Organic Chemistry
Organic Chemistry focuses on the structure, properties, and reactions of carbon-containing compounds. It’s essential in pharmaceuticals, polymers, and biochemistry, exploring mechanisms, functional groups, and synthesis of complex molecules.
-
Physical Properties and Molecular Structure of Organic compound
** So far, we have said little about one of the most obvious characteristics of organic compounds— that…
Read More » -
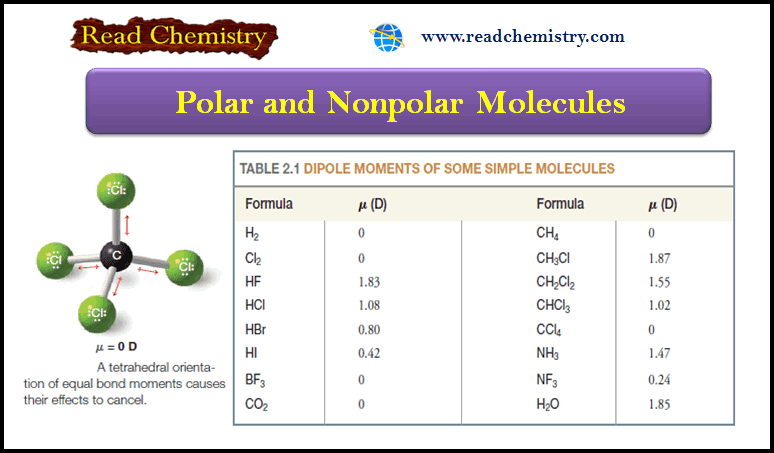
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
– In this subject, we will discuss the Polar and Nonpolar Molecules. Dipole moment – The dipole moment is a…
Read More » -
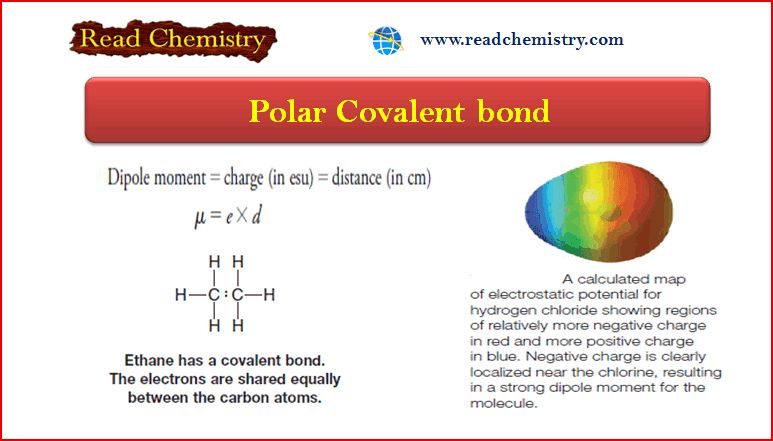
Polar Covalent Bond and Dipole moment
