Popular Posts
-
Organic Chemistry
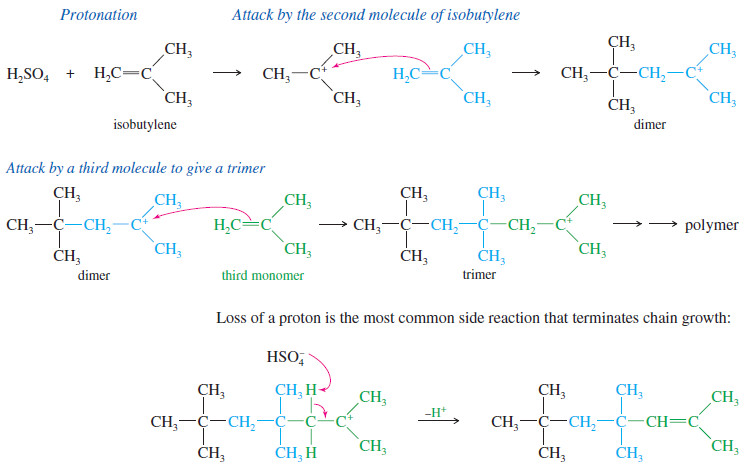
Polymerization of Alkenes
Polymerization of Alkenes – A polymer is a large molecule composed of many smaller repeating units (the monomers) bonded together.…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
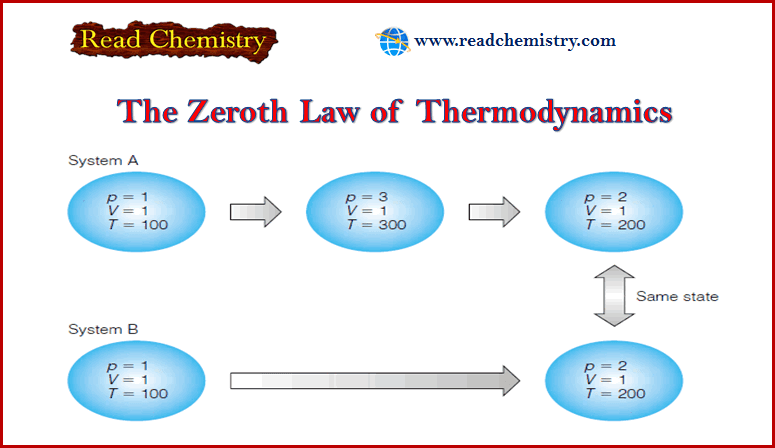
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
– In this subject, we will discuss The Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics Introduction to Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics – Thermodynamics…
Read More » -
Analytical Chemistry
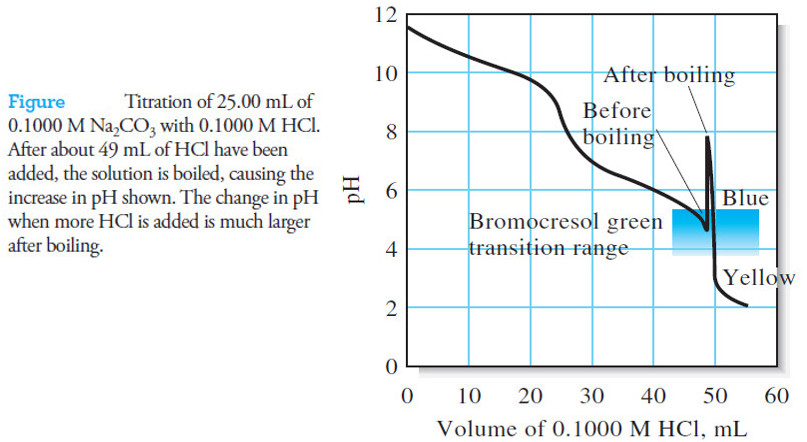
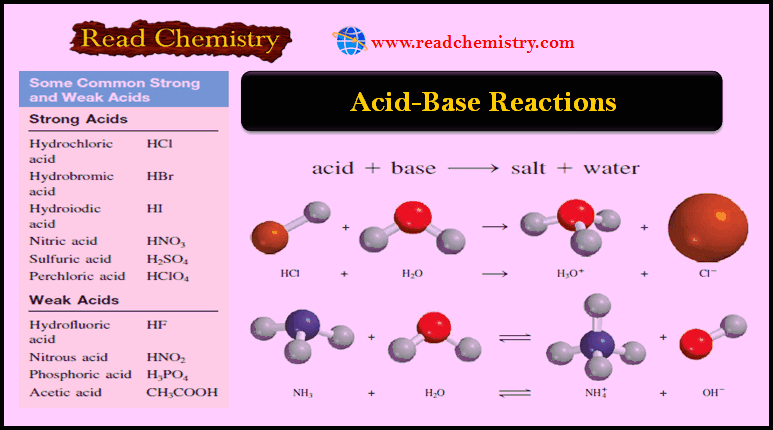
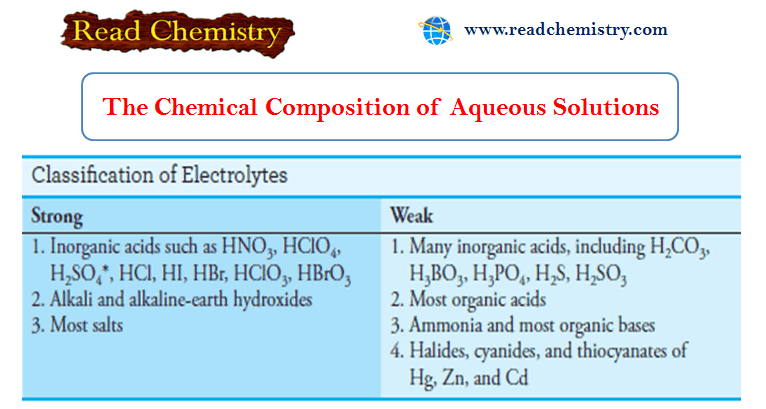
