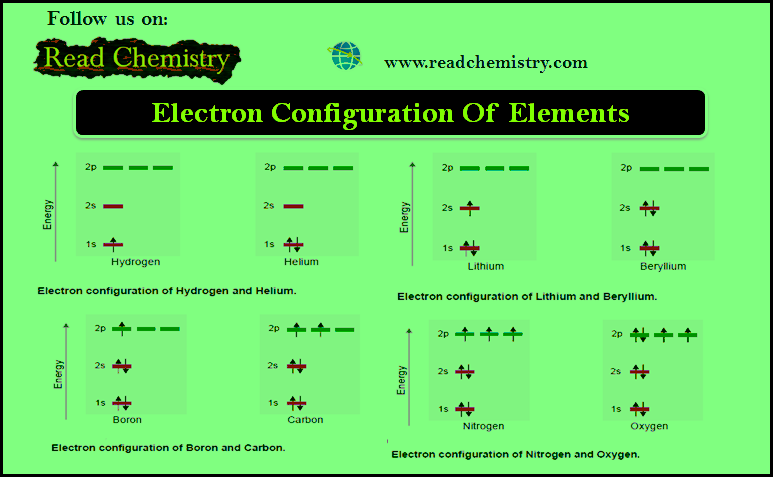
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
– In this subject, you will find 46 questions and answers MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
1. When a chemical bond between two atoms is formed, the potential energy of the system_______
(a) decreases
(b) increases
(c) remains the same
(d) cannot be predicted
Answer. (a)
2. According to valence bond theory, a bond between two atoms is formed when_______
(a) half filled atomic orbitals overlap
(b) fully filled atomic orbitals overlap
(c) non-bonding atomic orbitals overlap
(d) electrons of the two atoms overlap
Answer. (a)
3. The axial overlap between the two orbitals leads to the formation of a_______
(a) sigma bond
(b) pi bond
(c) multiple bond
(d) none of these
Answer. (a)
4. The free rotation about a bond exists when the bond is a_______
(a) sigma bond
(b) pi bond
(c) double bond
(d) hydrogen bond
Answer. (a)
5. The strength of a bond depends upon_______
(a) free rotation about σ bond
(b) extent of overlapping between the orbitals
(c) resonance in the molecule
(d) whether the overlap is axial or sidewise
Answer. (b)
6. In a N2 molecule there are_______
(a) one sigma and one pi bond
(b) two sigma and one pi bond
(c) one sigma and two pi bonds
(d) three sigma bonds
Answer. (c)
7. Out of the following, which statement is incorrect?
(a) half filled orbitals only take part in hydridization
(b) the orbitals taking part in hydridization should have very little energy difference
(c) the number of hybrid orbitals formed is equal to the number of orbitals intermixed
(d) the energy of hybrid orbitals is less than that of atomic orbitals
Answer. (a)
8. When one s and two p orbitals hybridize we get_______
(a) three new orbitals at 90° to each other
(b) three new orbitals at 120° to each other
(c) two new orbitals at 180° to each other
(d) two new orbitals at 90° to each other
Answer. (b)
9. In sp3, sp2 and sp hybridized carbon atom the p character is maximum in_______
(a) sp3
(b) sp2
(c) sp
(d) all have equal p-character
Answer. (a)
10. In H2O, NH3 and CH4 molecules the oxygen, nitrogen and carbon atom are_______
(a) sp3 hybridized
(b) sp3, sp2 and sp respectively
(c) sp, sp2 and sp3 respectively hybridized
(d) sp2 hybridized
Answer. (a)
11. sp3 hybridization leads to_______
(a) trigonal geometry with bond angles 120° each
(b) tetrahedral geometry with bond angles 109.5° each
(c) tetrahedral geometry with bond angles 90° each
(d) square planar geometry with bond angles 90° each
Answer. (b)
12. In dsp2 hybridization, the new orbitals have the following geometry_______
(a) square planar
(b) tetrahedral
(c) trigonal
(d) trigonal bipyramid
Answer. (d)
13. The shape of BF3 molecule is planar with bond angles equal to 120° each. It is due to_______
(a) sp3 hybridized B atom
(b) sp2 hybridized B atom
(c) sp hybridized B atom
(d) dsp2 hybridized B atom
Answer. (b)
14. The total number of orbitals taking part in sp hybridization in carbon atom is_______
(a) one
(b) two
(c) three
(d) four
Answer. (b)
15. A molecule of acetylene contains_______
(a) one σ and two π bonds
(b) two σ and two π bonds
(c) three σ and two π bonds
(d) two σ and three π bonds
Answer. (c)
16. In PCl5 molecule the phosphorus atom is_______
(a) sp3 hybridized
(b) sp3d hybridized
(c) sp3d2 hybridized
(d) sp2 hybridized
Answer. (b)
17. Valence bond theory was proposed by_______
(a) Rutherford
(b) Neils Bohr
(c) Heitler and London
(d) Hund and Mulliken
Answer. (c)
18. In the compound HC≡C-C*H=CH2, C* is_______
(a) sp hybridized
(b) sp2hybridized
(c) sp3 hybridized
(d) none of these
Answer. (b)
19. The carbon-carbon bond length is maximum in_______
(a) ethane
(b) ethene
(c) ethyne
(d) equal in all
Answer. (a)
20. The carbon-hydrogen bond length is shortest in_______
(a) ethane
(b) ethene
(c) ethyne
(d) CH4
Answer. (c)
21. In SO2 molecule, S atom is_______
(a) sp3 hybridized
(b) sp2 hybridized
(c) sp hybridized
(d) dsp2 hybridized
Answer. (b)
22. The molecular orbitals formed as a result of LCAO method obey_______
(a) Pauli’s exclusion principle
(b) Hund’s rule of maximum multiplicity
(c) Aufbau principle
(d) all of these
Answer. (d)
23. The energy of atomic orbitals taking part in molecular orbital formation_______
(a) is equal to the molecular orbitals formed
(b) is less than the molecular orbitals formed
(c) is greater than the molecular orbitals formed
(d) cannot be predicted
Answer. (c)
24. A He2 molecule is not formed because_______
(a) Na > Nb
(b) Nb = Na
(c) Nb > Na
(d) Nb – Na = +ve
Answer. (b)
25. A molecule or ion is stable if_______
(a) Nb = Na
(b) Nb < Na
(c) Na < Nb
(d) Na – Nb = +ve
Answer. (c)
26. The bond order in H2 molecule as compared to H2+ion is_______
(a) double
(b) half
(c) equal
(d) cannot be predicted
Answer. (a)
27. The bond order in He2+ ion is_______
(a) 0.5
(b) 1.0
(c) 1.5
(d) 2.0
Answer. (a)
28. In O2 molecule, the empty molecular orbital is_______
(a) σ (2 s)
(b) σ * (2 s)
(c) σ (2 pz)
(d) σ * (2 pz)
Answer. (d)
29. The O2 molecule is paramagnetic. It can be explained on the basis of_______
(a) hybridization
(b) valence bond theory
(c) molecular orbital theory
(d) none of these
Answer. (c)
30. The bond order in O2+, O2– and O22– respectively is_______
(a) 1, 1.5, 2.0
(b) 1.5, 2.0, 2.5
(c) 2.5, 1.5, 1
(d) 2.5, 1.0, 1.5
Answer. (c)
