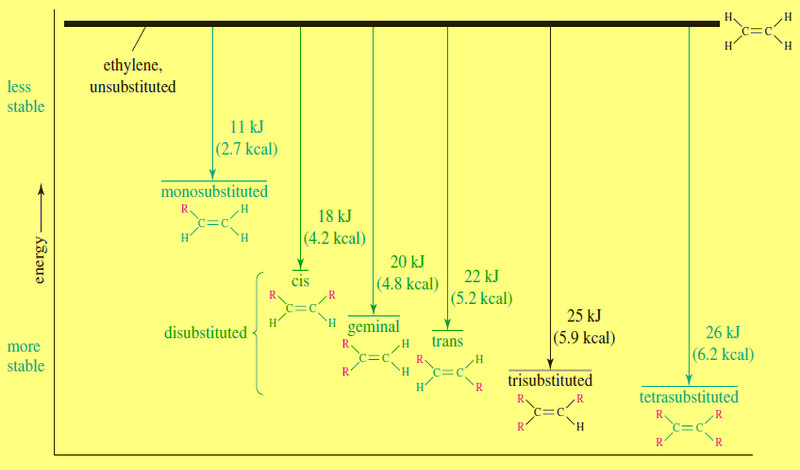
Commercial Importance of Alkenes
Commercial Importance of Alkenes
– Because the carbon–carbon double bond is readily converted to other functional groups, alkenes are important intermediates in the synthesis of polymers, drugs, pesticides, and other valuable chemicals.
– Ethylene is the organic compound produced in the largest volume, at around 160 billion pounds per year worldwide.
– Most of this ethylene is polymerized to form about 90 billion pounds of polyethylene per year.
– The remainder is used to synthesize a wide variety of organic chemicals including ethanol, acetic acid, ethylene glycol, and vinyl chloride.
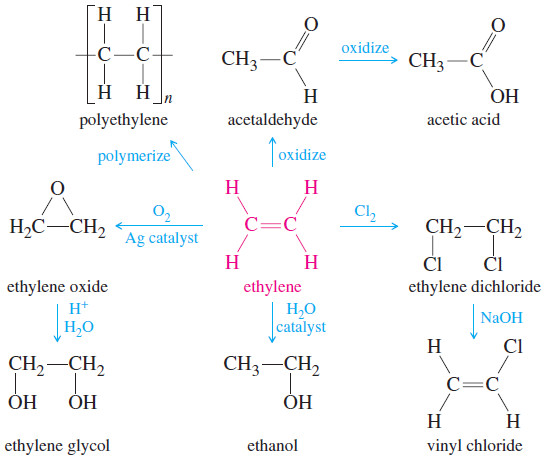
– Ethylene also serves as a plant hormone, accelerating the ripening of fruit.
– For example, tomatoes are harvested and shipped while green, then treated with ethylene to make them ripen and turn red just before they are placed on display.
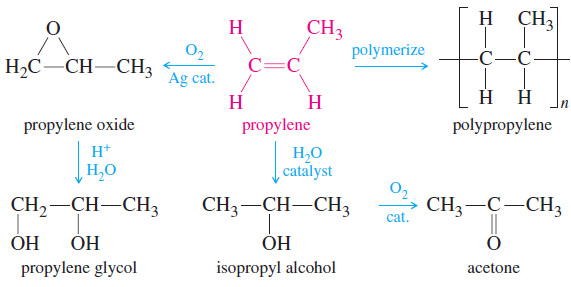
– Propylene is produced at the rate of about 90 billion pounds per year worldwide, with much of that going to make about 40 billion pounds of polypropylene.
– The rest is used to make propylene glycol, acetone, isopropyl alcohol, and a variety of other useful organic chemicals.
Alkenes as polymers
– Polymers is one of the common Commercial Importance of Alkenes
– Many common polymers are made by polymerizing alkenes.
– These polymers are used in consumer products from shoes to plastic bags to car bumpers.
– A polymer (Greek, poly, “many,” and meros, “parts”) is a large molecule made up of many monomer (Greek, mono, “one”) molecules.
– An alkene monomer can polymerize by a chain reaction where additional alkene molecules add to the end of the growing polymer chain.
– Because these polymers result from addition of many individual alkene units, they are called addition polymers.
– Polyolefins are polymers made from monofunctional (single functional group) alkenes such as ethylene and propylene.
– The following Figure shows some addition polymers made from simple alkenes and haloalkenes.
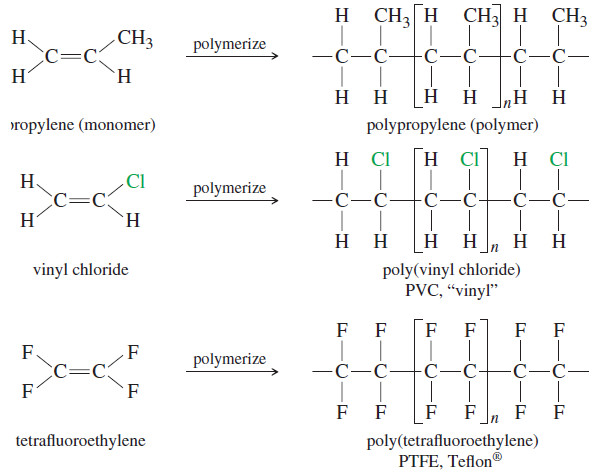
– We discuss polymerization reactions in the following subjects.