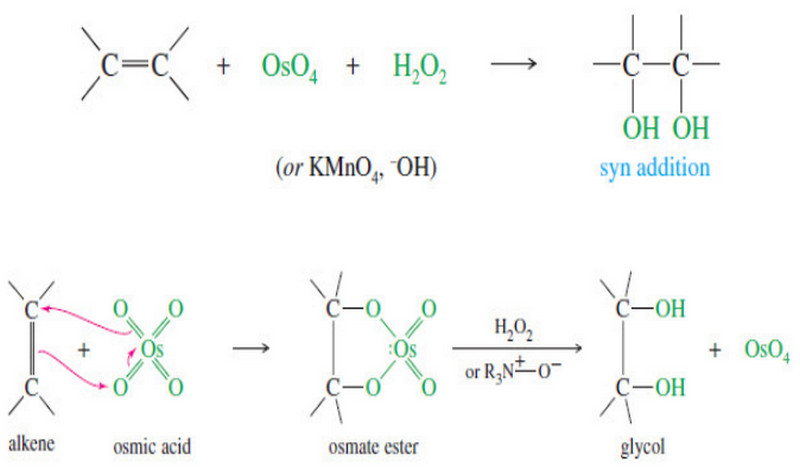
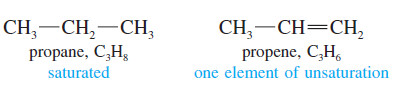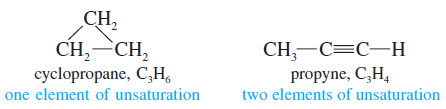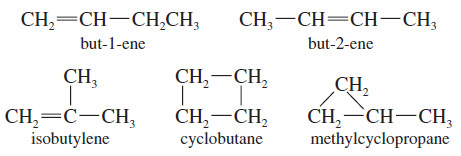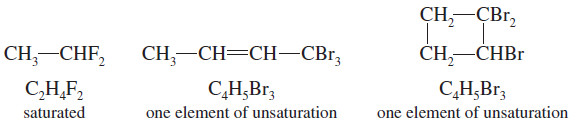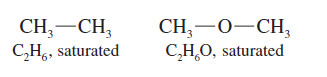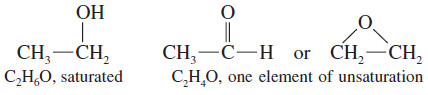Elements of Unsaturation
Elements of Unsaturation
(1) Elements of Unsaturation in Hydrocarbons
– Alkenes are said to be unsaturated because they are capable of adding hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst.
– The product, an alkane, is called saturated because it cannot react with any more hydrogen.
– The presence of a pi bond of an alkene (or an alkyne) or the ring of a cyclic compound decreases the number of hydrogen atoms in a molecular formula.
– These structural features are called elements of unsaturation.
– Each element of unsaturation corresponds to two fewer hydrogen atoms than in the “saturated” formula.
– Consider, for example, the formula C4H8.
– A saturated alkane would have a CnH(2n+2) formula, or C4H10.
– The formula C4H8 is missing two hydrogen atoms, so it has one element of unsaturation, either a pi bond or a ring.
– There are five constitutional isomers of formula C4H8:
– When you need a structure for a particular molecular formula, it helps to find the number of elements of unsaturation.
– Calculate the maximum number of hydrogen atoms from the saturated formula, CnH(2n+2) and see how many are missing.
– The number of elements of unsaturation is simply half the number of missing hydrogens.
– This simple calculation allows you to consider possible structures quickly, without always having to check for the correct molecular formula.
(2) Elements of Unsaturation with Heteroatoms
– Heteroatoms (hetero, “different”) are any atoms other than carbon and hydrogen.
– The rule for calculating elements of unsaturation in hydrocarbons can be extended to include heteroatoms.
– Let’s consider how the addition of a heteroatom affects the number of hydrogen atoms in the formula.
Halogens
– Halogens simply substitute for hydrogen atoms in the molecular formula.
– The formula C2H6 is saturated, so the formula C2H4F2 is also saturated.
– C4H8 has one element of unsaturation, and C4H5Br3 also has one element of unsaturation.
– In calculating the number of elements of unsaturation, simply count halogens as hydrogen atoms.
Oxygen
– An oxygen atom can be added to the chain (or added to a C-H bond to make a C-OH group) without changing the number of hydrogen atoms or carbon atoms.
– In calculating the number of elements of unsaturation, ignore the oxygen atoms.
Nitrogen
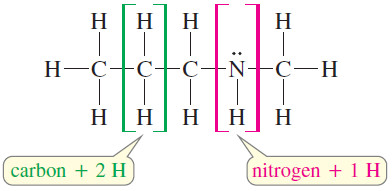
– A nitrogen atom can take the place of a carbon atom in the chain, but nitrogen is trivalent, having only one additional hydrogen atom, compared with two hydrogens for each additional carbon atom.
– In computing the elements of unsaturation, count nitrogen as half a carbon atom.
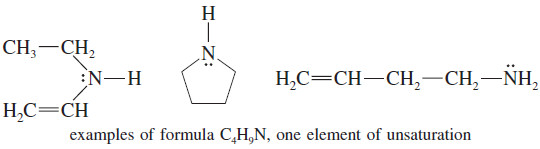
– The formula C4H9N is like a formula with 4.5 carbon atoms, with saturated formula C4.5H9+2
– The formula C4H9N has one element of unsaturation, because it is two hydrogen atoms short of the saturated formula.
Solved Problem
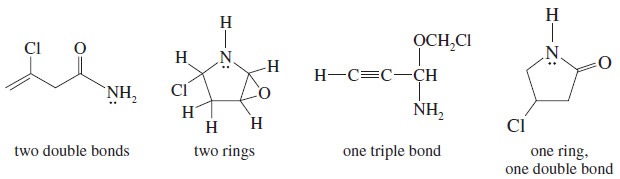
Draw at least four compounds of formula C4H6NOCl.
Solution:
– Counting the nitrogen as 1/2 carbon, ignoring the oxygen, and counting chlorine as a hydrogen shows the formula is equivalent to C4.5H7.
– The saturated formula for 4.5 carbon atoms is C4.5H11, so C4H6NOCl has two elements of unsaturation.
– These could be two double bonds, two rings, one triple bond, or a ring and a double bond.
– There are many possibilities, four of which are listed here.