital of the oxygen atom overlaps with 1s orbital of the second hydrogen atom forming another sigma (σ) bond.
– Thus in the H2O molecule two H atoms are bonded to an oxygen atom with sigma (σ) bonds as shown below:
Reference: Essentials of Physical Chemistry /Arun Bahl, B.S Bahl and G.D. Tuli / multicolour edition.