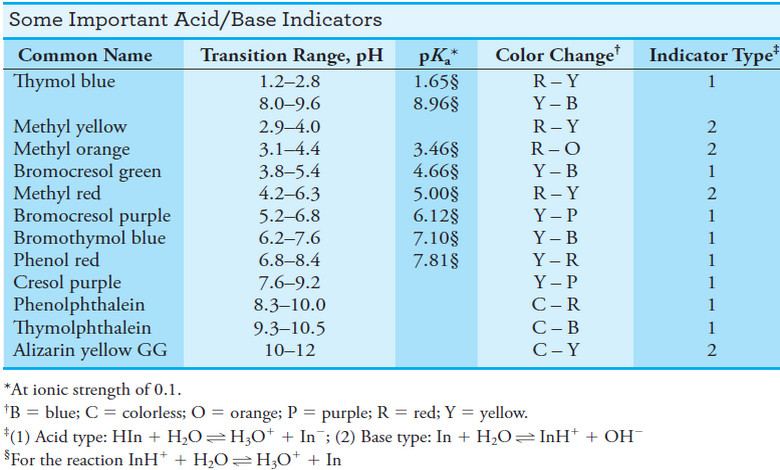
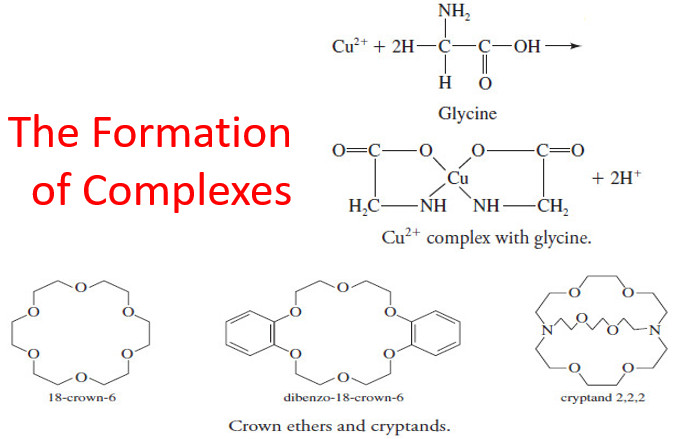
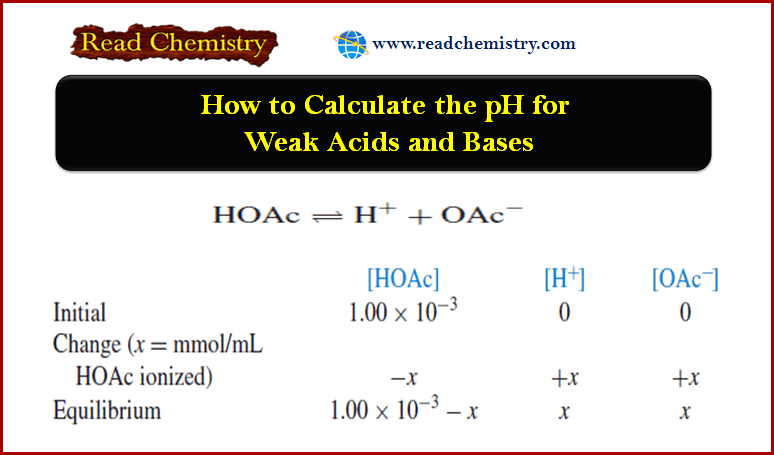
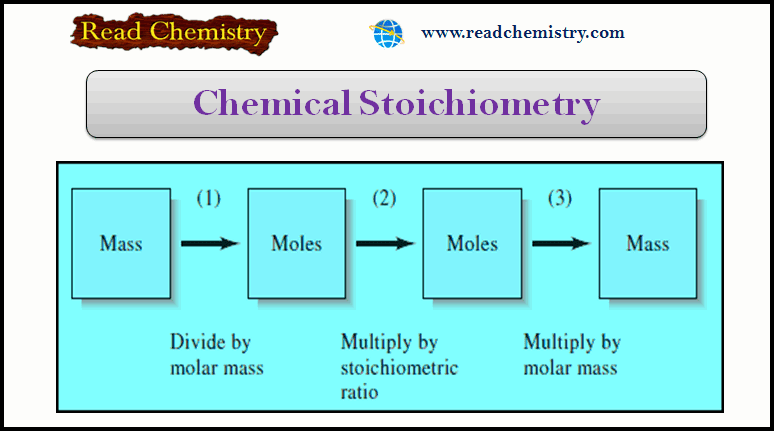
Popular Posts
-
Physical Chemistry
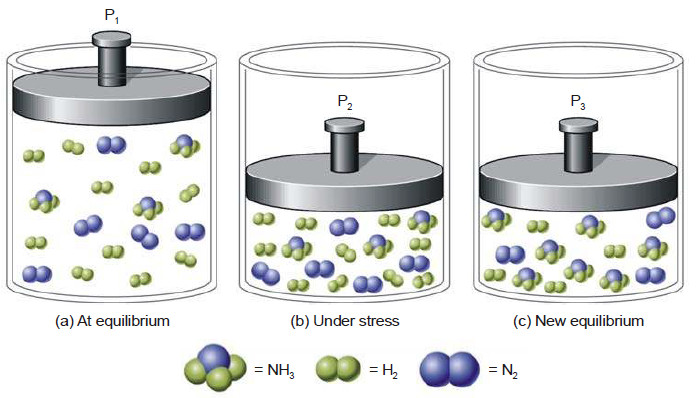
Le Chatelier’s principle
Le Chatelier’s principle – In 1884, the French Chemist Henry Le Chatelier proposed a general principle which applies to all…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
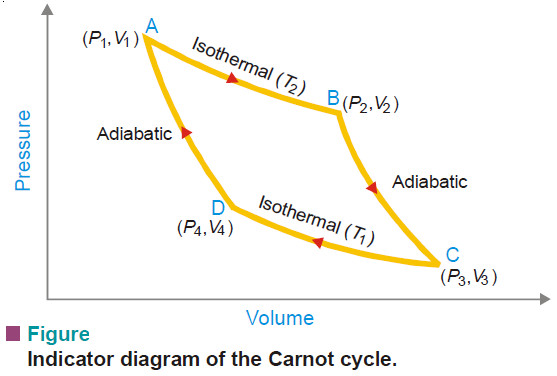
Carnot Cycle – Definition, Theorem, Efficiency, Derivation