31. Which among the species O2+, O2–, O2 and O22– is diamagnetic?
(a) O2+
(b) O2–
(c) O2
(d) O22–
Answer. (d)
32. The diamagnetic species among NO+, NO and NO–is_______
(a) NO+
(b) NO
(c) NO–
(d) none of these
Answer. (a)
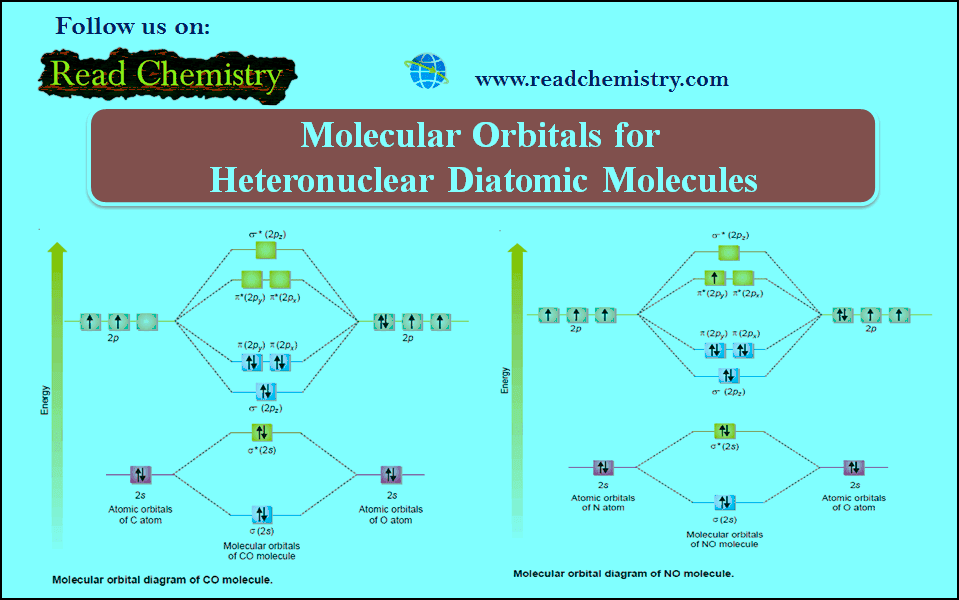
33. The number of bonding and antibonding electrons respectively in CO molecule is_______
(a) 8, 2
(b) 2, 8
(c) 4, 2
(d) 2, 4
Answer. (a)
34. Among CO, NO and CN molecules, the one which contains no unpaired electrons and hence is diamagnetic?
(a) CO
(b) NO
(c) CN
(d) none of these
Answer. (a)
35. The species with the highest bond order among NO, CO, CN and O2is_______
(a) NO
(b) CO
(c) CN
(d) O2
Answer. (b)
36. Which one of the following has a zero bond order?
(a) He2
(b) F2
(c) N2
(d) H–F
Answer. (a)
37. Which among the following pairs are paramagnetic?
(a) O2 and N2
(b) O2 and CO
(c) O2 and NO
(d) CO and NO
Answer. (c)
38. The bond order of a molecule is given by_______
Answer. (b)
39. Oxygen molecule is paramagnetic because it has_______
(a) less Nb than Na
(b) more Nb than Na
(c) all electrons are paired
(d) unpaired electrons
Answer. (d)
40. The increasing bond order in the species O2–, O2+ and O22– is_______
(a) O22– < O2+ < O2–
(b) O2– < O22– < O2+
(c) O22– < O2– < O2+
(d) O2+ < O2– < O22–
Answer. (c)
41. The molecules which are iso-electronic among CO, N2, O2 and NO are_______
(a) O2 and N2
(b) O2 and NO
(c) N2 and NO
(d) CO and N2
Answer. (d)
42. The last electron in F2 molecule is present in M.O._______
(a) σ (2s)
(b) σ * (2s)
(c) σ * 2pz
(d) π* 2px
Answer. (d)
43. The molecule Ne2 does not exist because_______
(a) Nb > Na
(b) Nb = Na
(c) Nb < Na
(d) none of these
Answer. (b)
44. The molecule with the highest bond order among CO, CN, NO and O2 is_______
(a) CO
(b) CN
(c) NO
(d) O2
Answer. (a)
45. Which of the following is not true regarding LCAO method?
(a) the energies of atomic orbitals should be comparable
(b) the atomic orbitals should overlap to a considerable extent
(c) the symmetry of the combining orbitals should be the same
(d) the energy of resulting antibonding orbital is less than that of bonding orbital
Answer. (d)
46. Which is not true about bonding MO?
(a) it is formed by the addition overlap of atomic orbitals
(b) the wave function of a bonding MO is given by ψMO = ψA – ψB
(c) the lobes of atomic orbitals should have the same signs
(d) every electron in bonding MO contributes towards the attractive force
Answer. (b)
Reference: Essentials of Physical Chemistry /Arun Bahl, B.S Bahl and G.D. Tuli / multicolour edition.