– In this subject, we will discuss the Polar Covalent Bond and Dipole moment. Polar Covalent Bonds – Covalent bonds…
Read More » -
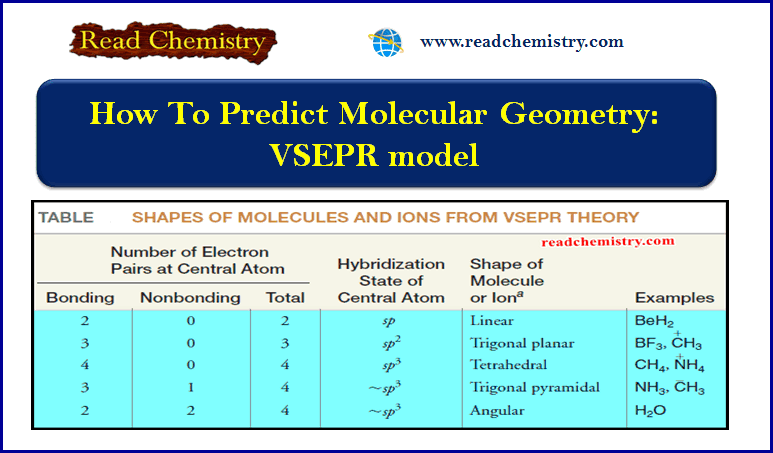
How To Predict Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model
How To Predict Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model ** We can predict the arrangement of atoms in molecules and…
Read More » -
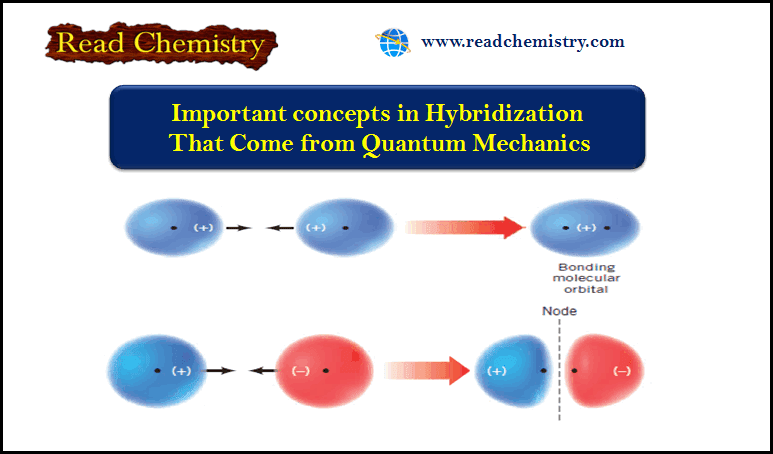
Important concepts in Hybridization That Come from Quantum Mechanics
Important concepts in Hybridization (1) An atomic orbital (AO) corresponds to a region of space about the nucleus of a single…
Read More » -
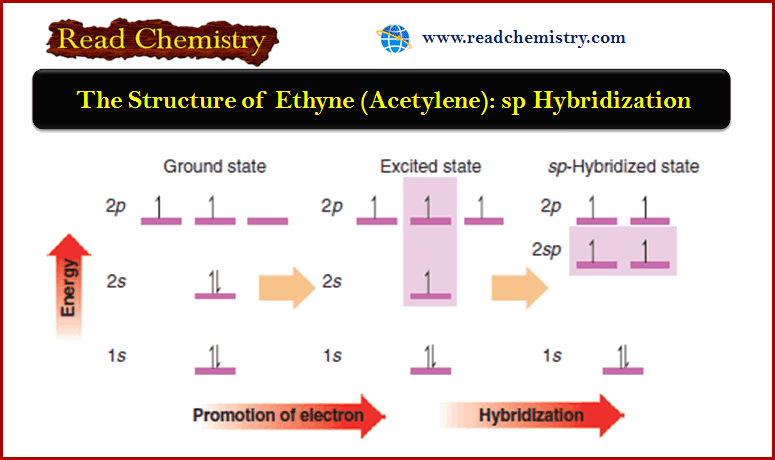
The Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene): sp Hybridization
The Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene): sp Hybridization ** Hydrocarbons in which two carbon atoms share three pairs of electrons between…
Read More » -
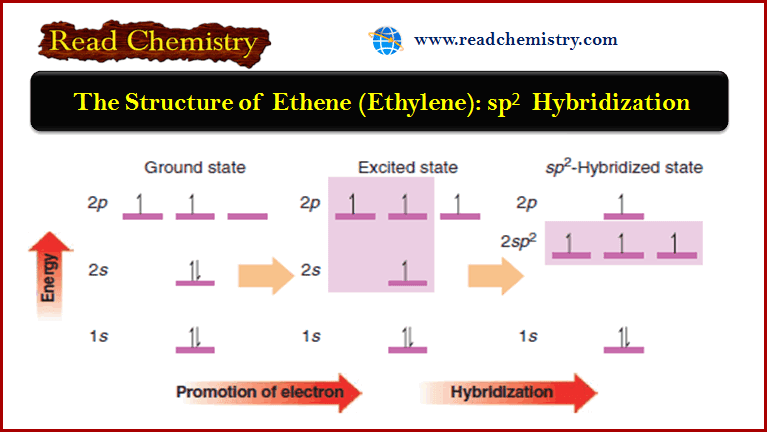
The Structure of Ethene (Ethylene): sp2 Hybridization
The Structure of Ethene (Ethylene): sp2 Hybridization ** The carbon atoms of many of the molecules that we…
Read More » -
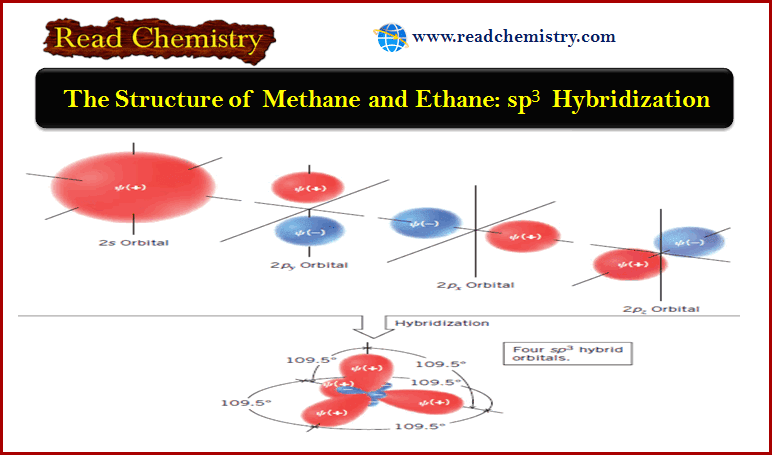
The Structure of Methane and Ethane: sp3 Hybridization
** The (s) and (p) orbitals used in the quantum mechanical description of the carbon atom, were based…
Read More » -
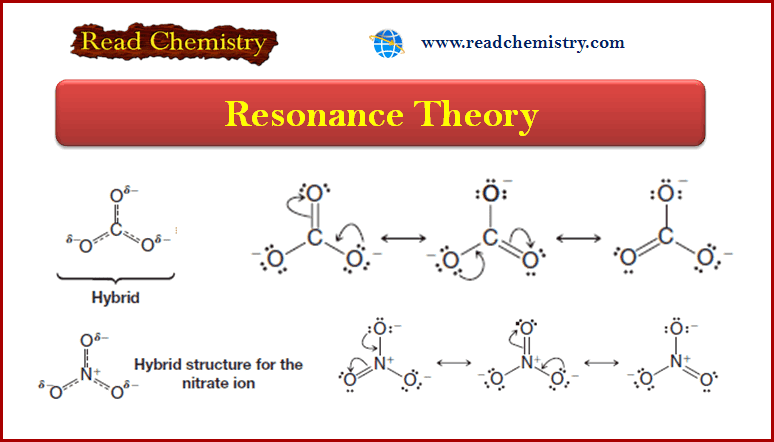
Resonance Theory
Introduction to Resonance (Resonance in carbonate ion (CO32-) ** Often more than one equivalent Lewis structure can be…
Read More » -
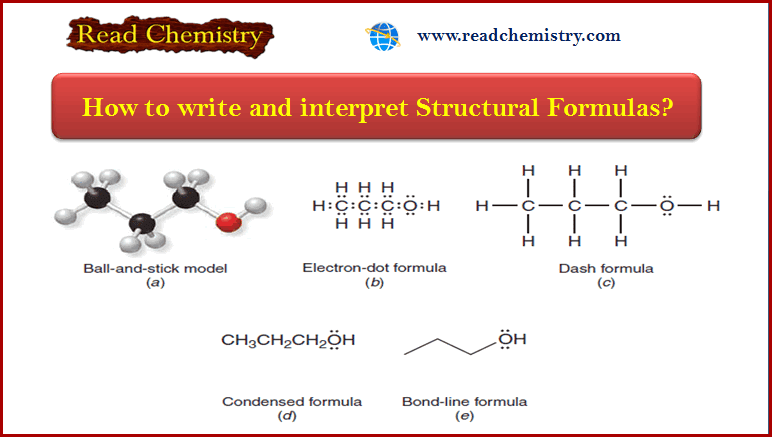
How to write and interpret Structural Formulas?
