Stabilities of Dienes
– In this topic, we will talk about Stabilities of Dienes
What are Dienes?
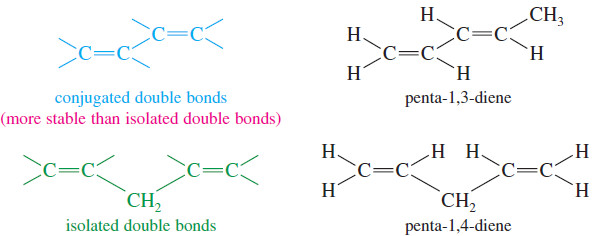
– Double bonds can interact with each other if they are separated by just one single bond.
– Such interacting double bonds are said to be conjugated.
– Double bonds with two or more single bonds separating them have little interaction and are called isolated double bonds.
– For example, penta-1,3-diene has conjugated double bonds, while penta-1,4-diene has isolated double bonds.
– Because of the interaction between the double bonds, systems containing conjugated double bonds tend to be more stable than similar systems with isolated double bonds.
– we consider the unique properties of conjugated systems, the theoretical reasons for this extra stability, and some of the characteristic reactions of molecules containing conjugated double bonds.
– We also study ultraviolet spectroscopy, a tool for determining the structures of conjugated systems.
Stabilities of Dienes
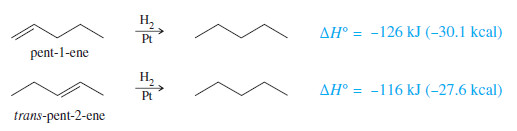
– we use heats of hydrogenation to compare the relative stabilities of alkenes.
– For example, the heats of hydrogenation of pent-1-ene and trans-pent-2-ene show that the disubstituted double bond in trans-pent-2-ene is 10 kJ mol (2.5 kcal mol) more stable than the monosubstituted double bond in pent-1-ene.
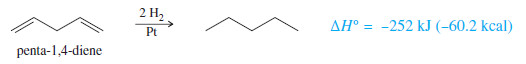
– When a molecule has two isolated double bonds, the heat of hydrogenation is close to the sum of the heats of hydrogenation for the individual double bonds.
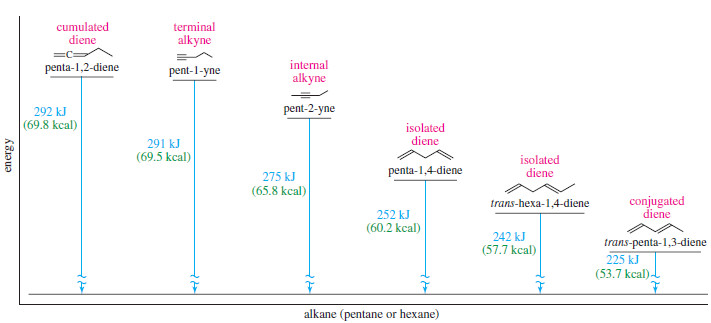
– For example, the heat of hydrogenation of penta-1,4-diene is -252 kJ/mol (-60.2 kcal/mol) about twice that of pent-1-ene.
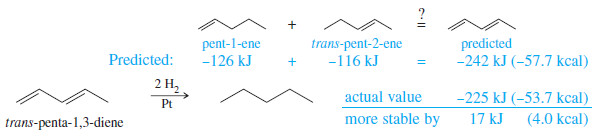
– For conjugated dienes, the heat of hydrogenation is less than the sum for the individual double bonds.
– Example, trans-penta-1,3-diene has a monosubstituted double bond like the one in pent-1 ene and a disubstituted double bond like the one in pent-2- ene.
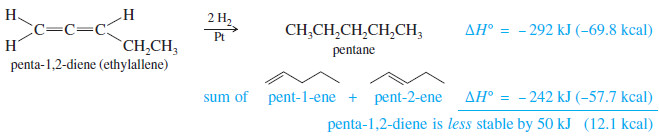
– The sum of the heats of hydrogenation of pent-1-ene and pent-2-ene is -242 kJ (-57.7 kcal), but the heat of hydrogenation of trans-penta-1,3-diene is only -225 kJ/mol (-53.7 kcal/mol) showing that the conjugated diene has about 17 kJ/mol (4.0 kcal/mol) extra stability.
– What happens if two double bonds are even closer together than in the conjugated case
– Successive double bonds with no intervening single bonds are called cumulated double bonds.
– Consider penta-1,2-diene, which contains cumulated double bonds.
– Such 1,2-diene systems are also called allenes, after the simplest member of the class, propa- 1,2-diene or “allene,” H2C=C=CH2 .
– The heat of hydrogenation of penta-1,2-diene is -292 kJ/mol (-69.8 kcal/mol), a larger value than any of the other pentadienes
– Because penta-1,2-diene has a larger heat of hydrogenation than penta-1,4-diene, we conclude that the cumulated double bonds of allenes are less stable than isolated double bonds and much less stable than conjugated double bonds.
– Figure summarizes Stabilities of Dienes (the relative stability of isolated, conjugated, and cumulated dienes and compares them with alkynes).
References
- Organic chemistry / L.G. Wade, Jr / 8th ed, 2013 / Pearson Education, Inc. USA.
- Fundamental of Organic Chemistry / John McMurry, Cornell University/ 8th ed, 2016 / Cengage Learningm, Inc. USA.
- Organic Chemistry / T.W. Graham Solomons, Craig B. Fryhle , Scott A. Snyder / 11 ed, 2014/ John Wiley & Sons, Inc. USA.
- Unergraduate Organic Chemistry /Dr. Jagdamba Singh, Dr. L.D.S Yadav / 1st ed, 2010/ Pragati prakashan Educational Publishers, India.