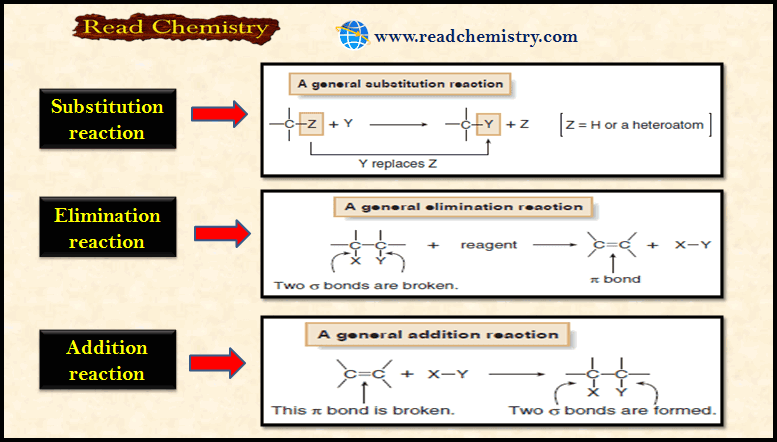
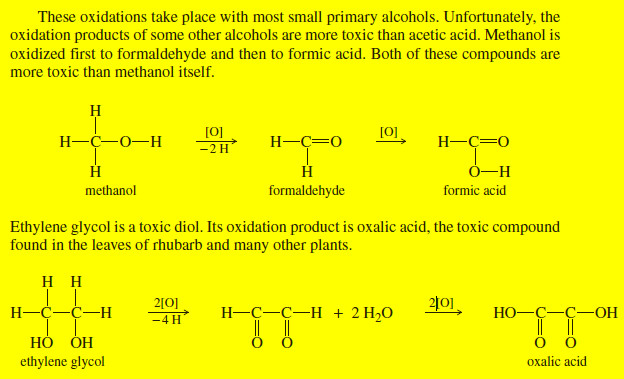
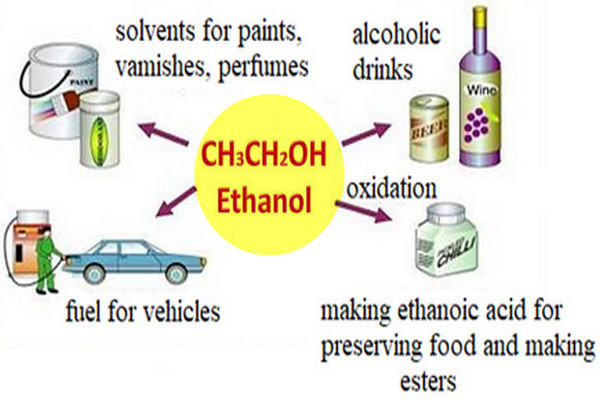
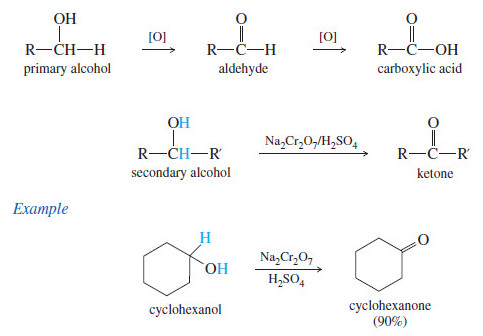
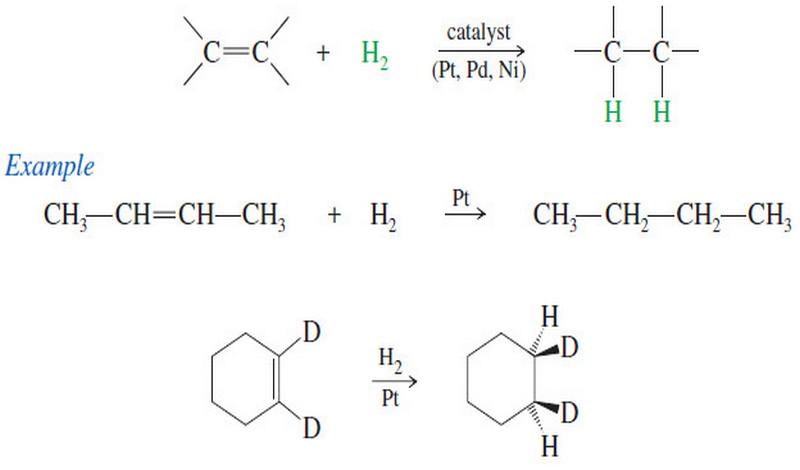
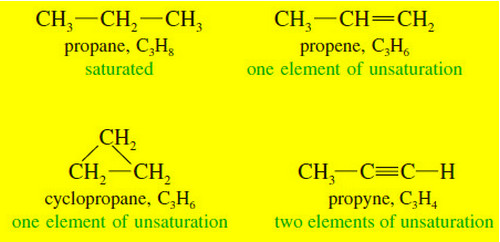
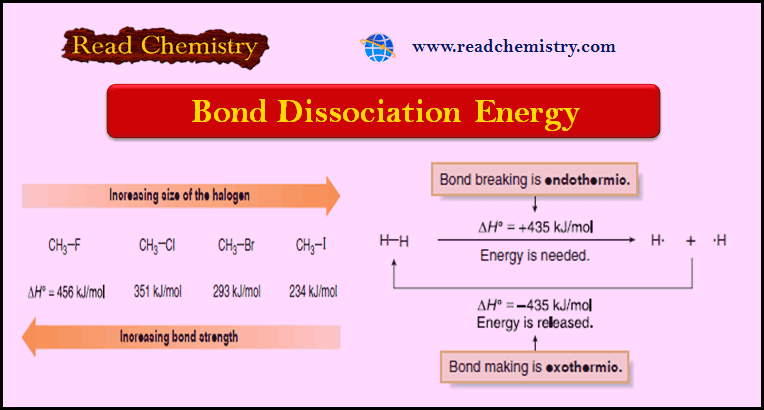
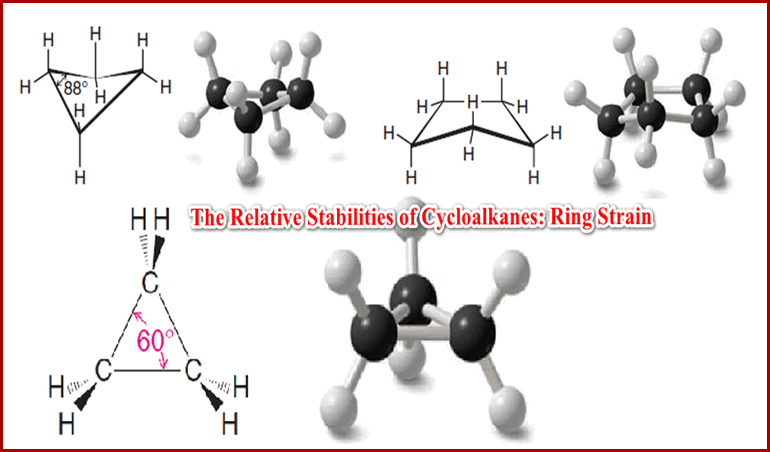
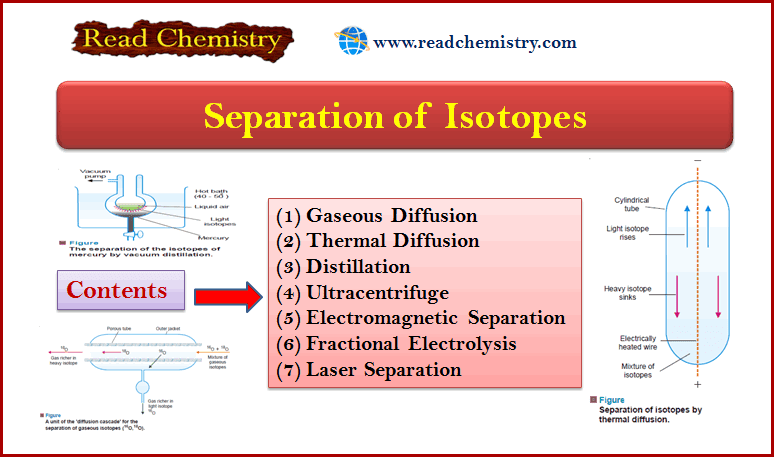
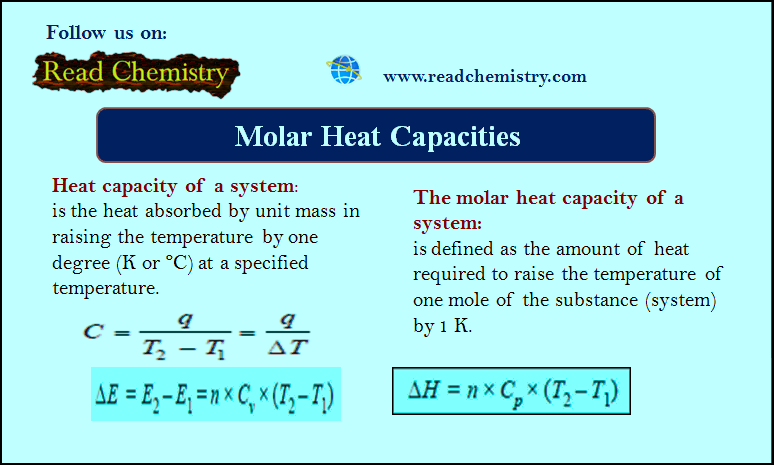
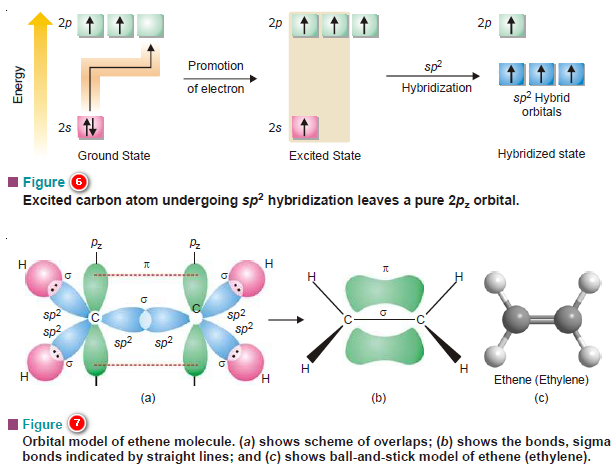
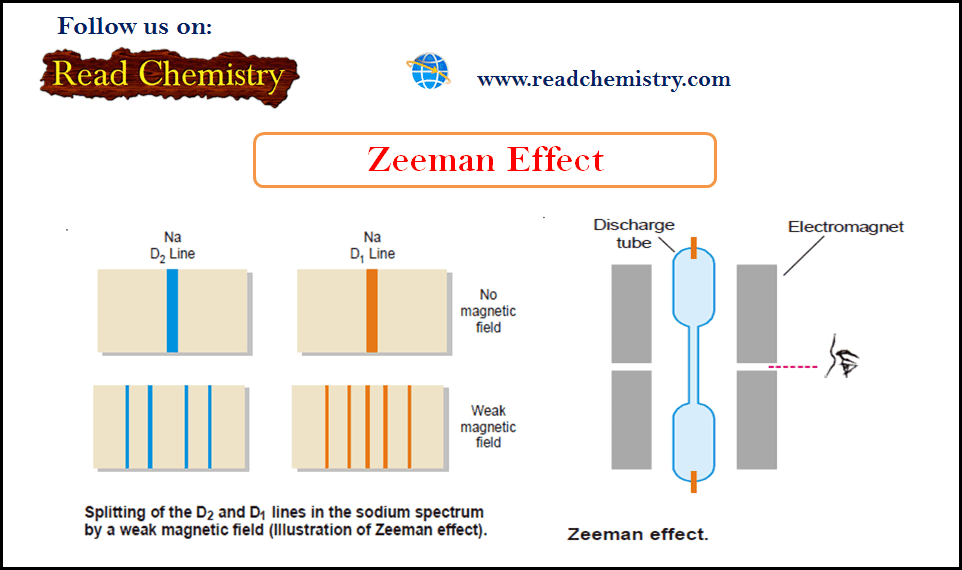
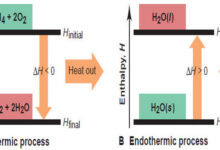
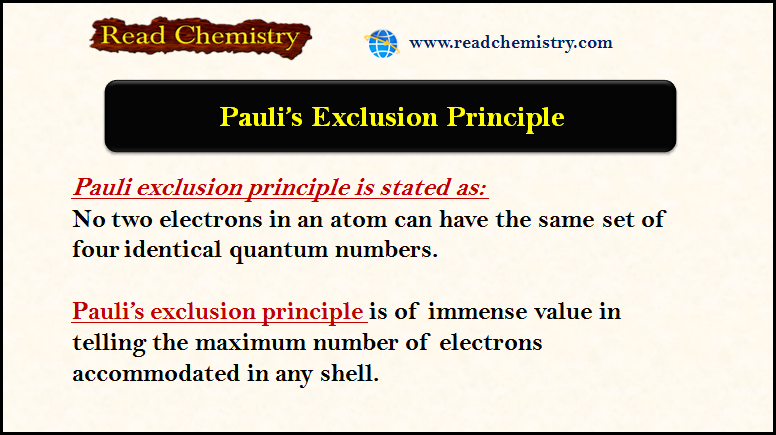
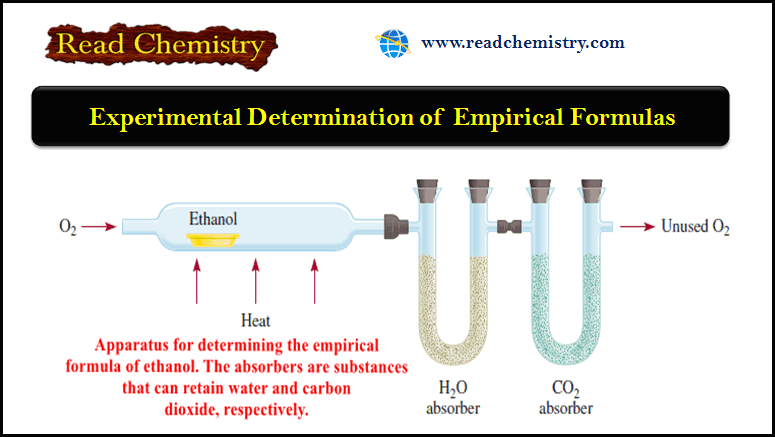
Popular Posts
-
General Chemistry
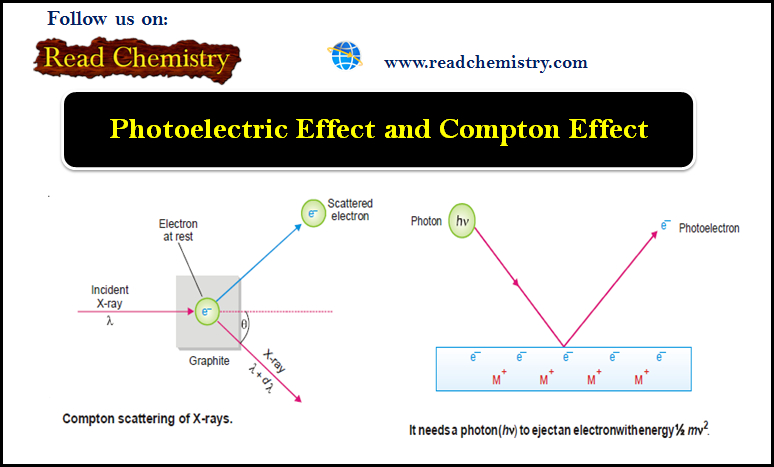
Photoelectric Effect and Compton Effect
– In this subject, we will discuss the Photoelectric Effect and Compton Effect Photoelectric Effect – When a beam of…
Read More » -
Online MCQ