– In this topic, we will discuss The Carnot Cycle : Definition, Theorem, Efficiency, Derivation and Sovled problems. The Carnot…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
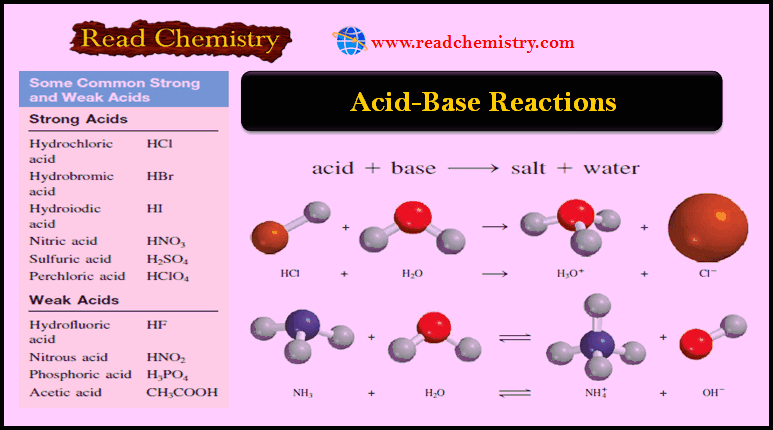
Acid-Base Reactions: Definition, Examples, and Uses
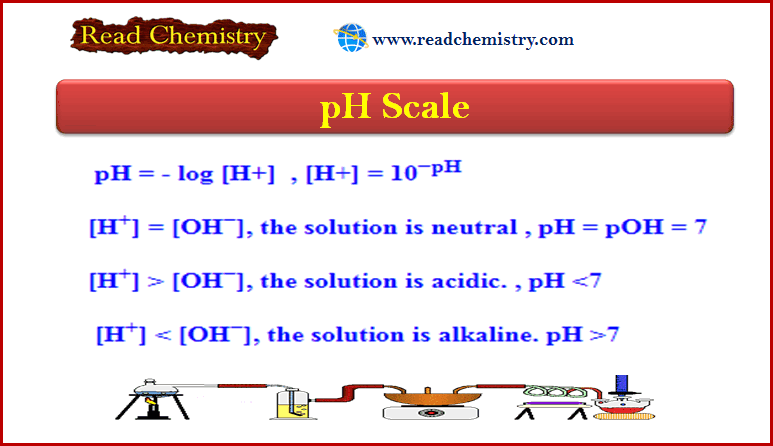
– In this subject, we will discuss the Acid-Base Reactions: Definition, Examples, and Uses – Acids and bases are as…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
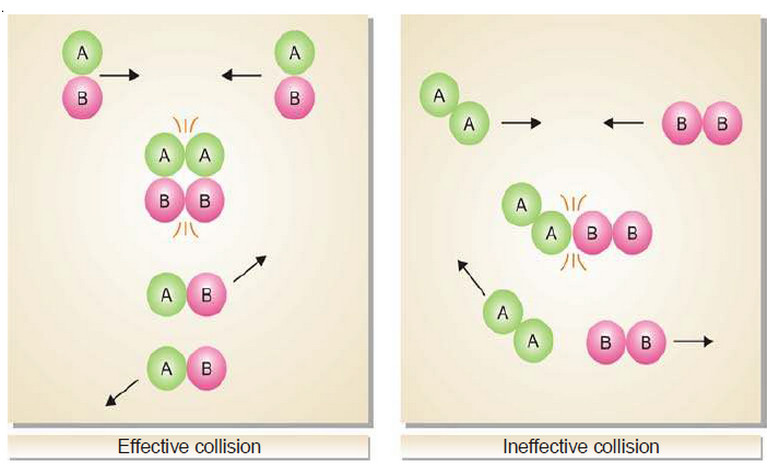
Collision theory of Reaction rates
Collision theory of Reaction rates – According to collision theory, a chemical reaction takes place only by collisions between the…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
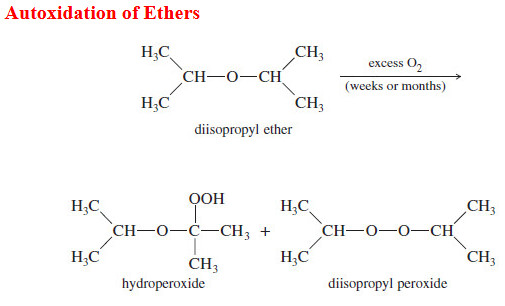
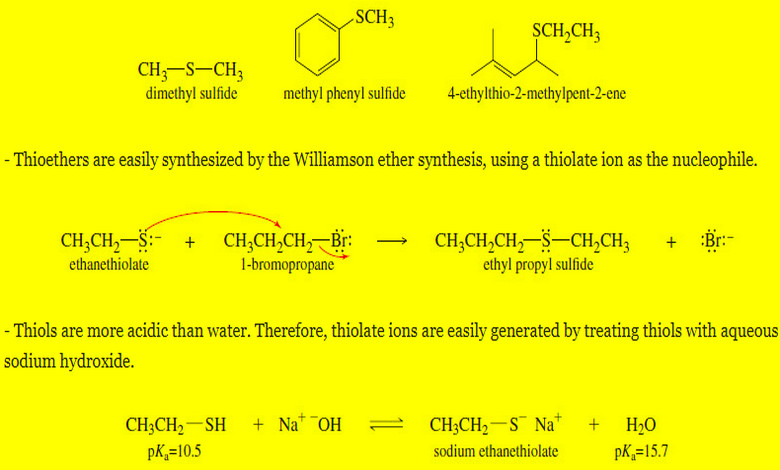
Autoxidation of Ethers
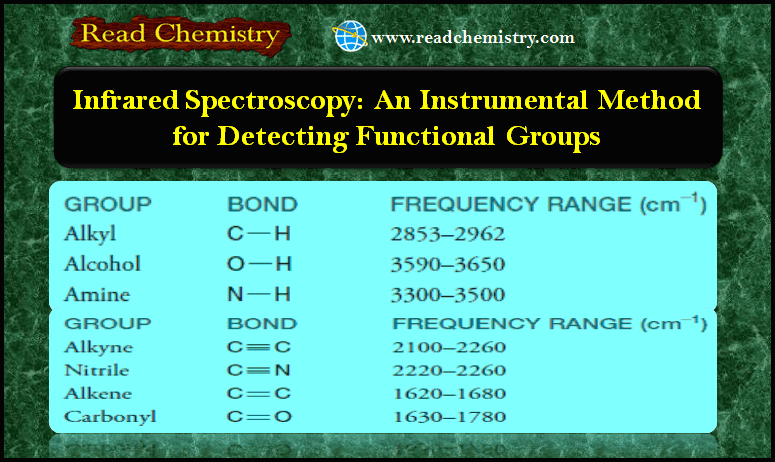
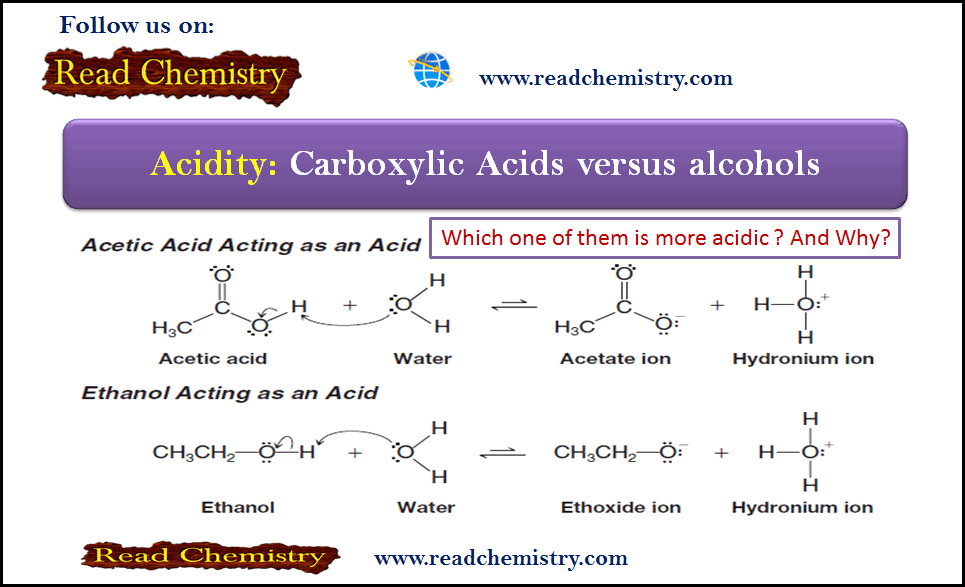
– In this topic, we will discuss The autoxidation of Ethers. What are Ethers? Ethers are compounds of formula R-O-R,…
Read More » -
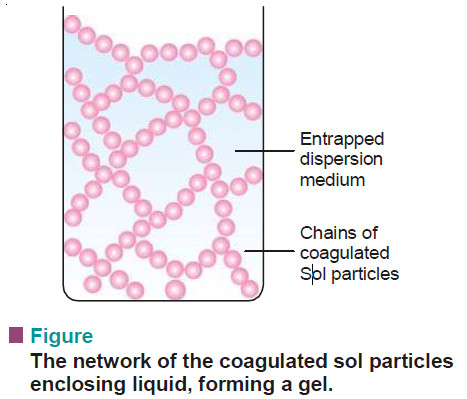
Physical Chemistry
Applications of Colloids
– In this topic, we will discuss The Applications of Colloids. Applications of Colloids – Colloids play an important role…
Read More »
-
Organic Chemistry
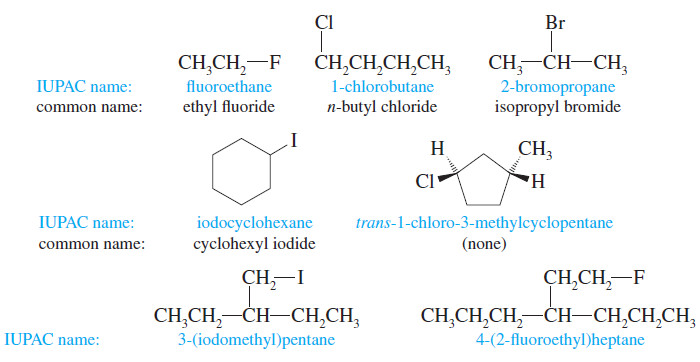
Nomenclature of Alkyl Halides
Introduction to Alkyl Halides – In this subject , we consider Nomenclature of alkyl halides.…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
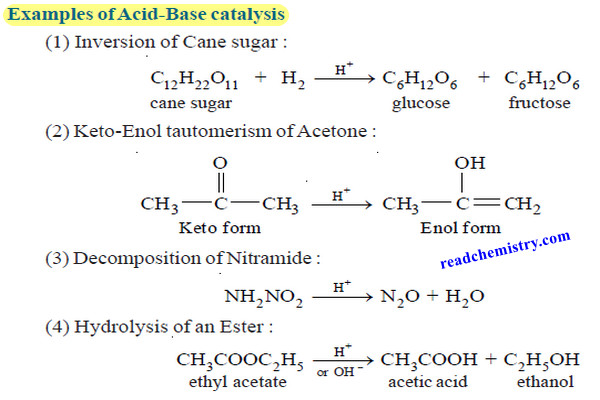
Physical Chemistry
Acid-Base catalysis (definition – Examples – Mechanism)
– In this topic, we will discuss Acid-Base catalysis: definition, Examples and Mechanism. Acid-Base catalysis…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
General Chemistry
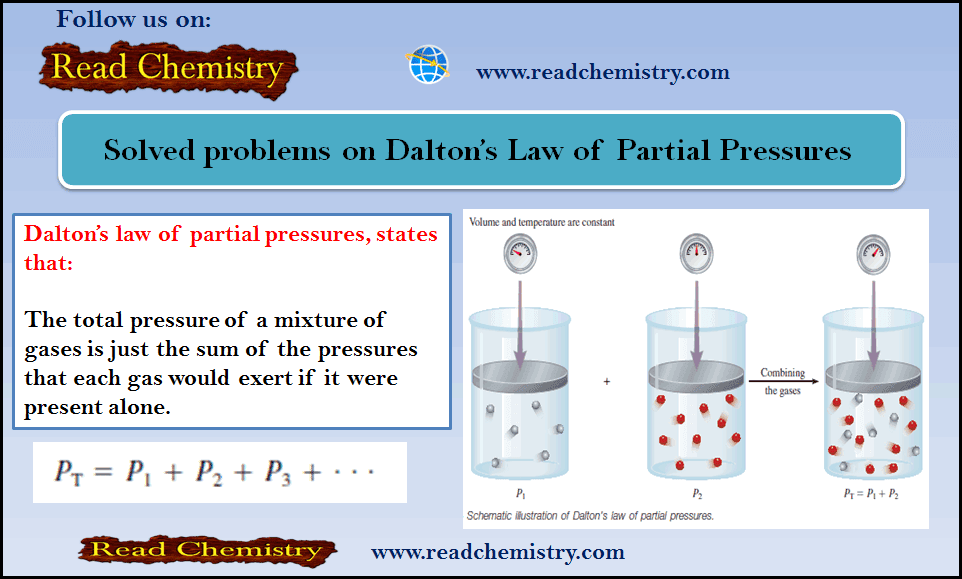
Solved problems: Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressures
– Before you solve these problems, you can read this subject for Dalton’s Law of…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
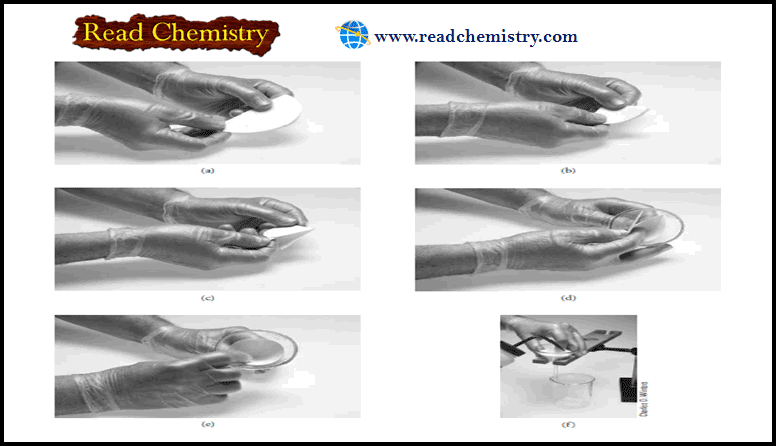
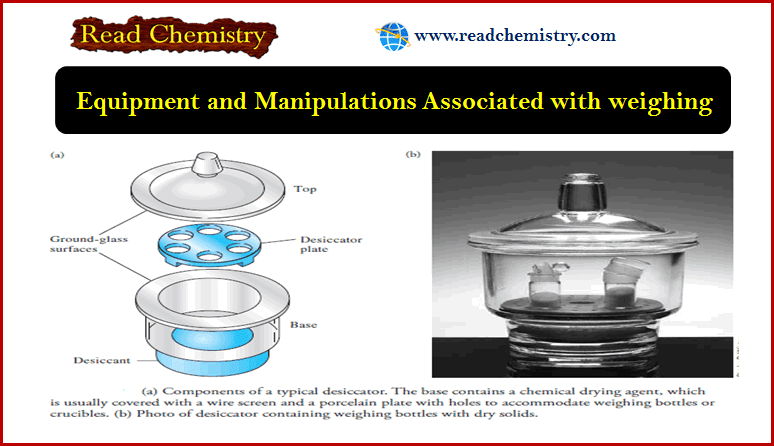
Analytical Chemistry
Filtration and Ignition of Solids
– In this subject, we will discuss the Filtration and Ignition of Solids. – Several…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-