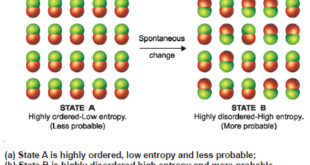
Spontaneous Processes – A process that proceeds of its own accord, without any outside assistance, is termed a spontaneous or natural process. – The reverse process which does not proceed on its own, is referred to as a nonspontaneous or unnatural process. – In general, the tendency of a process …
Read More »MCQ on Chapter Thermochemistry ΔH, ΔE
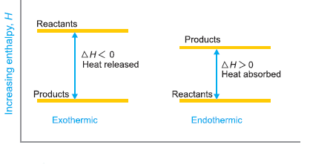
1. For exothermic reactions, ΔH is _______ while for endothermic reactions it is _______. (a) positive, negative (b) positive, positive (c) negative, negative (d) negative, positive Answer. (d) 2. The branch of chemistry which deals with the heat changes caused by chemical reactions is called _______ (a) thermodynamics (b) thermal …
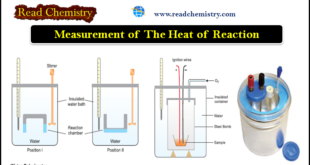
Read More »Measurement of The Heat of Reaction
Measurement of The Heat of Reaction – The experimental measurement of the heat of reaction or enthalpy change is known as calorimetry. – The name (calorimetry) evidently finds its origin in the unit of heat–the calorie. – The heat given out or absorbed in a chemical reaction is measured in …
Read More »Bond energy (definition, Illustration, solved Problems)
Bond energy – When a bond between two atoms is formed, there is a release of energy. – The same amount of energy is absorbed when the bond is broken. – The bond energy is defined as the average amount of energy required to break all bonds of a particular type …
Read More »Hess’s Law ( statement, Illustration, application, Problems)
– Hess’s Law may be stated as: (If a chemical change can be made to take place in two or more different ways whether in one step or two or more steps, the amount of total heat change is same no matter by which method the change is brought about). …
Read More »Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes
– In this subject, we will discuss Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes. Energy Changes During Transitions or Phase Changes – The three states of matter – solid, liquid and gas differ from one another in the arrangement of their constituent particles. – The magnitudes of intermolecular forces acting …
Read More »Heat of Combustion (Definition, Applications, Solved Problems)
Heat of Combustion – The heat of combustion of a substance is defined as The change in enthalpy of a system when one mole of the substance is completely burnt in excess of air or oxygen. – It is denoted by ΔHc. – For example, the heat of combustion …
Read More »Heat of Formation (Definition, Applications, Solved Problems)
Heat of Formation – The heat of formation of a compound is defined as The change in enthalpy that takes place when one mole of the compound is formed from its elements. – It is denoted by ΔHf . – For example, the heat of formation of ferrous sulphide and acetylene …
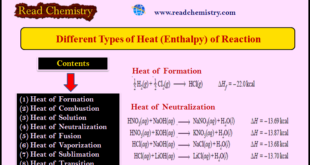
Read More »Different Types of Heat of Reaction (Enthalpy)
– The heat of reaction or enthalpy changes accompanying chemical reactions are expressed in different ways, depending on the nature of the reaction. These are discussed below. (1) Heat of Formation – The heat of formation of a compound is defined as The change in enthalpy that takes place when …
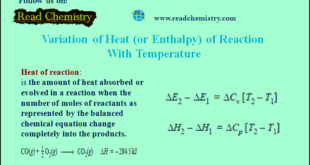
Read More »Variation of heat of reaction with temperature
– In this subject, the Variation of heat of reaction with temperature will be discussed. Heat of Reaction or Enthalpy of Reaction – The heat of a reaction is simply the amount of heat absorbed or evolved in the reaction. – We also know that the amount of heat absorbed …
Read More »Enthalpy of Reaction
– For reactions involving solids and liquids only the change in volume (ΔV) is very small and the term P × ΔV is negligible. For such reactions, the Change of Enthalpy of Reaction ΔH is equal to ΔE. Enthalpy of Reaction – Thermochemical measurements are made either at (a) constant …
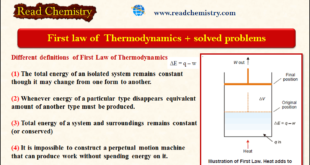
Read More »MCQ on the First law of Thermodynamics
MCQ on the First Law of Thermodynamics – In this subject, you will find 50 questions and answers MCQ on the First law of Thermodynamics 1. The first law of thermodynamics is_______ (a) the total energy of an isolated system remains constant though it may change from one form to …
Read More »Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas
Adiabatic Expansion of an Ideal Gas – A process carried in a vessel whose walls are perfectly insulated so that no heat can pass through them, is said to be adiabatic. – In the adiabatic process there is no heat exchange between a system and surroundings, and q = 0. …
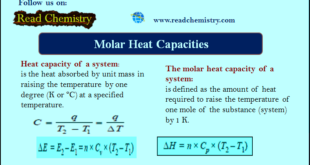
Read More »Heat Capacity – Molar Heat Capacity
Molar Heat Capacity – By heat capacity of a system, we mean the capacity to absorb heat and store energy. – As the system absorbs heat, it goes into the kinetic motion of the atoms and molecules contained in the system. – This increased kinetic energy raises the temperature of …
Read More »Enthalpy of A System
– Enthalpy (H) is the total heat content of a system at constant pressure and is equivalent to the internal energy E plus the PV energy. Enthalpy of A System – In a process carried at constant volume (say in a sealed tube), the heat content of a system is …
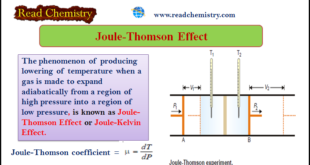
Read More »Joule-Thomson Effect
– The phenomenon of producing a lowering of temperature when a gas is made to expand adiabatically from a region of high pressure into a region of low pressure is known as the Joule-Thomson Effect or Joule-Kelvin Effect Joule-Thomson Effect – Joule and Thomson (later Lord Kelvin) showed that when …
Read More »The First Law of Thermodynamics + Solved Problems
– The first law of Thermodynamics states that The total energy of an isolated system remains constant though it may change from one form to another. Internal Energy – A thermodynamic system containing some quantity of matter has within itself a definite quantity of energy. – This energy includes not …
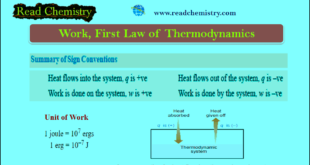
Read More »Work in Thermodynamics (Definition – Formula – Problems)
– In physics, mechanical work is defined as force multiplied by the distance through which the force acts. – In elementary thermodynamics, the only type of work generally considered is the work done in the expansion (or compression) of a gas Nature of Heat and Work – When a change …
Read More »Thermodynamic Processes
– Thermodynamic Processes involve the change of conditions (temperature, pressure, and volume). Thermodynamic Processes – When a thermodynamic system changes from one state to another, the operation is called a Process. – Thermodynamic Processes involve the change of conditions (temperature, pressure, and volume). – The various types of thermodynamic processes …
Read More »Thermodynamics – Basic terms and concepts in Thermodynamics
What is Thermodynamics? – Thermodynamics is The study of the flow of heat or any other form of energy into or out of a system as it undergoes a physical or chemical transformation. – In studying and evaluating the flow of energy into or out of a system, it will …
Read More » Read Chemistry
Read Chemistry