Structure of atom – Classical mechanics – Online MCQ test
Online MCQ test on Structure of atom – Classical mechanics – In this topic we offer you, online MCQ test…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
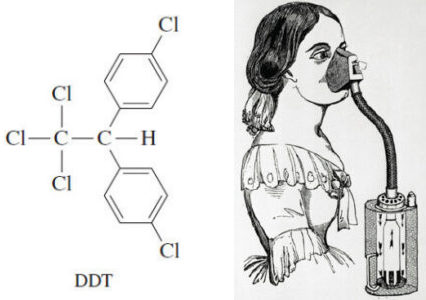
Common Uses of Alkyl Halides
Alkyl halides as Solvents – Alkyl halides are used primarily as industrial and household solvents. – Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) was…
Read More » -
Organic Chemistry
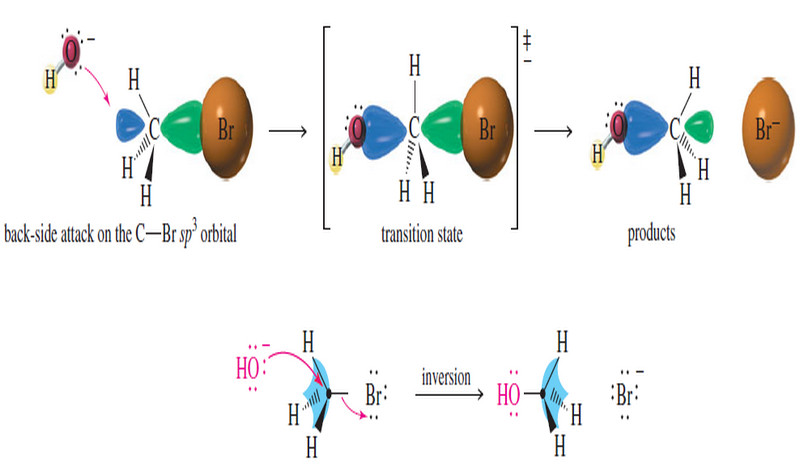
Stereochemistry of the SN2 Reaction
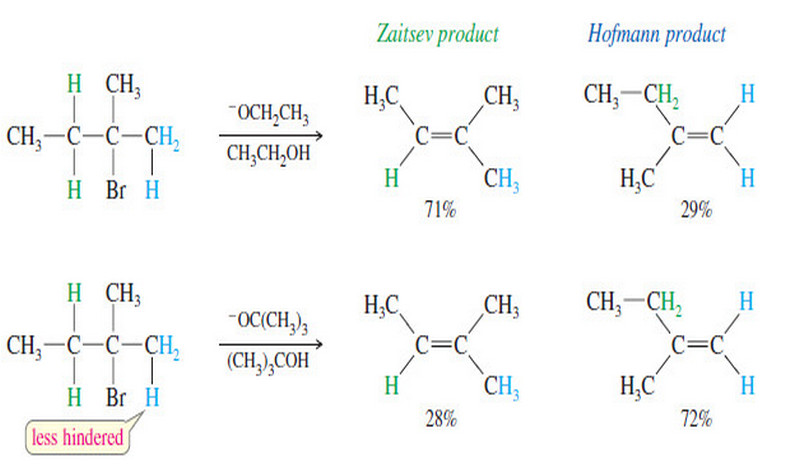
Stereochemistry of the SN2 Reaction – As we have seen, the reaction SN2 requires attack by a nucleophile on the…
Read More » -
General Chemistry
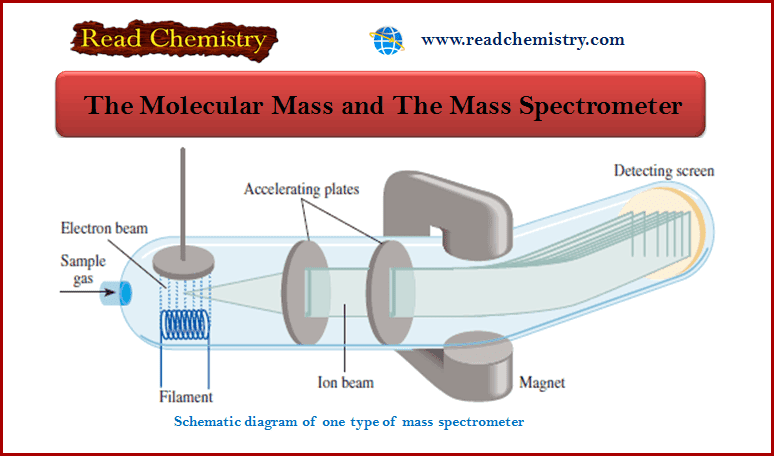
The Molecular Mass and The Mass Spectrometer
Molecular Mass ** If we know the atomic masses of the component atoms, we can calculate the mass of…
Read More » -
Physical Chemistry
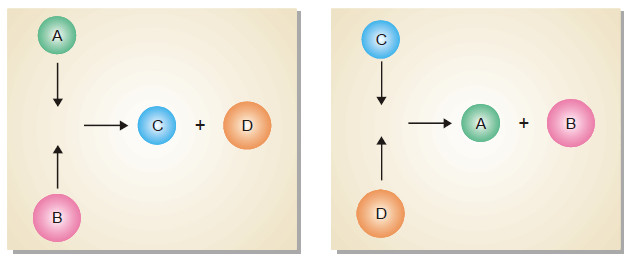
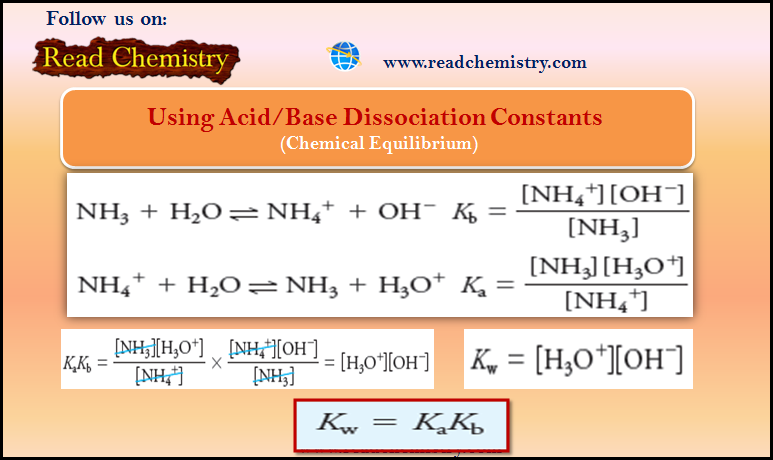
Characteristics of Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical Equilibrium is the state of a reversible reaction when the two opposing reactions occur at the same rate and…
Read More »
-
General Chemistry
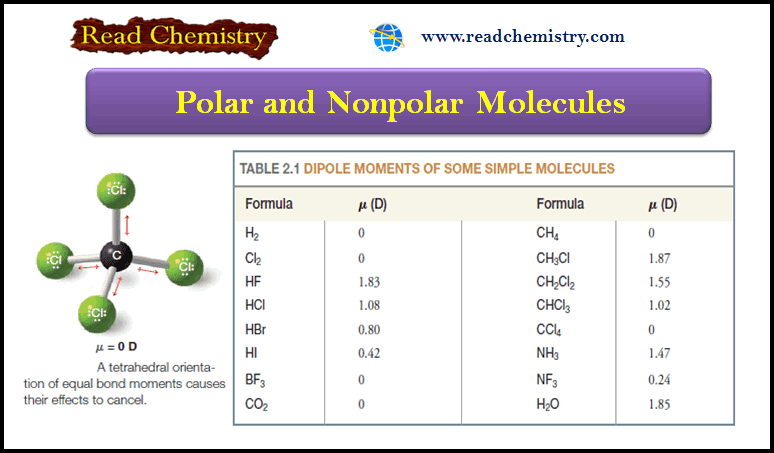
Polar and Nonpolar Molecules
