MCQ on the First Law of Thermodynamics – In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on the First law of Thermodynamics 1. The first law of thermodynamics is_______ (a) the total energy of an isolated system remains constant though it may change from one form to …
Read More »Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas
Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas – A process carried in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated so that no heat can pass through them, is said to be adiabatic. – In the adiabatic process there is no heat exchange between a system and surroundings, and q = 0. …
Read More »Heat Capacity – Molar Heat Capacity
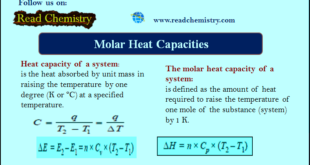
Molar Heat Capacity – By heat capacity of a system, we mean the capacity to absorb heat and store energy. – As the system absorbs heat, it goes into the kinetic motion of the atoms and molecules contained in the system. – This increased kinetic energy raises the temperature of …
Read More »Enthalpy of A System
– Enthalpy (H) is the total heat content of a system at constant pressure and is equivalent to the internal energy E plus the PV energy. Enthalpy of A System – In a process carried at constant volume (say in a sealed tube), the heat content of a system is …
Read More »Joule-Thomson Effect
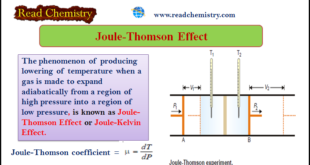
– The phenomenon of producing a lowering of temperature when a gas is made to expand adiabatically from a region of high pressure into a region of low pressure is known as the Joule-Thomson Effect or Joule-Kelvin Effect Joule-Thomson Effect – Joule and Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) showed that when …
Read More »The First Law of Thermodynamics + Solved Problems
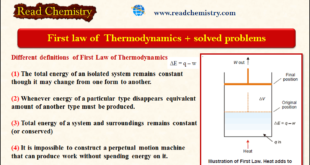
– The first law of Thermodynamics states that The total energy of an isolated system remains constant though it may change from one form to another. Internal Energy – A thermodynamic system containing some quantity of matter has within itself a definite quantity of energy. – This energy includes not …
Read More »Work in Thermodynamics (Definition – Formula – Problems)
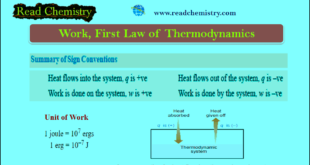
– In physics, mechanical work is defined as force multiplied by the distance through which the force acts. – In elementary thermodynamics, the only type of work generally considered is the work done in the expansion (or compression) of a gas Nature of Heat and Work – When a change …
Read More »Thermodynamic Processes
– Thermodynamic Processes involve the change of conditions (temperature, pressure, and volume). Thermodynamic Processes – When a thermodynamic system changes from one state to another, the operation is called a Process. – Thermodynamic Processes involve the change of conditions (temperature, pressure, and volume). – The various types of thermodynamic processes …
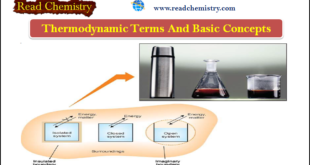
Read More »Thermodynamics – Basic terms and concepts in Thermodynamics
What is Thermodynamics? – Thermodynamics is The study of the flow of heat or any other form of energy into or out of a system as it undergoes a physical or chemical transformation. – In studying and evaluating the flow of energy into or out of a system, it will …
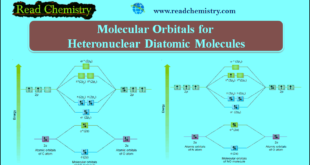
Read More »Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules
Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties of some of The homonuclear diatomic molecules. but in this subject, we will talk about Molecular Orbitals for Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules (MO Theory) – When two different atoms are bonded …
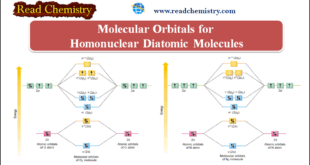
Read More »Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules
Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules – In the previous subject, we talk about but electronic structures and bonding properties of some of The Heteronuclear Diatomic Molecules. but in this subject, we will talk about Molecular Orbitals for Homonuclear Diatomic Molecules (MO Theory) – After having discussed the basic principles …
Read More »MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory
MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory – In this subject, you will find 46 questions and answers MCQ on Chemical Bonding – Orbital Theory 1. When a chemical bond between two atoms is formed, the potential energy of the system_______ (a) decreases (b) increases (c) remains the same (d) …
Read More »Molecular Orbital Theory
Molecular Orbital Theory – The molecular orbital theory proposed by Hund and Mulliken in 1932 explains the formation of a covalent bond in a better way. – According to molecular orbital theory all atomic orbitals of the atoms participating in molecule formation get disturbed when the concerned nuclei approach nearer. …
Read More »MCQ on Chapter: structure of atom – wave mechanical approach
MCQ on the structure of the atom – In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on Chapter structure of atom – wave mechanical approach 1. The number of unpaired electrons in oxygen atom is_______ (a) 1 (b) 2 (c) 3 (d) 4 Answer. (b) 2. The …
Read More »Electronegativity and Electron Affinity
– In this subject, we will discuss the difference Between Electronegativity and Electron Affinity Electron Affinity – A neutral atom can accept an electron to form a negative ion. In this process, in general, energy is released. – The electron affinity (EA) of an element is the amount of energy released …
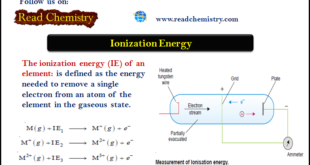
Read More »Ionization Energy (Definition – Trends – Measurement)
– The ionization energy (IE) of an element is defined as the energy needed to remove a single electron from an atom of the element in the gaseous state. Ionization Energy – The process of removing an electron from an isolated atom to form a positive ion is called ionization. …
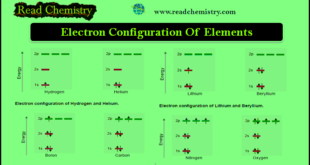
Read More »Electron Configuration Of Elements
– In this subject, we will discuss the rules of Electron Configuration Of Elements Electron Configuration Of Elements – We have seen before that to define completely the state of an atom it is obligatory to refer to all the four quantum numbers (n, l, m, and s) of every …
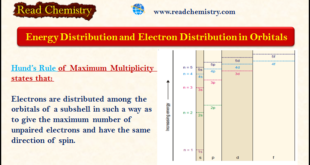
Read More »Distribution of Electrons in Orbitals
– In this subject, we will discuss the Distribution of Electrons in Orbitals according to Hund’s Rule. Energy Distribution and Orbitals – In our earlier discussion, we have seen that the energy of an electron is determined by the first two quantum numbers (n) and (l), while the other two …
Read More »Pauli Exclusion Principle
– The Pauli exclusion principle is of immense value in telling the maximum number of electrons accommodated in any shell. Quantum Numbers and the Energy of an Orbital – The nature of an electron, its position, and energy, is fully implied only by mentioning the values of four quantum numbers ascribed …
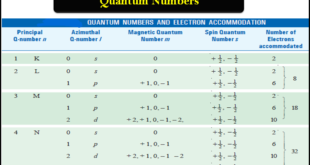
Read More »Quantum Numbers (Principal, Azimuthal, Magnetic and Spin)
Quantum Numbers – Bohr’s electronic energy shells or levels, designated as Principal Quantum Numbers (n), could hardly explain the hydrogen spectrum adequately. – Spectra of other elements that are quite complex, also remained unexplained by this concept. – Many single lines of the spectra are found to consist of a …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry