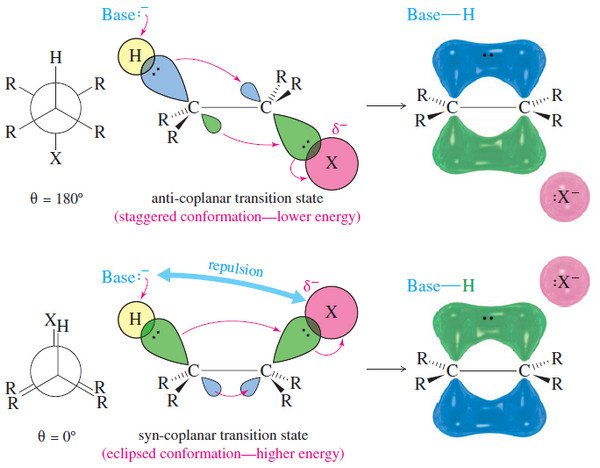
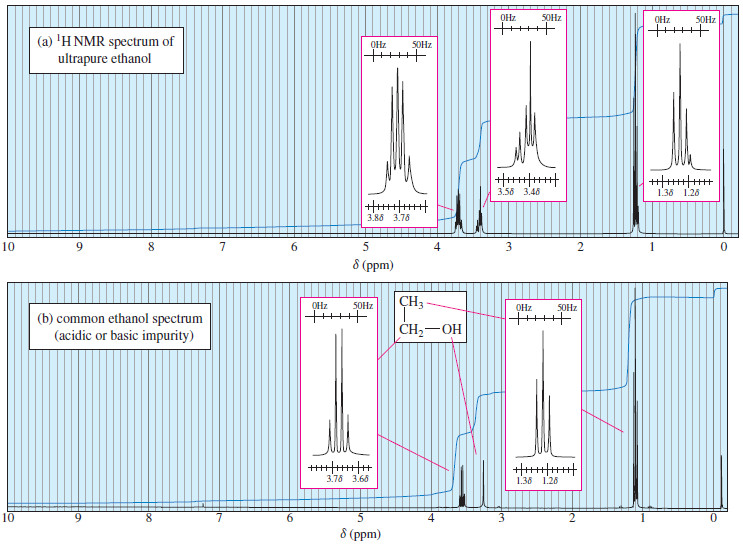
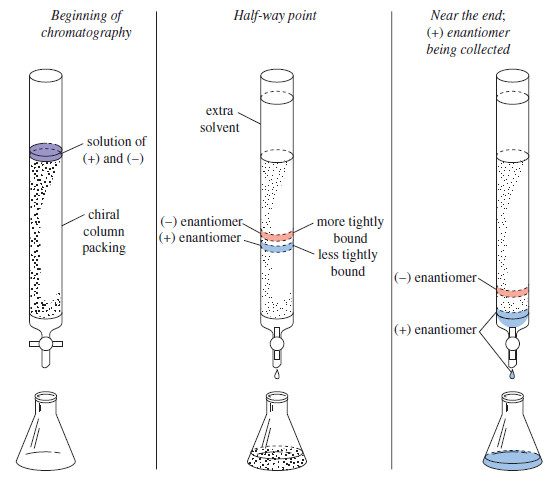
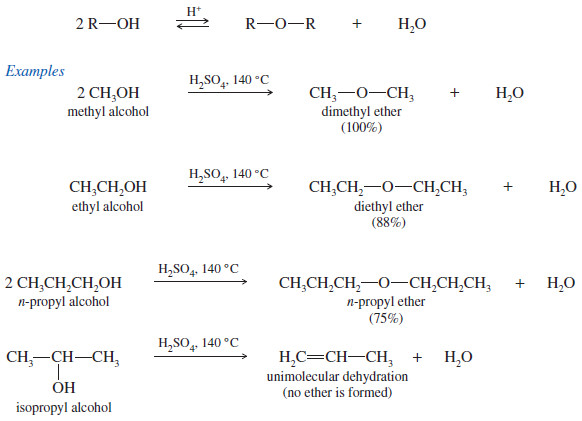
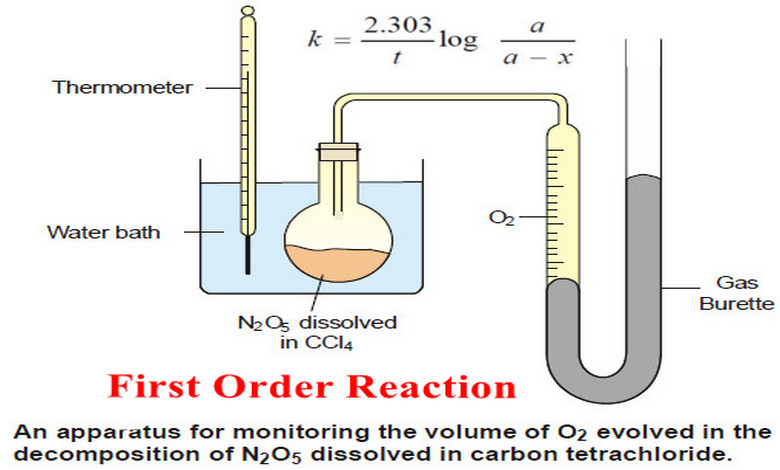
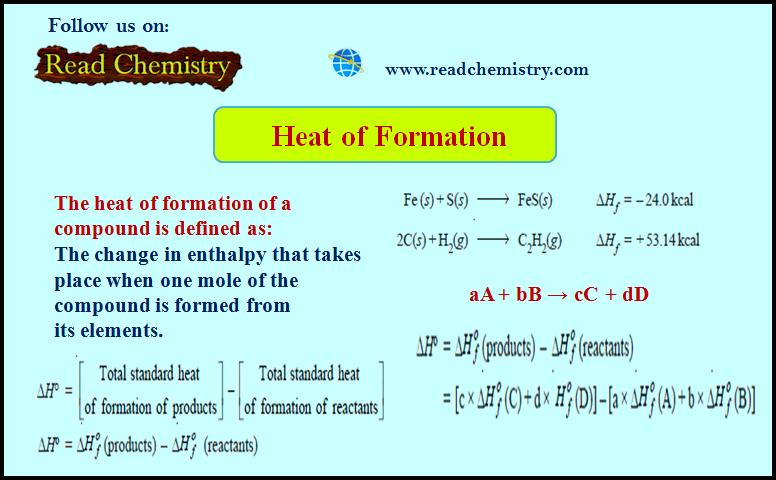
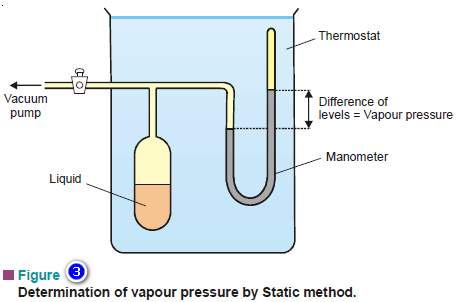
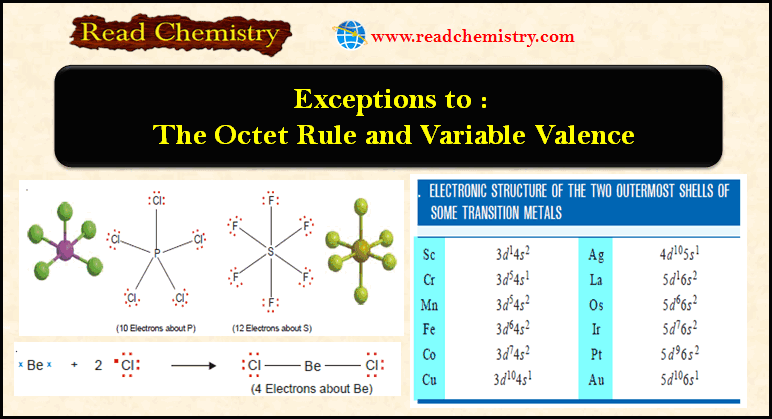
Popular Posts
-
Organic Chemistry
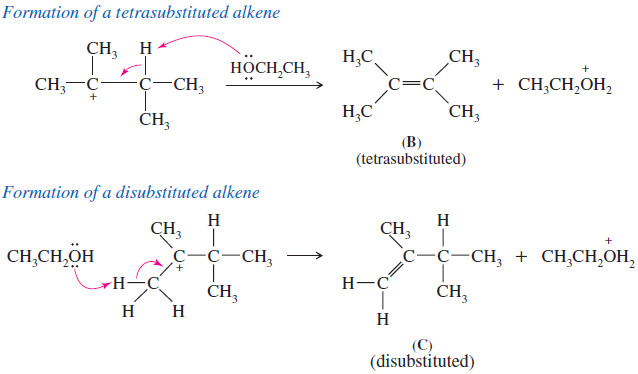
Zaitsev’s Rule : Positional Orientation of Elimination
Positional Orientation of Elimination: Zaitsev’s Rule – In this subject , Positional Orientation of Elimination: Zaitsev’s Rule will be discussed…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
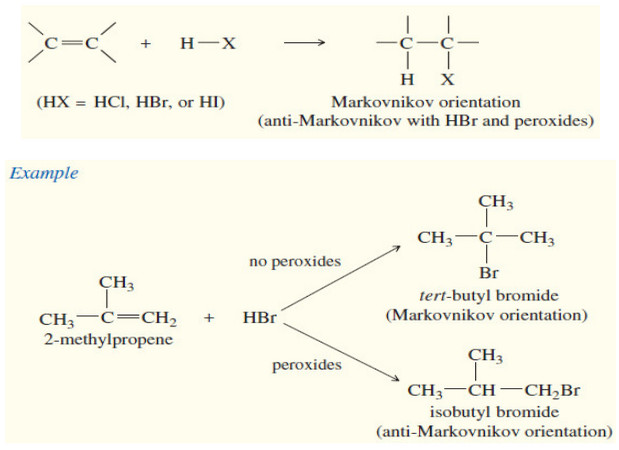
Reactions of Alkenes
– In this subject we will discuss all famous reactions of alkenes. – The reactions of alkenes include five basic…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
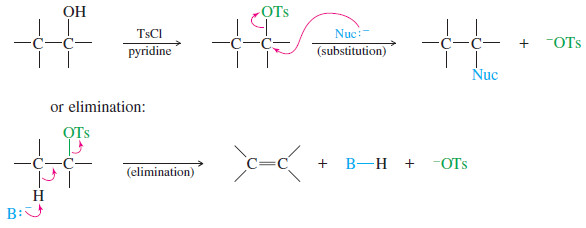
Alcohols as Nucleophiles and Electrophiles
Alcohols as Nucleophiles and Electrophiles; Formation of Tosylates – One reason alcohols are such versatile chemical intermediates is that they…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
Importance of Alkynes : Acetylene
Commercial Importance of Alkynes : Acetylene and Methylacetylene Uses of Acetylene and Methylacetylene – Acetylene is by far the most…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
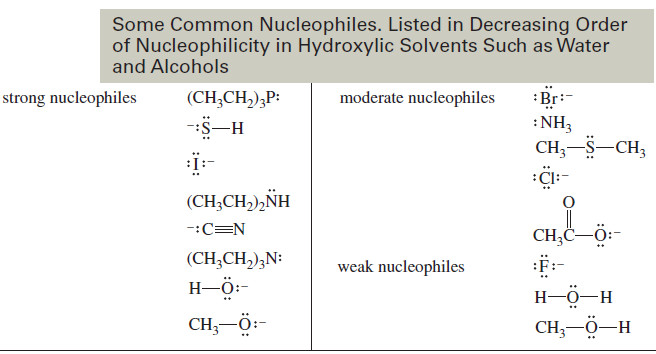
Factors Affecting SN2 Reactions: Strength of the Nucleophile
Factors Affecting SN2 Reactions: Strength of the Nucleophile – we will discuss Factors Affecting SN2 Reactions especially Strength of the…
Read More » -
Online MCQ
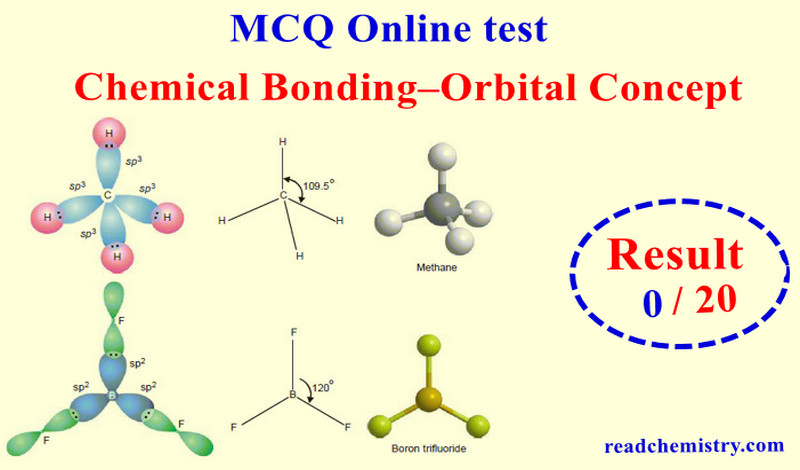
Chemical Bonding – Orbital Concept – MCQ test
Online MCQ test on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Concept – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test in…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
How to interpret IR spectrum without Knowledge of the structure
– In this subject, we will discuss How to interpret an IR spectrum without any…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Physical Chemistry
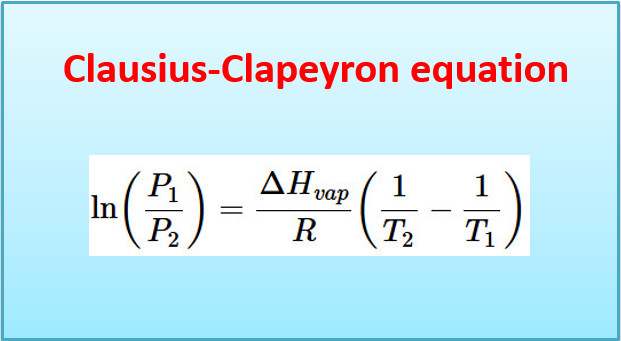
Clausius-Clapeyron equation – Derivation with Applications
– In this topic, we will discuss Clausius-Clapeyron equation – Derivation with Applications. The Clapeyron…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
General Chemistry
Avogadro’s Number and the Molar Mass of an Element
Avogadro’s Number (NA) ** Atomic mass units provide a relative scale for the masses of…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Analytical Chemistry
Safety in the laboratory
– In this subject, we will discuss the Safety in the laboratory Safety in The…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-