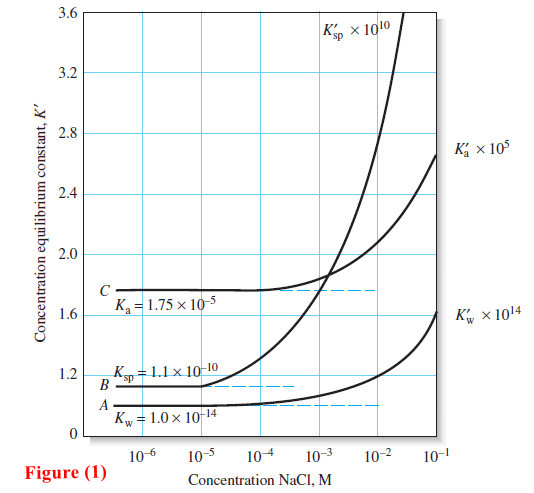
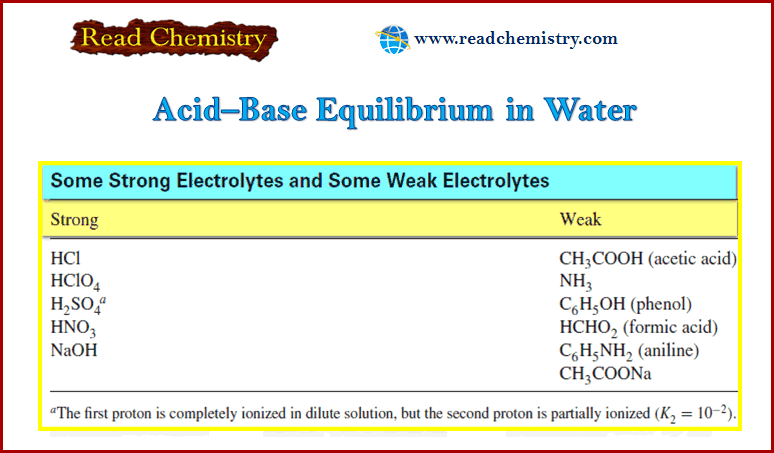
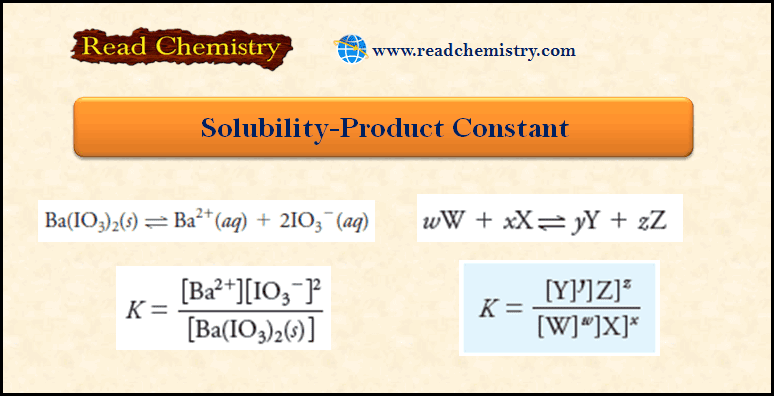
Reagents for Neutralization Titrations
– In this subject, we will discuss the Reagents for Neutralization Titrations. Reagents for Neutralization Titrations – we noted before…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
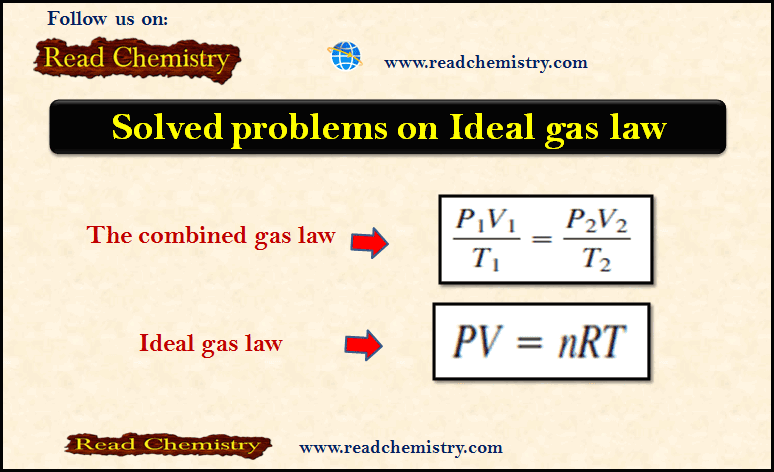
The Ideal gas law: Solved Problems
– In this subject, we will discuss Solved Problems on The Ideal gas law Problem (1) on The ideal gas…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
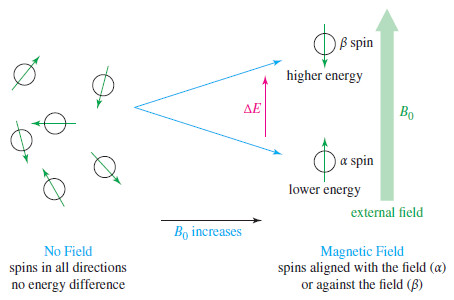
NMR – Theory of Magnetic Nuclear Resonance
Introduction to NMR – Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) is the most powerful tool available for organic structure determination. –…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
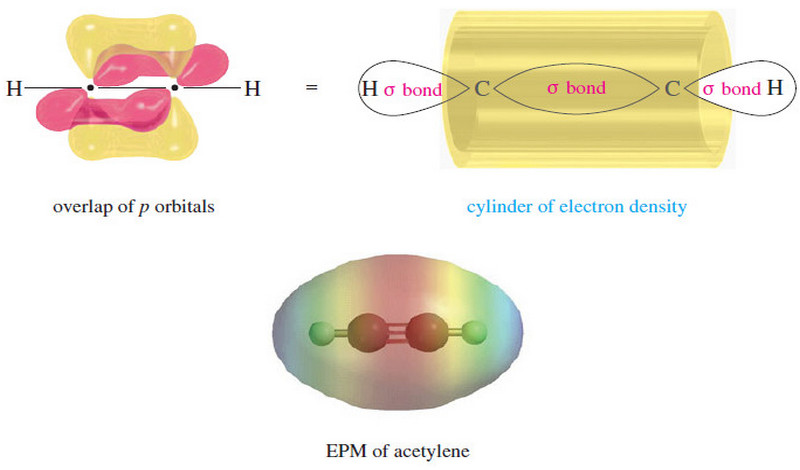
The electronic structure of Alkynes
– we studied theThe electronic structureof Alkynes (a triple bond) in This subject: The Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene): sp Hybridization…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
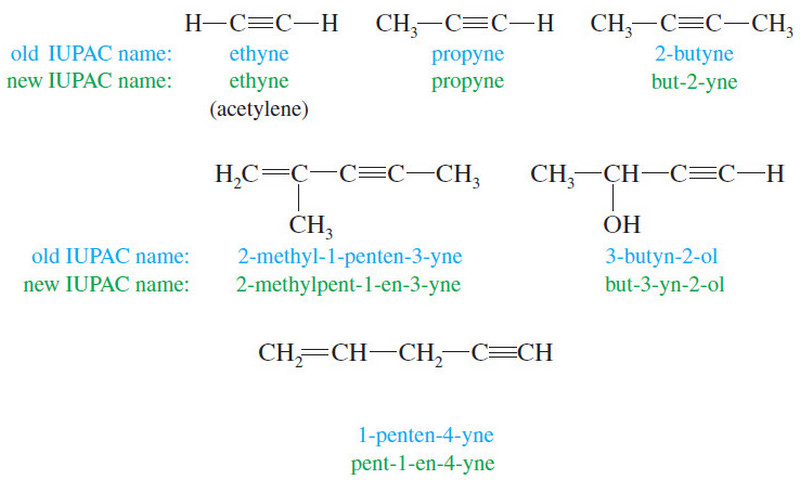
Nomenclature of Alkynes
What are Alkynes? – Alkynes are hydrocarbons that contain carbon–carbon triple bonds. – Alkynes are…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Physical Chemistry
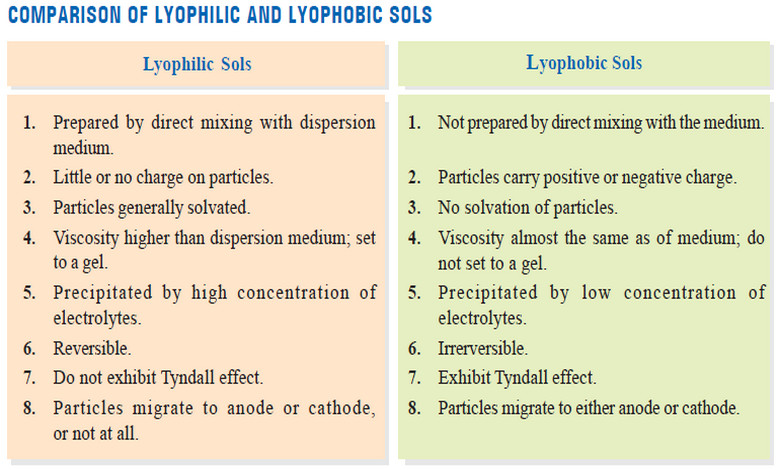
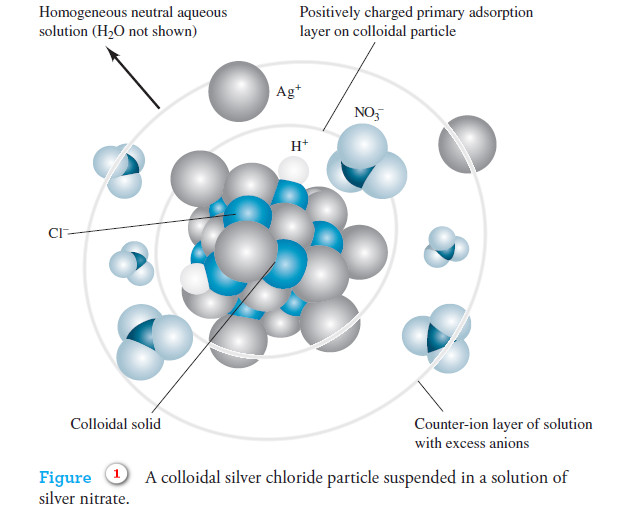
