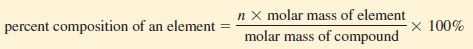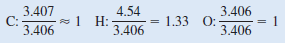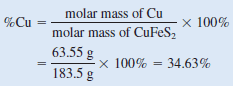Analytical ChemistryGeneral Chemistry
Percent Composition of Compounds
Percent Composition of Compounds
**As we have seen, the formula of a compound tells us the numbers of atoms of each element in a unit of the compound.
** However, suppose we needed to verify the purity of a compound for use in a laboratory experiment. We could calculate what percent of the total mass of the compound is contributed by each element from the formula. Then, by comparing the result to the percent composition obtained experimentally for our sample, we could determine the purity of the sample.
** The percent composition: is the percent by mass of each element in a compound.
** Percent composition is obtained by dividing the mass of each element in 1 mole of the compound by the molar mass of the compound and multiplying by 100 percent.
** Mathematically, the percent composition of an element in a compound is expressed as:
Where n is the number of moles of the element in 1 mole of the compound.
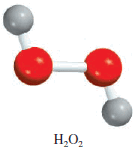
** For example, in 1 mole of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) there are 2 moles of H atoms and 2 moles of O atoms.
The molar masses of H2O2, H, and O are 34.02 g, 1.008 g, and 16.00 g, respectively. Therefore, the percent composition of H2O2 is calculated as follows:
The sum of the percentages is 5.926 percent + 94.06 percent = 99.99 percent. The small discrepancy from 100 percent is due to the way we rounded off the molar masses of the elements. If we had used the empirical formula HO for the calculation, we would have obtained the same percentages. This is so because both the molecular formula and empirical formula tell us the percent composition by mass of the compound.
Example (1): Phosphoric acid (H3PO4) is a colorless, syrupy liquid used in detergents, fertilizers, toothpastes, and in carbonated beverages for a “tangy” flavor. Calculate the percent composition by mass of H, P, and O in this compound.
Strategy:
** Recall the procedure for calculating a percentage.
** Assume that we have 1 mole of H3PO4. The percent by mass of each element (H, P, and O) is given by the combined molar mass of the atoms of the element in 1 mole of H3PO4 divided by the molar mass of H3PO4, then multiplied by 100 percent.
Solution:
The molar mass of H3PO4 is 97.99 g. The percent by mass of each of the elements in H3PO4 is calculated as follows:
Check:
Do the percentages add to 100 percent? The sum of the percentages is:
3.086% + 31.61% + 65.31% = 100.01%.
The small discrepancy from 100 percent is due to the way we rounded off.
** The procedure used in Example (1) can be reversed if necessary.
** Given the percent composition by mass of a compound, we can determine the empirical formula of the compound:
** Because we are dealing with percentages and the sum of all the percentages is 100 percent, it is convenient to assume that we started with 100 g of a compound, as Example (2) shows.
Example (2): Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) cures scurvy. It is composed of 40.92 percent carbon (C), 4.58 percent hydrogen (H), and 54.50 percent oxygen (O) by mass. Determine its empirical formula.
Strategy:
In a chemical formula, the subscripts represent the ratio of the number of moles of each element that combine to form one mole of the compound. How can we convert from mass percent to moles? If we assume an exactly 100-g sample of the compound, do we know the mass of each element in the compound? How do we then convert from grams to moles?
Solution:
** If we have 100 g of ascorbic acid, then each percentage can be converted directly to grams.
** In this sample, there will be 40.92 g of C, 4.58 g of H, and 54.50 g of O. Because the subscripts in the formula represent a mole ratio, we need to convert the grams of each element to moles.
** The conversion factor needed is the molar mass of each element. Let n represent the number of moles of each element so that:
Thus, we arrive at the formula C3.407H4.54O3.406 , which gives the identity and the mole ratios of atoms present. However, chemical formulas are written with whole numbers. Try to convert to whole numbers by dividing all the subscripts by the smallest subscript (3.406):
where the ~ sign means “approximately equal to.” This gives CH1.33O as the formula for ascorbic acid. Next, we need to convert 1.33, the subscript for H, into an integer. This can be done by a trial-and-error procedure:
** Because 1.33 × 3 gives us an integer (4), we multiply all the subscripts by 3 and obtain C3H4O3as the empirical formula for ascorbic acid
Check:
Are the subscripts in C3H4O3reduced to the smallest whole numbers?
** Chemists often want to know the actual mass of an element in a certain mass of a compound. For example, in the mining industry, this information will tell the scientists about the quality of the ore.
** Because the percent composition by mass of the elements in the substance can be readily calculated, such a problem can be solved in a rather direct way.
** Because the percent composition by mass of the elements in the substance can be readily calculated, such a problem can be solved in a rather direct way.
Example (3): Chalcopyrite (CuFeS2) is a principal mineral of copper. Calculate the number of kilograms of Cu in 5.93 × 103 kg of chalcopyrite.
Strategy:
Chalcopyrite is composed of Cu, Fe, and S. The mass due to Cu is based on its percentage by mass in the compound. How do we calculate mass percent of an element?
Solution:
The molar mass of Cu and CuFeS2 are 63.55 g and 183.5 g, respectively. The mass percent of Cu is therefore:
To calculate the mass of Cu in a 5.93 × 103 kg sample of CuFeS2, we need to convert the percentage to a fraction (that is, convert 34.63 percent to 34.63/100, or 0.3463) and write:
We can also solve the problem by reading the formula as the ratio of moles of chalcopyrite to moles of copper using the following conversions:
Try it.
Check:
As a ballpark estimate, note that the mass percent of Cu is roughly 33 percent, so that a third of the mass should be Cu; that is:
This quantity is quite close to the answer.
Reference: General Chemistry: The Essential Concepts / Raymond Chang , Jason Overby. (sixth edition).
Reference: General Chemistry: The Essential Concepts / Raymond Chang , Jason Overby. (sixth edition).