** Organic chemists use a variety of formats to write structural formulas. ** Structural Formulas are written…
Read More » -
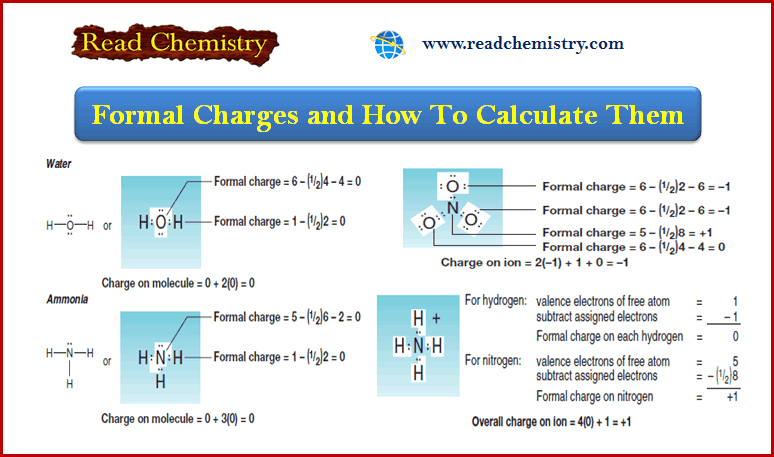
Formal Charge: Definition, Formula, Calculation, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Formal Charge: Definition, Formula, Calculation, Examples Formal Charge and How To Calculate…
Read More » -
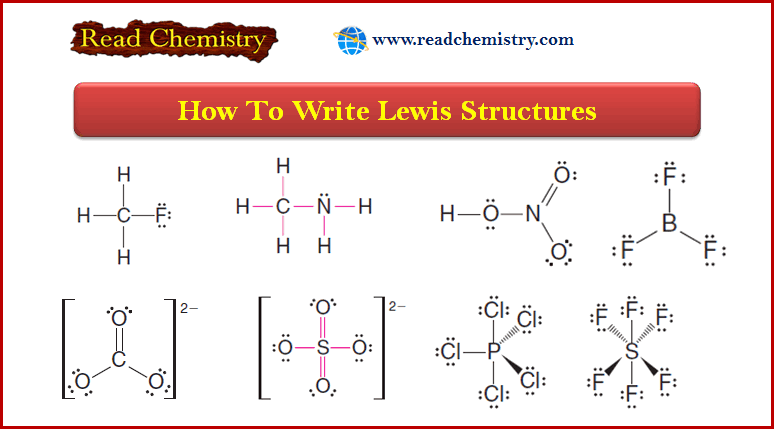
Lewis Structures: Definition, Structural Formula, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Lewis Structures: Definition, Overview, Structural Formula, Examples Definition of Lewis structures –…
Read More » -
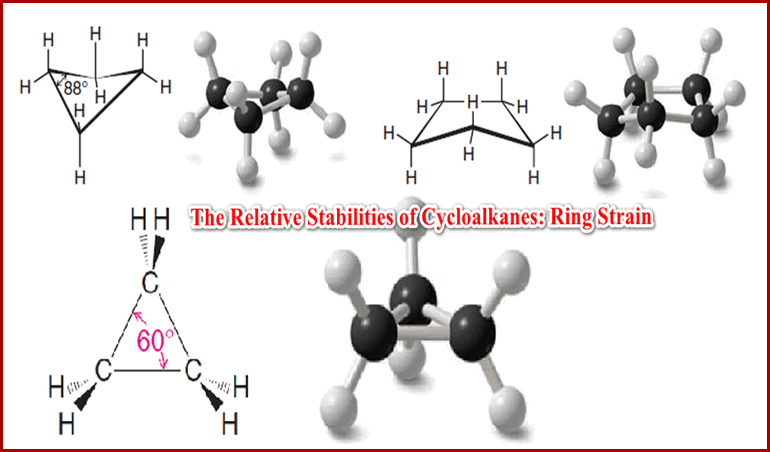
The Relative Stabilities of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain
The Relative Stabilities of Cycloalkanes: Ring Strain ** Cycloalkanes do not all have the same relative stability. Experiments have…
Read More » -
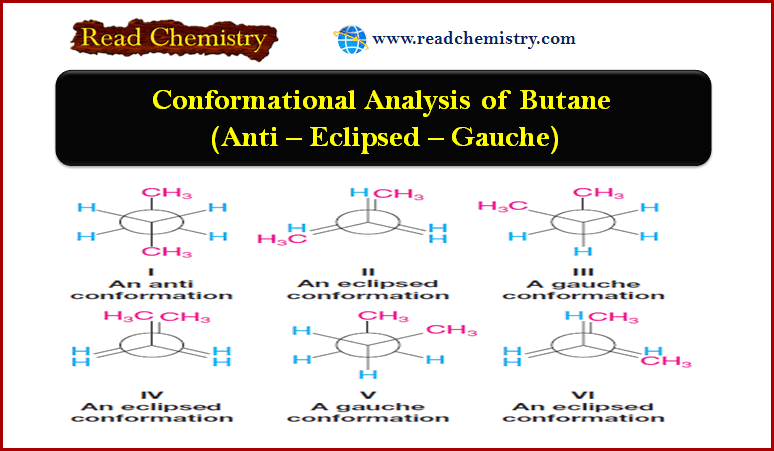
Conformational Analysis of Butane (Anti – Eclipsed – Gauche)
Conformational Analysis of Butane ** Now let us consider rotation about the C2—C3 bond of butane. The barriers to…
Read More » -
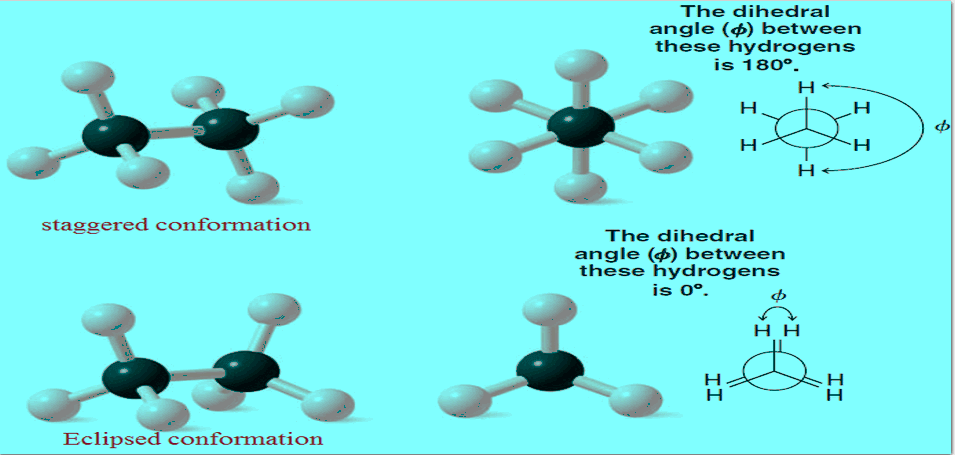
Sigma Bond and Bond Rotation
– In this subject, we will discuss the Sigma Bond and Bond Rotation – Two groups bonded by only a…
Read More » -
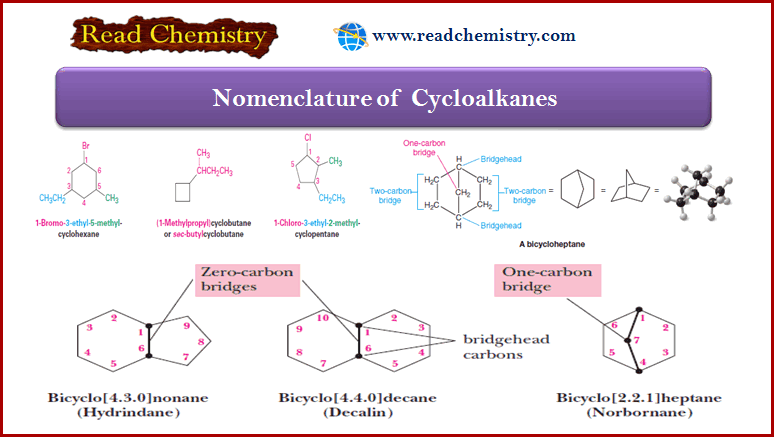
Nomenclature of Cycloalkanes: Monocyclic, Bicyclic
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nomenclature of Cycloalkanes: Monocyclic, Bicyclic What are Cycloalkanes? – Saturated cyclic hydrocarbons…
Read More » -
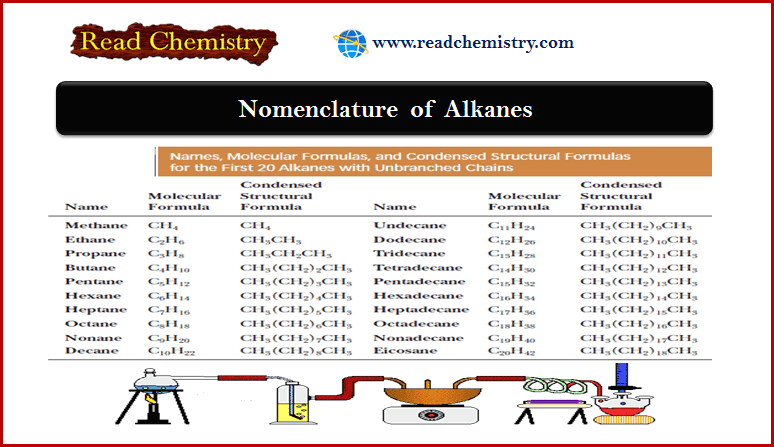
Nomenclature of Alkanes: Rules, IUPAC Name, Common Name
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nomenclature of Alkanes: Rules, IUPAC Name, Common Name What is Alkanes? –…
Read More » -
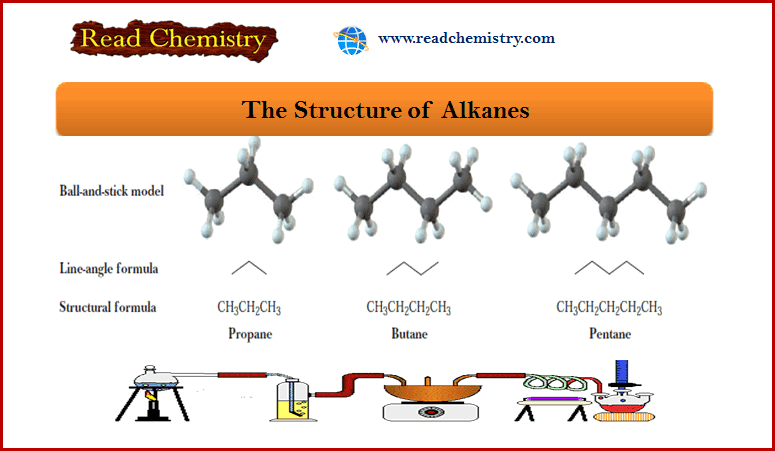
Alkanes: Definition, Formula, Structure, List, Examples
What is Alkanes? – Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons; that is, they contain only carbon-carbon single bonds. – In this context,…
Read More » -
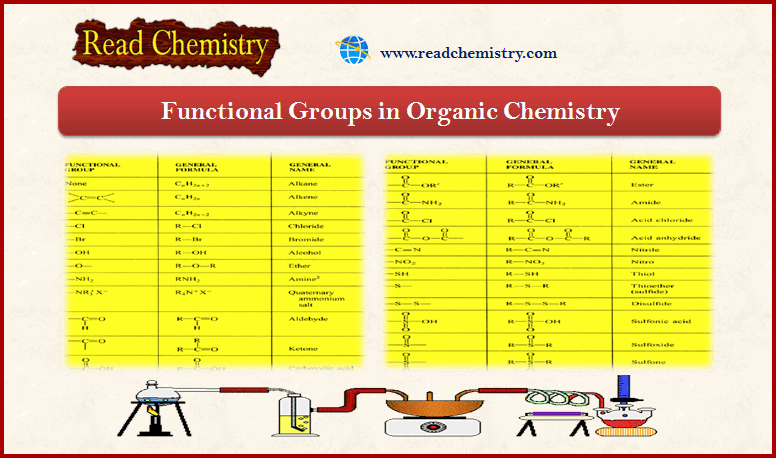
Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry
– In this subject, we will discuss the Functional Groups in Organic Chemistry. Functional Groups – Carbon combines with other…
Read More »