Lyophilic and Lyophobic sols : Defination, Properties, Comparison
– In this topic, we will discuss The Lyophilic and Lyophobic sols : Defination, Characteristics,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
General Chemistry
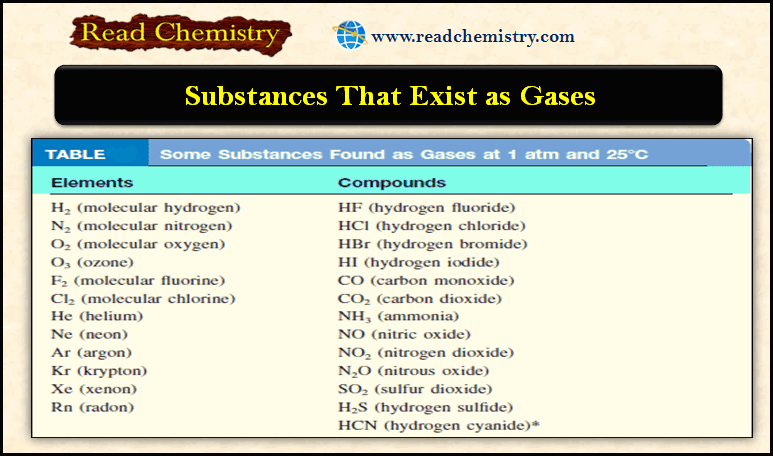
Gaseous Substances: Substances That Exist as Gases
– In this subject, we will discuss the Gaseous Substances: Substances That Exist as Gases…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Analytical Chemistry
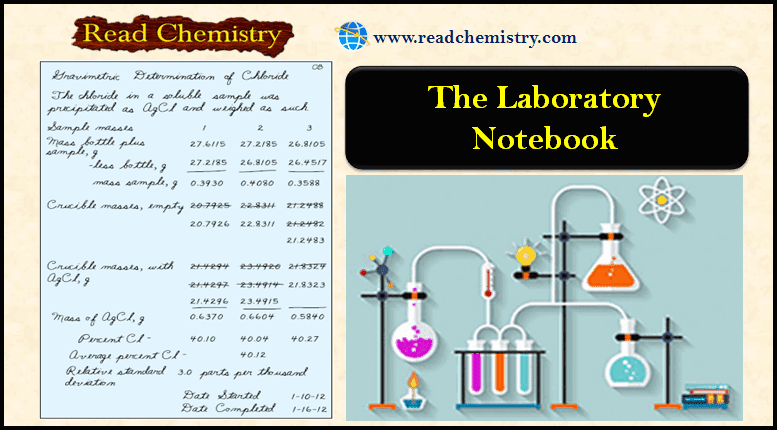
The Laboratory Notebook
The Laboratory Notebook – A laboratory notebook is needed to record measurements and observations concerning…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-