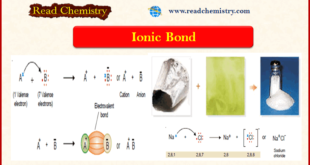
– In this subject, we will discuss the Ionic Bond (Definition, Examples, Types, Properties) Ionic Bond – This type of bond is established by the transfer of an electron from one atom to another. – Let us consider a general case when an atom (A) has one electron in …
Read More »Bond Breaking and Bond Making in Organic Compounds
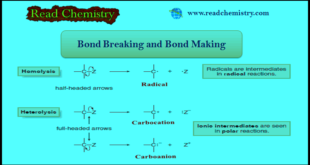
– In this subject, we will discuss bond Breaking and Bond Making in Organic Compounds. Bond Breaking and Bond Making – Having now learned how to write and identify some common kinds of organic reactions, we can turn to a discussion of reaction mechanisms. – A reaction mechanism is a …
Read More »Types of Equilibrium Constants used in Analytical Chemistry
– In this subject, we will discuss Types of Equilibrium Constants used in Analytical Chemistry. Chemical Equilibrium and Equilibrium constants – Many reactions used in analytical chemistry never result in the complete conversion of reactants to products. – Instead, they proceed to a state of chemical equilibrium in which the …
Read More »Chemical Bonding: Important terms and Definitions
– In this subject, we will discuss the important Terms and Definitions of Chemical Bonding. Chemical Bond – Molecules of chemical substances are made of two or more atoms joined together by some force, acting between them. – This force which results from the interaction between the various atoms that …
Read More »The Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solution
– In this subject, we will discuss the Chemical Composition of Aqueous Solution – Water is the most plentiful solvent on Earth, is easily purified, and is not toxic. – It is, therefore, widely used as a medium for chemical analyses. Classifying Solutions of Electrolytes – Most of the solutes …
Read More »Nuclear Chemistry Quiz: Questions and Answers
Nuclear Chemistry Quiz – In this subject, you will find 40 questions and answers MCQ on Nuclear Chemistry 1. Which is the correct symbol for an alpha particle? (a) 4He2 (b) 1n0 (c) 0e-1 (d) 1p1 Answer. (a) 2. Of the following, which is the most damaging when ingested? (a) …
Read More »Chemical Stoichiometry: Definition, Formula, Examples
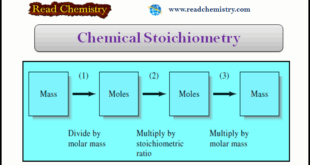
In this subject, we will discuss the Chemical Stoichiometry: Definition, Formula, Example Chemical Stoichiometry – Stoichiometry is the quantitative relationship among the amounts of reacting chemical species. – This subject provides a brief review of stoichiometry and its applications to chemical calculations. – The stoichiometry of a reaction is the …
Read More »Nuclear Fusion: Definition, Occurrence, Examples, Applications
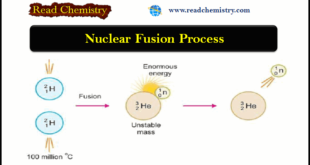
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Fusion Process ( Definition, Occurrence, Examples, Applications) Nuclear Fusion Process – The Nuclear Fusion Process is the opposite of nuclear fission. – Nuclear fusion may be defined as the process in which two lightweight nuclei combine or fuse to form a …
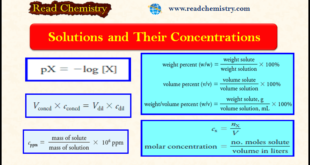
Read More »Concentration of Solutions: Definitions, Formulas, Solved Problems
– In this subject, we will discuss the Concentration of Solutions Concentration of Solutions (Definitions, Formulas, Solved Problems). Concentration of Solutions – For history, measurements and their corresponding units were invented at the local level. – By necessity of primitive communication and local technology, standards were nearly nonexistent, and conversions …
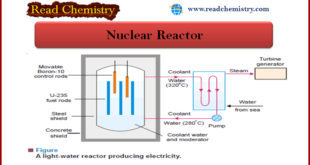
Read More »Nuclear Reactor: Definition, Components
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Reactor (Definition, Components) Nuclear Reactor – It has been possible to control the fission of U-235 so that energy is released slowly at a usable rate. – Controlled fission is carried out in a specially designed plant called a nuclear power …
