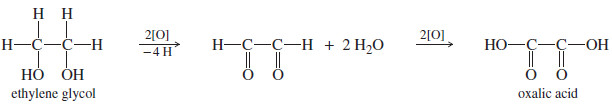Biological Oxidation of Alcohols
– In this topic, the Biological Oxidation of Alcohols and their effect on the humans and animals will be discussed
Biological Oxidation of Alcohols
– Although it is the least toxic alcohol, ethanol is still a poisonous substance.
– When someone is suffering from a mild case of ethanol poisoning, we say that he or she is intoxicated.
– Animals often consume food that has fermented and contains alcohol.
– Their bodies must detoxify any alcohol in the food to keep it from building up in the blood and poisoning the brain.
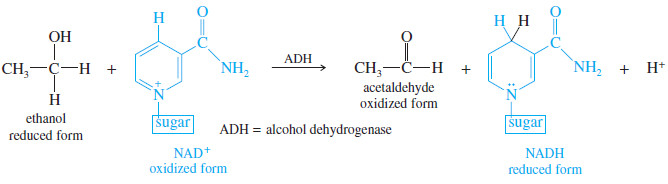
– To detoxify ethanol, the liver produces an enzyme called alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH).
– Alcohol dehydrogenase catalyzes an oxidation: the removal of two hydrogen atoms from the alcohol molecule.
– The oxidizing agent is nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). NAD exists in two forms: the oxidized form, called NAD+,and the reduced form, called NADH.
– The following equation shows that ethanol is oxidized to acetaldehyde, and NAD+ is reduced to NADH.
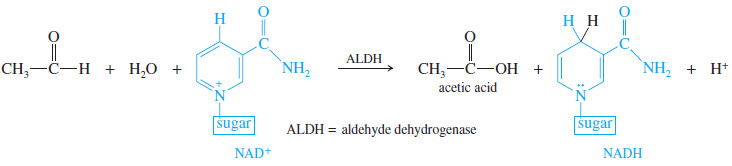
– A subsequent oxidation, catalyzed by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH), converts acetaldehyde to acetic acid, a normal metabolite.
– These oxidations take place with most small primary alcohols.
– Unfortunately, the oxidation products of some other alcohols are more toxic than acetic acid.
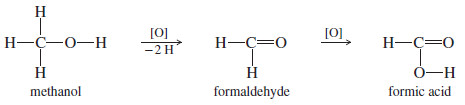
– Methanol is oxidized first to formaldehyde and then to formic acid.
– Both of these compounds are more toxic than methanol itself.
– Ethylene glycol is a toxic diol. Its oxidation product is oxalic acid, the toxic compound
found in the leaves of rhubarb and many other plants.
Many poisonings by Alcohol
– Many poisonings by methanol and ethylene glycol occur each year.
– Alcoholics occasionally drink ethanol that has been denatured by the addition of methanol.
– Methanol is oxidized to formic acid, which may cause blindness and death.
– Dogs are often poisoned by sweet-tasting ethylene glycol when antifreeze is left in an open container.
– Once the glycol is metabolized to oxalic acid, the dog’s kidneys fail, causing death.
– The treatment for methanol or ethylene glycol poisoning is the same.
– The patient is given intravenous infusions of diluted ethanol.
– The ADH enzyme is swamped by all the ethanol, allowing time for the kidneys to excrete most of the methanol (or ethylene glycol) before it can be oxidized to formic acid (or oxalic acid). This is an example of competitive inhibition of an enzyme.
– The enzyme catalyzes oxidation of both ethanol and methanol, but a large quantity of ethanol ties up the enzyme, allowing time for excretion of most of the methanol before it is oxidized
What is NAD+?
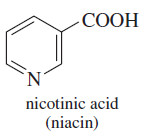
– NAD+ is derived from vitamin B3, known as niacin.
– There is a misconception that taking large supplements of niacin before a night of drinking ethanol will lessen the severity of the (hangover) the next morning.
– Metabolism is more complex than this simple idea suggests.
– One common effect of taking large amounts of niacin is flushing caused by dilation of the capillaries in the skin.
– This flushing looks like a severe sunburn and can be quite uncomfortable, but it usually subsides in a few hours.