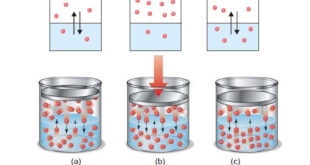
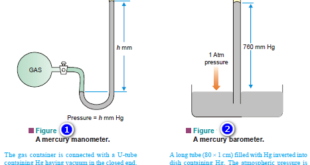
The subject of Solutions of gases in gases – Henry’s Law will be discused Types of Solutions – The common solutions that we come across are those where the solute is a solid and the solvent is a liquid. – In fact, substance in any three states of matter (solid, …
Read More »Ways of Expressing Concentration
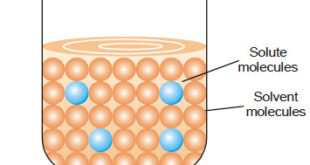
Concentration of A Solution – The concentration of a solution is defined as : the amount of solute present in a given amount of solution. – Concentration is generally expressed as the quantity of solute in a unit volume of solution. A solution containing a relatively low concentration of solute …
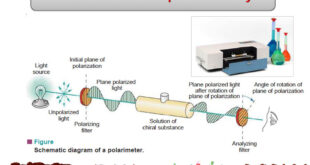
Read More »Measurement of Optical Activity
Optical Activity – Optical activity is one of imortant physcial properties of liqiuds – A beam of ordinary light consists of electromagnetic waves oscillating in many planes. – When passed through a polarizer (e.g., a Polaroid lens), only waves oscillating in a single plane pass through. – The emerging beam …
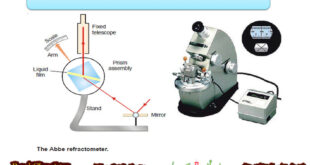
Read More »Determination of Refractive Index
Refractive Index – The refractive index (n) of a substance is defined as the ratio of the velocity of light in vacuum or air, to that in the substance: – When a ray of light passes from air into a liquid, its direction is changed. This change of direction is …
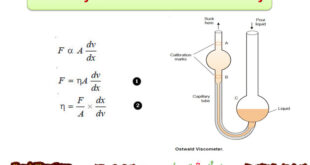
Read More »Viscosity – Measurement of Viscosity
Viscosity – Viscosity is the resistance of a liquid to flow. – A liquid may be considered to be consisting of molecular layers arranged one over the other. – When a shearing force is applied to a liquid, it flows. However, the forces of friction between the layers offer resistance …
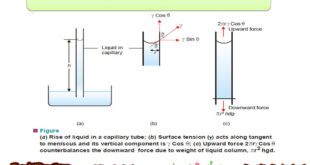
Read More »Determination of Surface Tension
Surface Tension – Surface Tension property of liquids arises from the intermolecular forces of attraction. – A molecule in the interior of a liquid is attracted equally in all directions by the molecules around it. – A molecule in the surface of a liquid is attracted only sideways and toward …
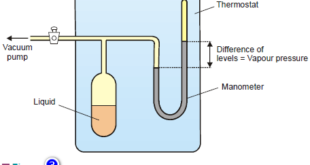
Read More »Vapour Pressure , Factors affecting on Vapour Pressure
– The vapour pressure of a liquid is defined as the pressure exerted by the vapour in equilibrium with the liquid at a fixed temperature. Vapour Pressure – When a liquid is placed in an open vessel, it evaporates. – The molecules in the liquid are moving with different kinetic …
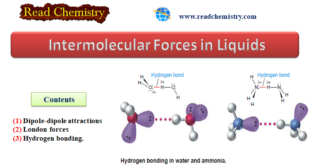
Read More »Intermolecular Forces in Liquids
Intermolecular Forces in Liquids – Intermolecular forces in liquids are collectively called van der Waals forces. – These forces are essentially electrical in nature and result from the attraction of charges of opposite sign. – The principal kinds of intermolecular attractions are: (1) Dipole-dipole attractions (2) London forces (3) Hydrogen bonding. …
Read More »Gases – General Characteristics of gases
States of the matter – All matter exists in three states: gases, liquids and solids. – A molecular-level representation of gaseous, liquid and solid states is shown in the following Figure. – A gas consists of molecules separated wide apart in empty space. The molecules are free to move …
Read More »Spontaneous Processes – Second Law of Thermodynamics
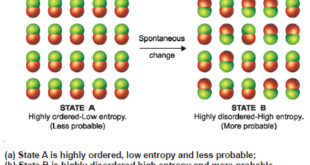
Spontaneous Processes – A process that proceeds of its own accord, without any outside assistance, is termed a spontaneous or natural process. – The reverse process which does not proceed on its own, is referred to as a nonspontaneous or unnatural process. – In general, the tendency of a process …