– In this subject, we will discuss the Polar and Nonpolar Molecules. Dipole moment –…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Physical Chemistry
Derivation of the phase rule
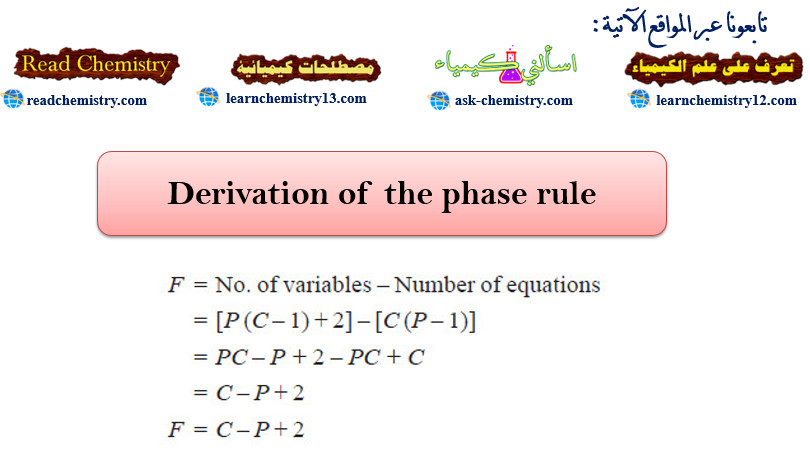
Derivation of the phase rule – Here the derivation of the phase rule for one-component…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
General Chemistry
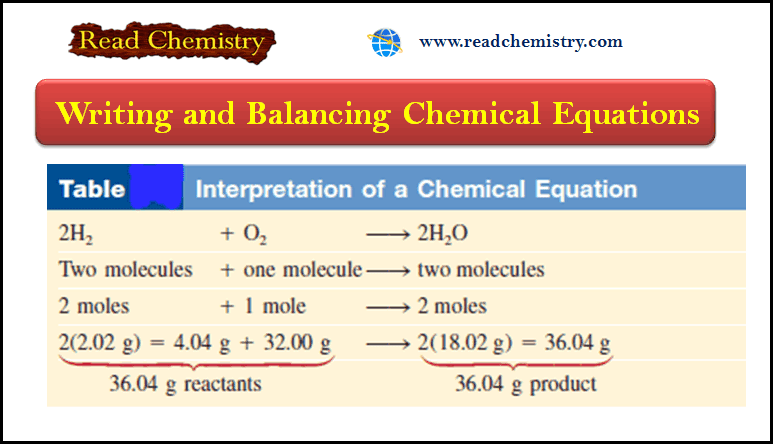
Chemical Equations – Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations
– In this subject, we will discuss Writing and Balancing Chemical Equations. Chemical Reactions and…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Analytical Chemistry
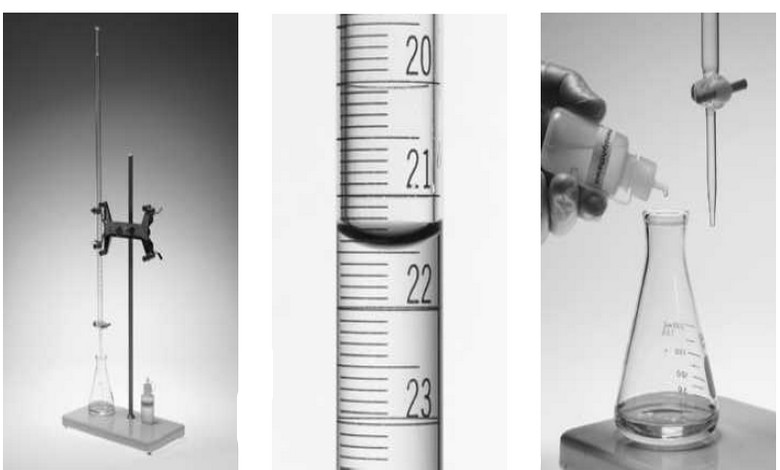
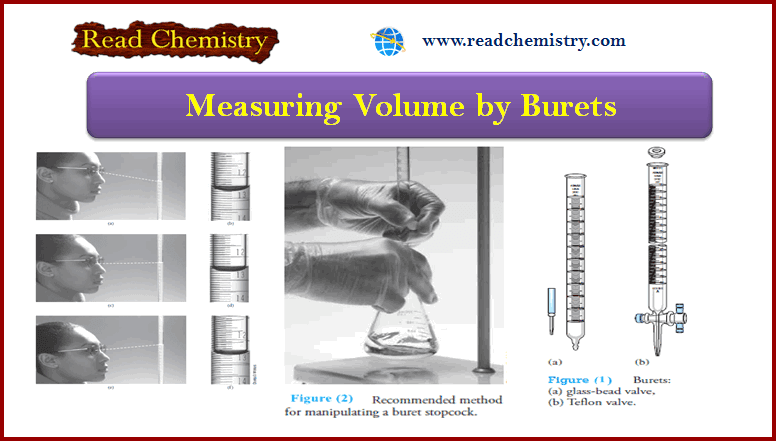
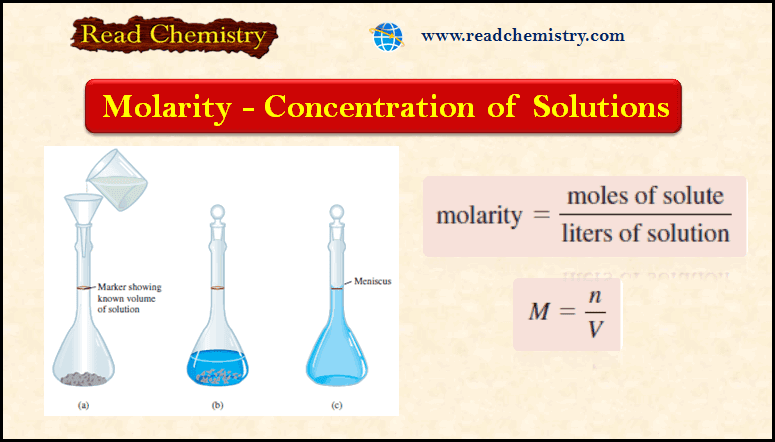
Measuring Volume by Pipets, Burets, Volumetric Flask
– The precise measurement of volume is as important to many analytical methods as the…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Online MCQ
First law of thermodynamics – MCQ online test
Online MCQ test on First law of thermodynamics – In this topic we offer you,…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Free book
Physical Chemistry book , 3rd edition by Robert G. Mortimer
– In this subject, we will discuss free download of Physical Chemistry book, 3rd edition…
Read More » -
-
-
-
-