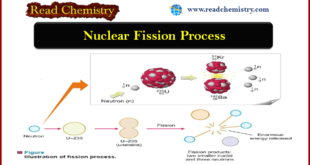
Read More »Nuclear Fission: Definition, Properties, Examples, Applications
– In this subject, we will discuss the Nuclear Fission (Definition, Properties, Examples, Applications) Nuclear Fission Process – In 1939, Hahn and Stassmann discovered that a heavy atomic nucleus of uranium-235 upon bombardment by a neutron splits apart into two or more nuclei. – U-235 first absorbs a neutron …
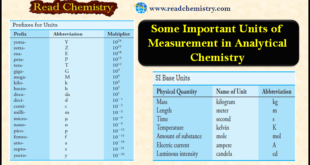
Read More »Some Important Units of Measurement in Analytical Chemistry
SI Units – Scientists throughout the world have adopted a standardized system of units known as the International System of Units (SI). – This system (SI) is based on the seven fundamental base units shown in Table (1). – Numerous other useful units, such as volts, hertz, coulombs, …
Read More »Safety in the laboratory
– In this subject, we will discuss the Safety in the laboratory Safety in The Laboratory – There is necessarily a degree of risk associated with any work in a chemical laboratory. – Accidents can and do happen. – Strict adherence to the following rules will go far toward preventing …
Read More »The Laboratory Notebook
The Laboratory Notebook – A laboratory notebook is needed to record measurements and observations concerning an analysis. – The book should be permanently bound with consecutively numbered pages (if necessary, the pages should be hand-numbered before any entries are made). – Most notebooks have more than ample room, so there …
Read More »Calibration of Volumetric Glassware in the laboratory
– In this subject, we will discuss How to Calibrate Volumetric Glassware in the laboratory Calibration of Volumetric Glassware – Volumetric glassware is calibrated by measuring the mass of a liquid (usually distilled or deionized water) of known density and temperature that is contained in (or delivered by) the volumetric …
Read More »Volumetric Flask: Overview, Uses, Function
Volumetric Flask – A volumetric flask is manufactured with capacities ranging from 5 mL to 5 L and is usually calibrated to contain (TC) a specified volume when filled to a line etched on the neck. – They are used for the preparation of standard solutions and the dilution …
Read More »Pipets : Overview, Uses, Function, Cleaning
Pipets – Pipets permit the transfer of accurately known volumes from one container to another. – Common types are shown in Figure (1), and information concerning their use is given in Table (1). – A volumetric, or transfer, pipet (Figure 1a) delivers a single, fixed volume between 0.5 and 200 …
Read More »Burets : Overview, Uses, Function, Cleaning
Burets – Burets, like measuring pipets, make it possible to deliver any volume up to the maximum capacity of the device. – The precision attainable with a buret is substantially greater than the precision with a pipet. – A buret consists of a calibrated tube to hold the titrant plus …
Read More »Measuring Volume by Pipets, Burets, Volumetric Flask
– The precise measurement of volume is as important to many analytical methods as the precise measurement of mass. (1) Units of Volume – The unit of volume is the liter (L), defined as one cubic decimeter. – The milliliter (mL) is one one-thousandth of a liter (0.001 L) and …
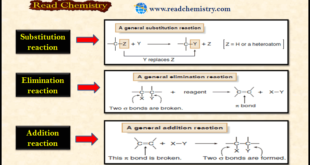
Read More »Types of Organic Reactions
– In this subject, we will discuss the general Types of Organic Reactions Types of Organic Reactions – Like other compounds, organic molecules undergo acid-base and oxidation-reduction reactions. – Organic molecules also undergo substitution, elimination, and addition reactions. (1) Substitution Reactions – Substitution reaction is a reaction in which an …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry