Popular Posts
-
Physical Chemistry
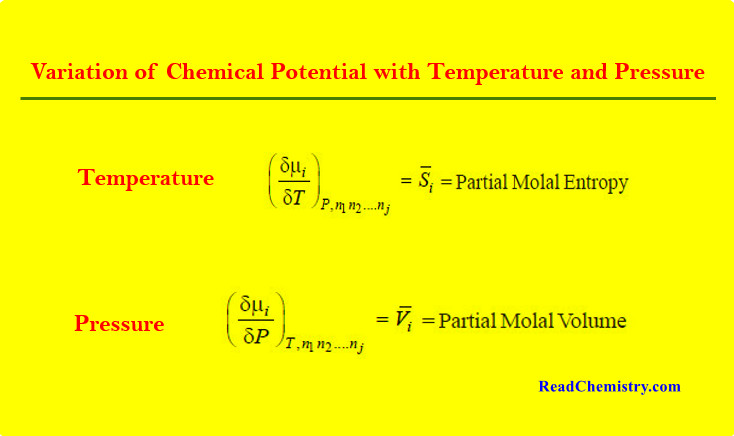
Chemical Potential
– In this topic, we will discuss The Chemical Potential and Variation of Chemical Potential with Temperature and Pressure. Partial…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
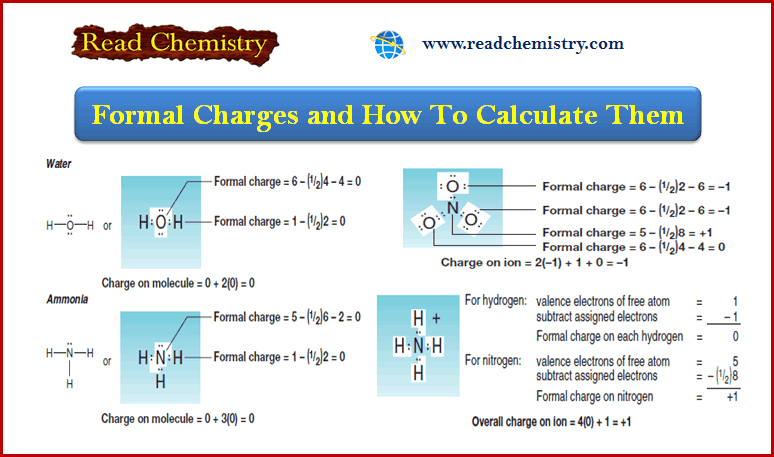
Formal Charge: Definition, Formula, Calculation, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Formal Charge: Definition, Formula, Calculation, Examples Formal Charge and How To Calculate…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
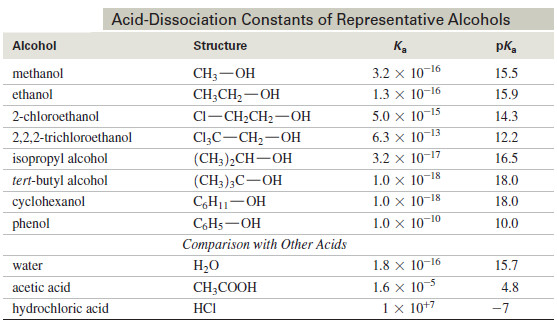
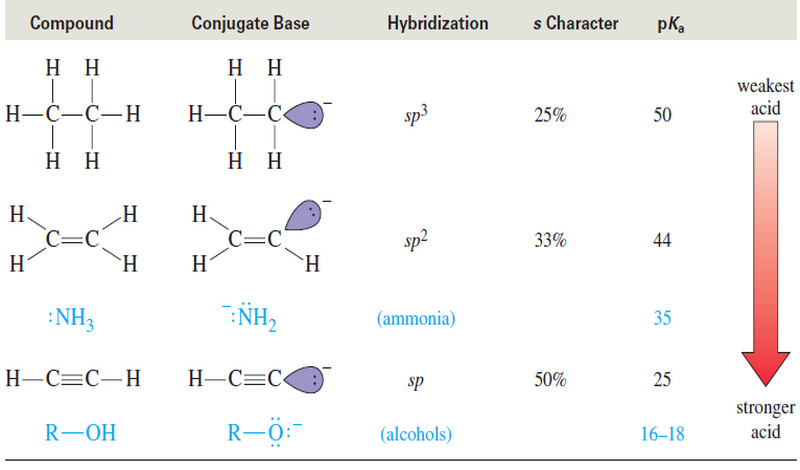
Acidity of Alcohols and Phenols
Acidity of Alcohols and Phenols – we will talk here about some Acidity of Alcohols and Phenols. – Like the…
Read More » -
Analytical Chemistry
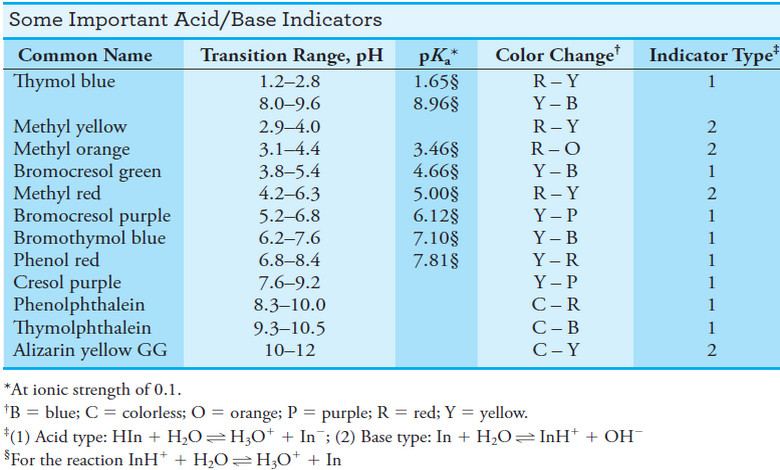
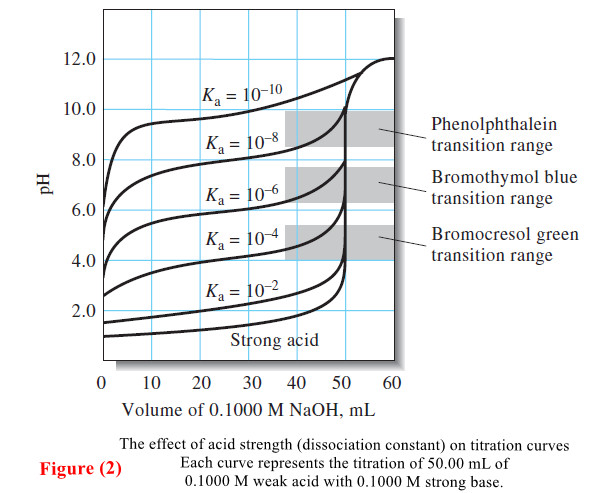
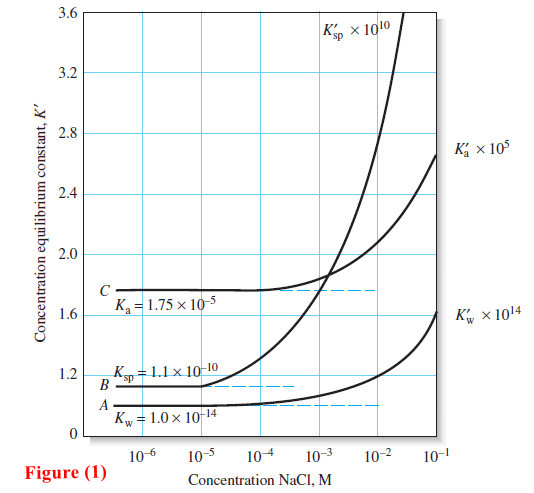
Indicators and Solutions for acid-base titration
– In this topic, we will discuss the Indicators and Solutions for acid-base titration. Indicators and Solutions for acid-base titration…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
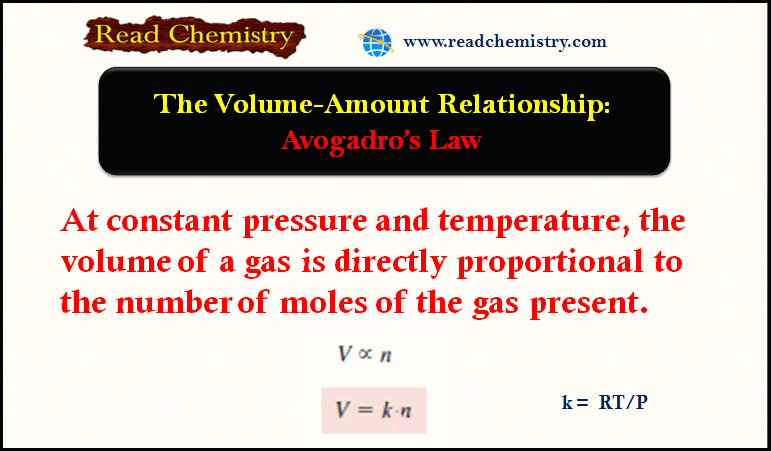
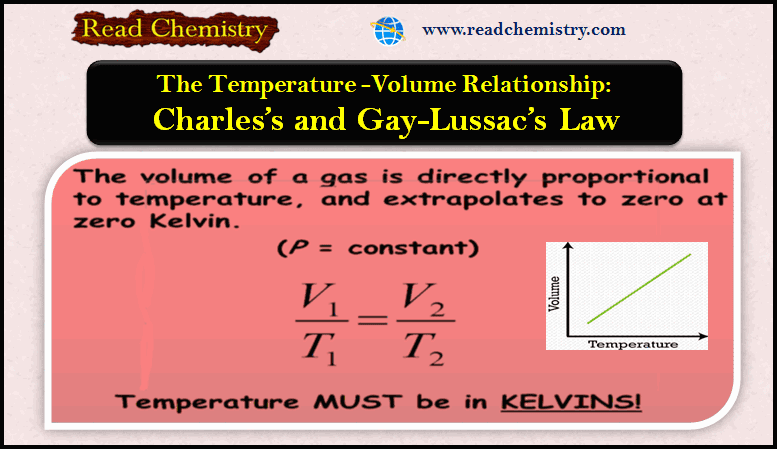
Avogadro’s Law: The Volume-Amount Relationship
– In this subject, we will discuss the Avogadro’s Law: The Volume-Amount Relationship Avogadro’s Law: The Volume-Amount Relationship – The…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
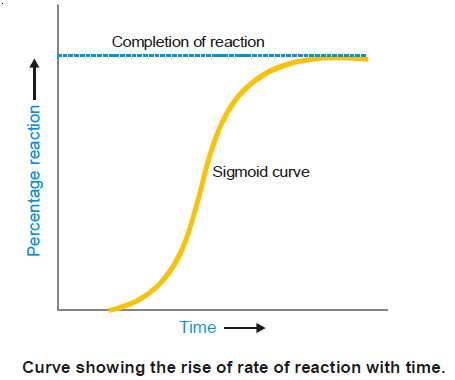
Autocatalysis, Catalytic poisoning and Negative Catalysis
– In this topic, we will discuss Autocatalysis, Catalytic poisoning and Negative Catalysis. Catalytic poisoning – Very often a heterogeneous…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
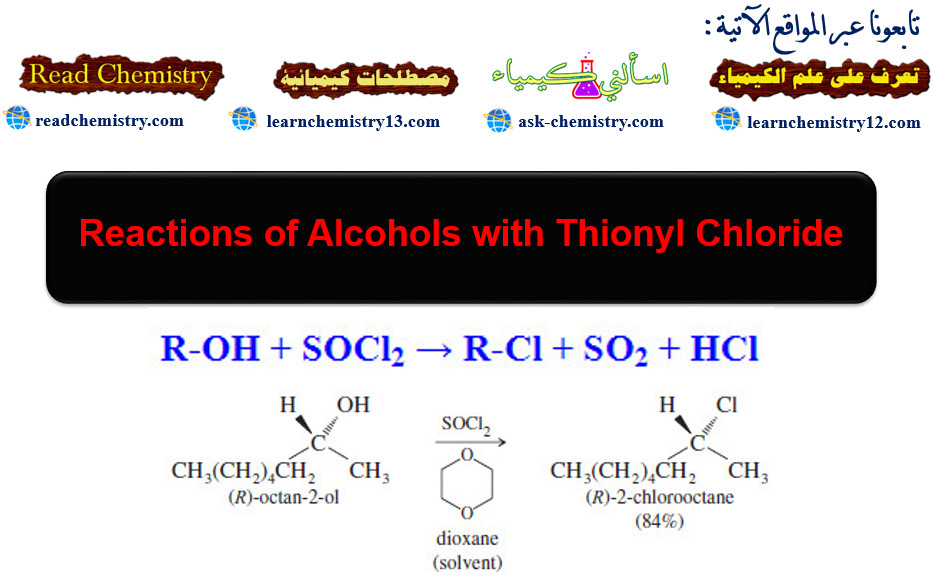
Reactions of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride
Reactions of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride – Reactions of Alcohols with Thionyl Chloride give alkyl…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Physical Chemistry
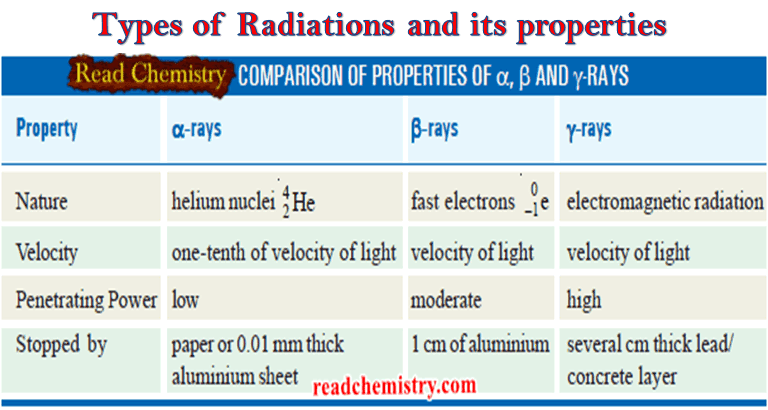
Types of Radiations and its properties
Nuclear reaction ** A nuclear reaction is different from a chemical reaction. **…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
General Chemistry
Gas Pressure: Definition, Formula and Solved problems
– In this subject, we will discuss Gas Pressure: Definition, Formula, and Solved problems Gas…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Analytical Chemistry
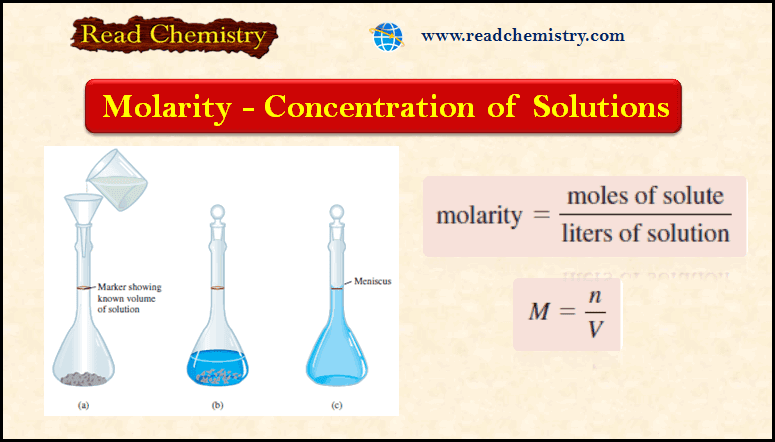
Molarity: definition, formula, solved Problems
– In this subject, we will discuss the Molarity: definition, formula, solved Problems – To…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-