Read More »MCQ on Chapter Thermochemistry ΔH, ΔE
1. For exothermic reactions, ΔH is _______ while for endothermic reactions it is _______. (a) positive, negative (b) positive, positive (c) negative, negative (d) negative, positive Answer. (d) 2. The branch of chemistry which deals with the heat changes caused by chemical reactions is called _______ (a) thermodynamics (b) thermal …
Read More »Measurement of The Heat of Reaction
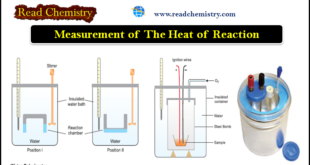
Measurement of The Heat of Reaction – The experimental measurement of the heat of reaction or enthalpy change is known as calorimetry. – The name (calorimetry) evidently finds its origin in the unit of heat–the calorie. – The heat given out or absorbed in a chemical reaction is measured in …
Read More »Bond energy (definition, Illustration, solved Problems)
Bond energy – When a bond between two atoms is formed, there is a release of energy. – The same amount of energy is absorbed when the bond is broken. – The bond energy is defined as the average amount of energy required to break all bonds of a particular type …
Read More »Hess’s Law ( statement, Illustration, application, Problems)
– Hess’s Law may be stated as: (If a chemical change can be made to take place in two or more different ways whether in one step or two or more steps, the amount of total heat change is same no matter by which method the change is brought about). …
Read More »Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes
– In this subject, we will discuss Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes. Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes – The three states of matter – solid, liquid and gas differ from one another in the arrangement of their constituent particles. – The magnitudes of intermolecular forces acting …
Read More »Heat of Combustion (Definition, Applications, Solved Problems)
Heat of Combustion – The heat of combustion of a substance is defined as The change in enthalpy of a system when one mole of the substance is completely burnt in excess of air or oxygen. – It is denoted by ΔHc. – For example, the heat of combustion …
Read More »Heat of Formation (Definition, Applications, Solved Problems)
Heat of Formation – The heat of formation of a compound is defined as The change in enthalpy that takes place when one mole of the compound is formed from its elements. – It is denoted by ΔHf . – For example, the heat of formation of ferrous sulphide and acetylene …
Read More »Different Types of Heat of Reaction (Enthalpy)
– The heat of reaction or enthalpy changes accompanying chemical reactions are expressed in different ways, depending on the nature of the reaction. These are discussed below. (1) Heat of Formation – The heat of formation of a compound is defined as The change in enthalpy that takes place when …
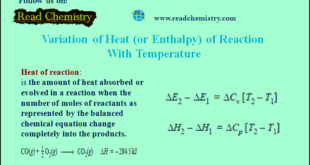
Read More »Variation of heat of reaction with temperature
– In this subject, the Variation of heat of reaction with temperature will be discussed. Heat of Reaction or Enthalpy of Reaction – The heat of a reaction is simply the amount of heat absorbed or evolved in the reaction. – We also know that the amount of heat absorbed …
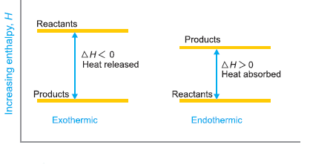
Read More »Enthalpy of Reaction
– For reactions involving solids and liquids only the change in volume (ΔV) is very small and the term P × ΔV is negligible. For such reactions, the Change of Enthalpy of Reaction ΔH is equal to ΔE. Enthalpy of Reaction – Thermochemical measurements are made either at (a) constant …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry