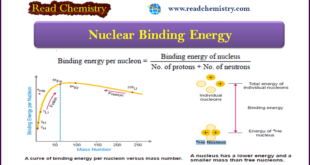
– In this subject, we will discuss Nuclear Binding Energy: (Definition, Formula, Explanation) Nuclear Binding Energy – The atomic nucleus is made of protons and neutrons closely packed in a small volume. – Although there exist intensive repulsive forces between the component protons, the nucleus is not split apart. This …
Read More »Energy released in Nuclear Reactions: Nuclear Binding Energy
– In this subject, we will discuss the energy released in Nuclear Reactions: Nuclear Binding Energy Einstein’s Equation Relating Mass and Energy – According to Albert Einstein, mass can be converted into energy and vice versa. – His famous equation relating mass and energy is: where E = energy ; m …
Read More »Nuclear Equations: Balancing, Rules, Practice
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Equations: Balancing, Rules, Practice Nuclear Equations – Similar to a chemical reaction, nuclear reactions can be represented by equations. – These equations involving the nuclei of the reactants and products are called nuclear equations. – The nuclear reactions occur by redistribution …
Read More »Solubility of Organic Compounds
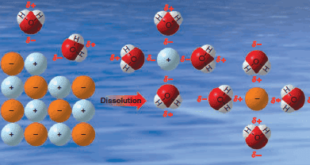
Solubility of Organic Compounds – Intermolecular forces are of primary importance in explaining the solubility of substances. – Dissolution of a solid in a liquid is, in many respects, like the melting of a solid. – The orderly crystal structure of the solid is destroyed, and the result is the …
Read More »Intermolecular Forces in Organic compounds
– In this subject, we will discuss the Intermolecular Forces in Organic compounds Intermolecular Forces in Organic Compounds – The forces that act between molecules are not as strong as those between ions, but they account for the fact that even completely nonpolar molecules can exist in liquid and solid …
Read More »Limiting Reagent: Definition, Examples, Problems
– In this subject, we will discuss the Limiting Reagent (Definition, Examples, Problems) Limiting Reagent – When a chemist carries out a reaction, the reactants are usually not present in exact stoichiometric amounts, that is, in the proportions indicated by the balanced equation. – Because the goal of a reaction …
Read More »Amounts of Reactants and Products
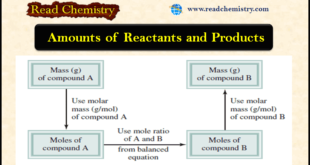
– In this subject, we will discuss Amounts of Reactants and Products Amounts of Reactants and Products – A basic question raised in the chemical laboratory is (How much product will be formed from specific amounts of starting materials (reactants)?) Or in some cases, we might ask the reverse question: …
Read More »Physical Properties and Molecular Structure of Organic compound
** So far, we have said little about one of the most obvious characteristics of organic compounds— that is, their physical state or phase. Whether a particular substance is a solid, or a liquid, or a gas would certainly be one of the first observations that we would …
Read More »Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
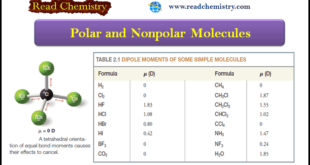
– In this subject, we will discuss the Polar and Nonpolar Molecules. Dipole moment – The dipole moment is a physical property that can be measured experimentally. – It is defined as the product of the magnitude of the charge in electrostatic units (esu) and the distance that separates them …
Read More »Polar Covalent Bond and Dipole moment
– In this subject, we will discuss the Polar Covalent Bond and Dipole moment. Polar Covalent Bonds – Covalent bonds form by sharing of electrons between atoms of similar electronegativities to achieve the configuration of a noble gas. – If we have a compound such as LiF in which the …
Read More »Nuclear Reaction: Definition, Types, Examples, Equations
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Reaction: Definition, Types, Examples, and Equations. Nuclear Reaction – In a chemical reaction, there is merely a rearrangement of extranuclear electrons. – The atomic nucleus remains intact. – A nuclear reaction involves a change in the composition of the nucleus. – …
Read More »Radioactive Dating: Definition, Formula, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Radioactive Dating: Definition, Formula, Examples Radioactivity – Several elements such as uranium and radium are unstable. – Their atomic nucleus breaks off its own accord to form a smaller atomic nucleus of another element. – The protons and neutrons in the unstable …
Read More »Experimental Determination of Empirical Formulas
Experimental Determination of Empirical Formulas ** The fact that we can determine the empirical formula of a compound if we know the percent composition enables us to identify compounds experimentally. ** The procedure is as follows. (1) Chemical analysis tells us the number of grams of each element …
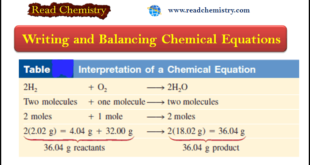
Read More »Chemical Equations – Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
– In this subject, we will discuss Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations. Chemical Reactions and Chemical Equations – A chemical reaction is a process in which a substance (or substances) is changed into one or more new substances. – To communicate with one another about chemical reactions, chemists have devised …
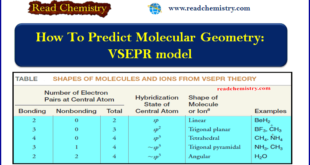
Read More »How To Predict Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model
How To Predict Molecular Geometry: VSEPR model ** We can predict the arrangement of atoms in molecules and ions on the basis of a relatively simple idea called the valence shell electron pair repulsion (VSEPR) model. ** We apply the VSEPR model in the following way: (1) We …
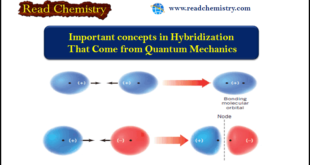
Read More »Important concepts in Hybridization That Come from Quantum Mechanics
Important concepts in Hybridization (1) An atomic orbital (AO) corresponds to a region of space about the nucleus of a single atom where there is a high probability of finding an electron. Atomic orbitals called s orbitals are spherical; those called p orbitals are like two almost-tangent spheres. Orbitals can hold …
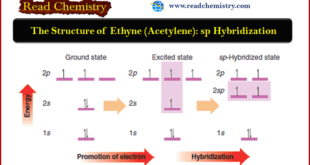
Read More »The Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene): sp Hybridization
The Structure of Ethyne (Acetylene): sp Hybridization ** Hydrocarbons in which two carbon atoms share three pairs of electrons between them, and are thus bonded by a triple bond, are called alkynes. The two simplest alkynes are ethyne and propyne. ** Ethyne, a compound that is also called acetylene, …
Read More »Half-life time and radioactive decay: Equations, Calculations
– In this subject, we will discuss the Half-life time and radioactive decay: Equations, Calculations Rate of radioactive decay – The decay of a radioactive isotope takes place by disintegration of the atomic nucleus. – It is not influenced by any external conditions. – Therefore the rate of decay is …
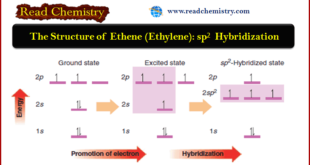
Read More »The Structure of Ethene (Ethylene): sp2 Hybridization
The Structure of Ethene (Ethylene): sp2 Hybridization ** The carbon atoms of many of the molecules that we have considered so far have used their four valence electrons to form four single covalent (sigma) bonds to four other atoms. ** We find, however, that many important organic compounds …
Read More »Radioactive Disintegration Series: Definition, Examples
– In this subject, we will discuss the Radioactive Disintegration Series: Definition, Examples Radioactivity – Several elements such as uranium and radium are unstable. – Their atomic nucleus breaks off its own accord to form a smaller atomic nucleus of another element. – The protons and neutrons in the unstable …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry